Types of Magnesium

Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a critical role in over 300 biochemical reactions in the human body. From supporting muscle function and heart health to aiding sleep and mental well-being, magnesium is a powerhouse nutrient. However, not all magnesium supplements are created equal.
Below is a comprehensive guide to the different types of magnesium, their specific benefits, and important considerations before using them.
1. Magnesium Citrate
What it is: A combination of magnesium and citric acid, commonly used as a saline laxative.
Benefits:
-
Relieves constipation
-
Promotes relaxation and improves sleep
-
May help reduce hot flashes, muscle cramps, mood swings, and insomnia
Considerations:
-
Highly bioavailable and easily absorbed
-
Budget-friendly
-
Can have a laxative effect, especially in higher doses
2. Magnesium Glycinate
What it is: A combination of magnesium and the amino acid glycine.
Benefits:
-
Reduces migraines, anxiety, inflammation, and restless leg syndrome
-
Supports restful sleep
-
Eases mood swings and hot flashes
Considerations:
-
Excellent bioavailability
-
Gentle on the stomach
-
Does not cause laxative effects
3. Magnesium Taurate
What it is: A compound of magnesium and the amino acid taurine.
Benefits:
-
Supports heart health, blood sugar balance, and bone density
-
Calms anxiety and enhances mood
-
Helps with migraines and sleep issues
Considerations:
-
Well-absorbed and highly bioavailable
-
Often chosen for cardiovascular support
4. Magnesium Aspartate
What it is: A magnesium salt of aspartic acid.
Benefits:
-
Boosts cellular energy
-
Helps combat fatigue
-
Reduces hot flashes, irritability, mood swings, and sleep disturbances
Considerations:
-
Best taken in the morning
-
High bioavailability
5. Magnesium Malate
What it is: A blend of magnesium and malic acid.
Benefits:
-
Supports energy production and helps with chronic fatigue
-
Reduces symptoms of menopause including mood swings and sleep disturbances
Considerations:
-
Absorbs efficiently
-
Ideal for daytime use due to its energy-boosting properties
6. Magnesium L-Threonate
What it is: A newer, advanced form of magnesium designed to cross the blood-brain barrier.
Benefits:
-
Enhances cognitive function, memory, and mental clarity
-
May help with brain fog and neurological support
-
Can aid bone health
Considerations:
-
Highly bioavailable to the brain
-
Best taken in the morning to support alertness
7. Topical Magnesium (Chloride or Sulphate)
What it is: Applied to the skin via sprays, lotions, or Epsom salt baths.
Benefits:
-
Relieves muscle cramps, restless legs, and skin irritation
-
Supports relaxation and sleep
-
Promotes bone strength
Considerations:
-
Great for those with sensitive digestive systems
-
Best used in the evening, especially in baths
8. Magnesium Oxide
What it is: An inorganic salt composed of magnesium and oxygen.
Benefits:
-
Can ease constipation
-
May provide some support for menopausal symptoms
Considerations:
-
Very low bioavailability
-
Inexpensive, but not ideal for therapeutic use
-
Strong laxative effect
🏆 Which Type of Magnesium Is the Best?
It depends on your specific health needs:
| Health Concern | Recommended Type |
|---|---|
| Sleep and Relaxation | Magnesium Glycinate, Citrate |
| Mood & Anxiety | Magnesium Glycinate, Taurate |
| Energy & Fatigue | Magnesium Malate, Aspartate |
| Cognitive Support | Magnesium L-Threonate |
| Digestive Support | Magnesium Citrate, Oxide |
| Heart Health | Magnesium Taurate |
| Muscle Pain / Topical Relief | Magnesium Chloride / Sulphate |
✅ Final Tips Before Supplementing
-
Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any supplement.
-
Start with a low dose, especially if you're new to magnesium.
-
Look for supplements labeled "highly bioavailable" for better absorption.
-
Consider timing: energizing forms (e.g., malate, L-threonate) are best taken in the morning; relaxing forms (e.g., glycinate, citrate) are ideal in the evening.
News in the same category


Natural Remedy for Cleansing Blood Vessels: Just One Tablespoon a Day!

Discover the Magic of Castor Oil and Apple Cider Vinegar

The Power of Onion and Cloves: A Natural Remedy for Health and Home
Say Goodbye to Nail Fungus with Rosemary – A Natural Remedy

Don’t Throw Away Lemon Seeds – They’re Worth Their Weight in Gold!

Boil Bananas and Drink the Liquid Before Bed – Sleep Like Never Before! 🍌🌙

Enhance Your Morning Nescafé with Cloves

Grandma’s Beetroot & Carrot Delight – A Simple Recipe for Health and Flavor!

Discover the Power of the Tahitian Nut: A Natural Remedy Against Cancer
Discover the Power of Thyme: Fight Diseases Like Poor Circulation, Fatty Liver, High Blood Pressure, and Anxiety

Say Goodbye to Urinary Infections, Asthma, and More: The Benefits of Tradescantia Spathacea

Discover the Benefits of Chayote: A Natural Remedy for Your Health

Restore Your Vision, Eliminate Anemia, and Detox Your Liver with This Powerful Natural Smoothie
Vitamin Deficiency and Leg or Bone Pain: What You Need to Know

Unlocking the Power of Black Cumin Seeds: A Natural Health Boost

The Power of Red Onion and Other Vegetables for Balanced Blood Sugar
Discover the Amazing Health Benefits of Chewing Black Pepper Before Bed 🌿🔥
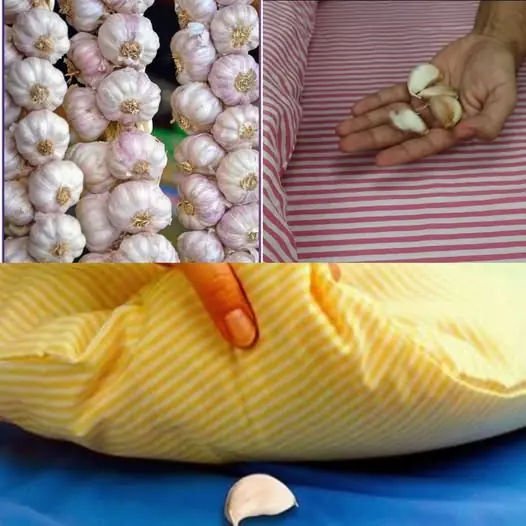

Discover the Benefits of Sleeping with Garlic Under Your Pillow
News Post

🍒🍫 Cherry Chocolate Chip Cake 🍫🍒

🍪✨ Peanut Butter Hazelnut Swirl Cookies ✨🍪

🍪❤️ Raspberry Chocolate Chip Cookies ❤️🍪

🌌🍦 Ultimate Galaxy Ice Cream Cake 🍦🌌

🍍🍓🍫 Pineapple Strawberry Chocolate Ice Cream Cake 🍫🍓🍍

🫐🍰 Indulge in Blueberry Mousse Heaven Cheesecake 🍰🫐

🍪🍊 Cranberry Orange Cookies 🍊🍪

💚🍰 Moist Velvet Lime Cake 🍰💚

🤍🍰 Sour Cream Pound Cake with Caramel Frosting 🍰🤍

💕😋 Raspberry Ice Cream Cheesecake 😋💕

💕😋 Swirled Chocolate Dream Bundt 😋💕

Twisted Doughnuts: Golden, Sweet, and Irresistibly Fluffy 🍩✨

Busy Work Schedule: Is Sleeping Only 5–6 Hours a Night Harmful?
What Your Urine Color Really Says About Your Health (It’s More Interesting Than You Think)
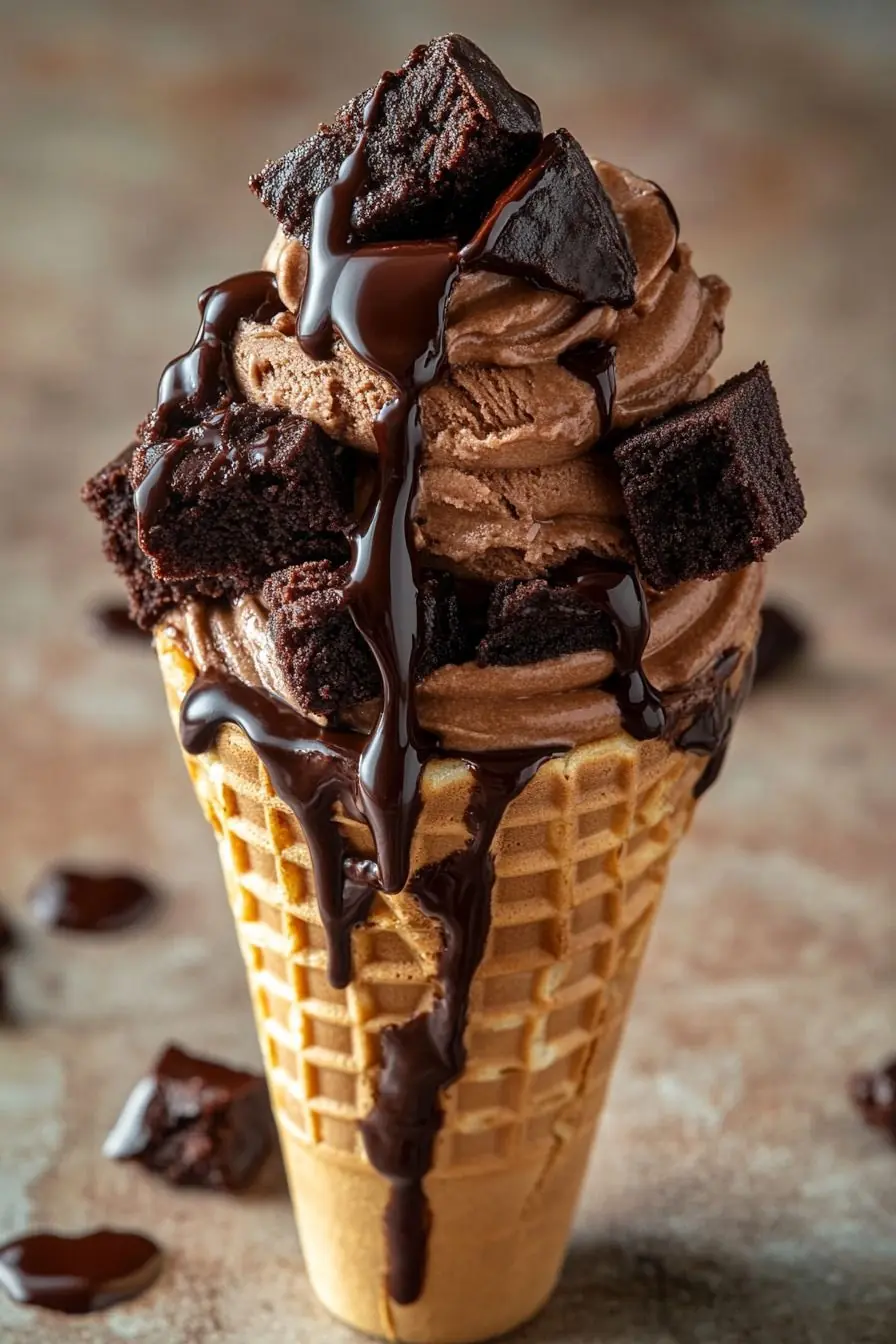

Chocolate Ice Cream Cone with Brownie Chunks & Fudge Drizzle: A Decadent Dessert Dream 🍫🍦
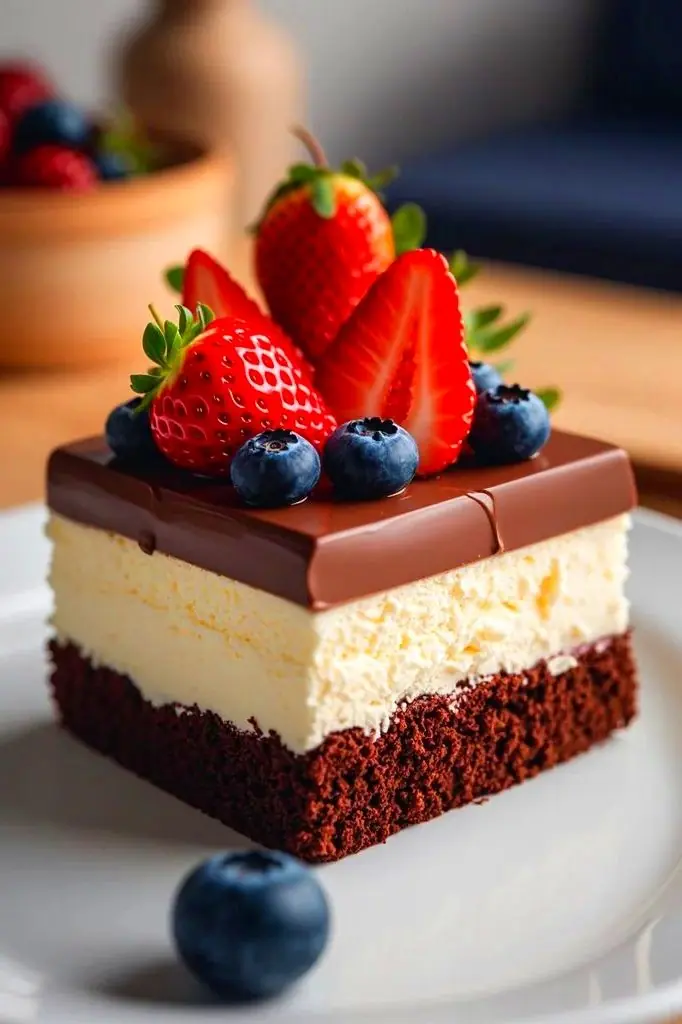

Triple Chocolate Mousse Cake with Berries: A Decadent, Showstopping Dessert 🍫🍓
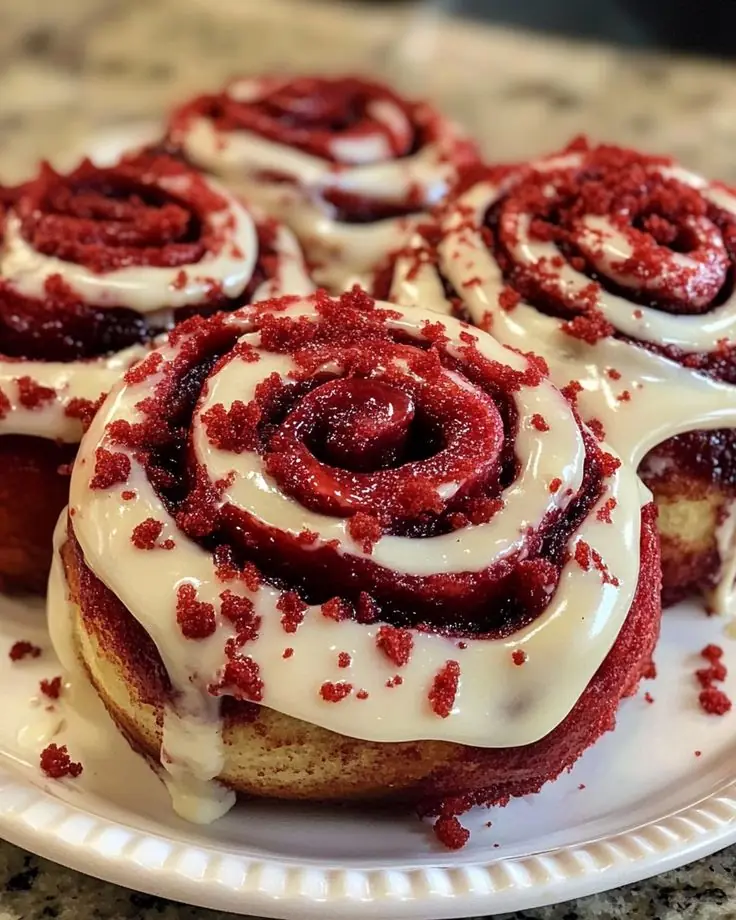

Red Velvet Cinnamon Rolls with Cream Cheese Glaze: A Stunning Twist on a Classic Favorite ❤️🍥

Mango Layer Cake with Whipped Cream Frosting: A Light & Tropical Dessert Delight 🍰🥭
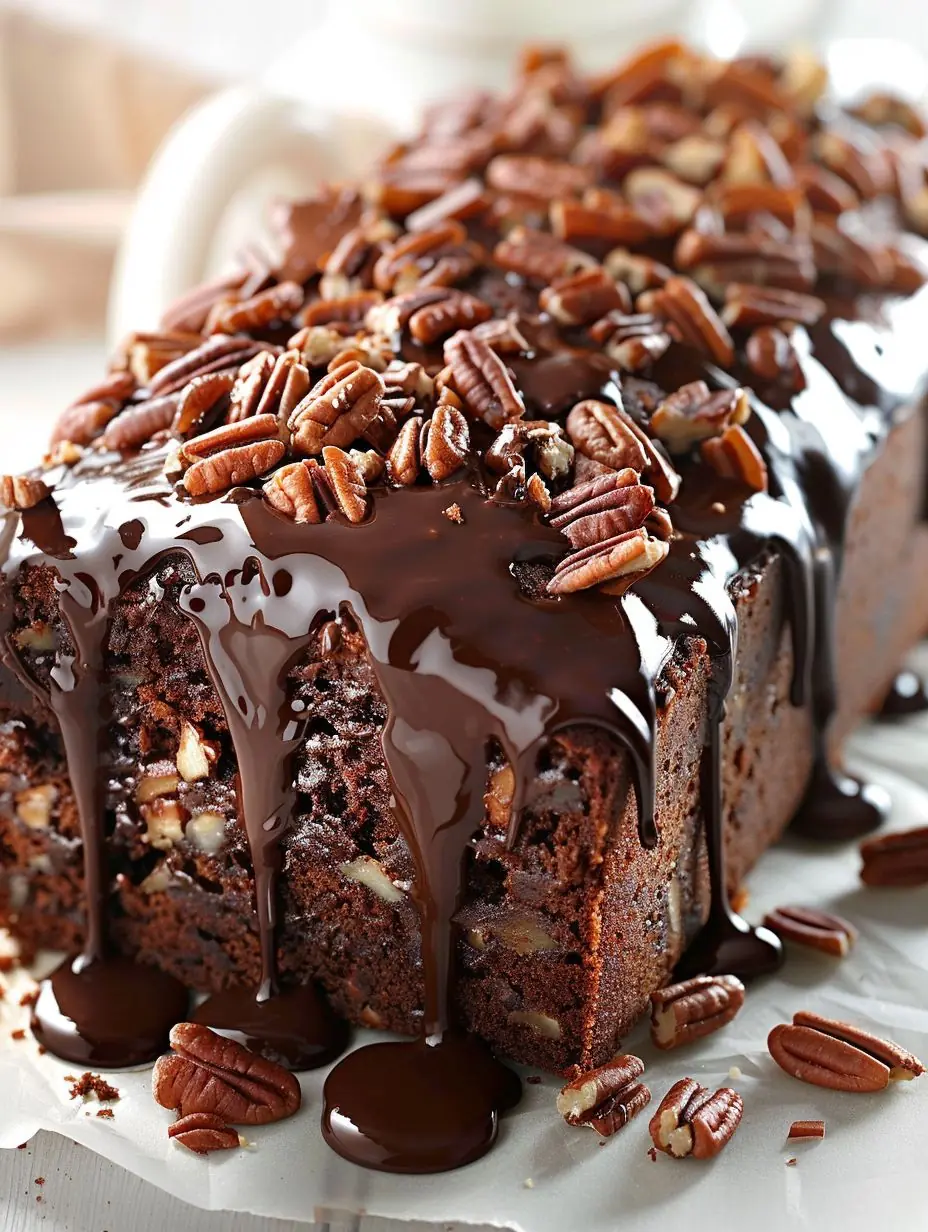

Date Coffee Loaf Cake with Walnuts & Espresso Glaze: A Cozy, Caffeinated Delight ☕🍰