
If you drool while sleeping often, check for these 6 diseases
The Problem of Drooling While Sleeping Should Not Be Ignored
Drooling while sleeping is a common phenomenon, but if it occurs frequently in adults, it may be a sign of certain serious health conditions.
Where Does Saliva Come From?
The process of saliva secretion is controlled by the autonomic nervous system, functioning involuntarily like the heartbeat. The salivary glands in the mouth are divided into major and minor salivary glands. There are three pairs of major salivary glands:
-
Sublingual glands
-
Parotid glands
-
Submandibular glands
These salivary glands work continuously, keeping the oral environment moist, disinfecting, cleaning the mouth, and aiding digestion. In healthy adults, the amount of saliva secreted daily ranges from 1 to 1.5 liters, averaging about 30 ml per hour. Saliva secretion increases when eating or when the brain's nerves are stimulated.
Mouth breathing, stress, fatigue, or incorrect sleeping positions can all lead to drooling while sleeping.
When Should You Be Concerned About Drooling?
In children, this phenomenon is common as their oral muscles are not yet fully developed. However, if an adult suddenly experiences frequent drooling while sleeping, they should be aware of the following health conditions:
1. Oral Diseases
Pharyngitis, gingivitis, and maxillofacial inflammation can stimulate the salivary glands to produce more saliva, leading to drooling. Additionally, misaligned teeth, loose teeth, or discomfort from wearing dentures can also cause this condition. If the problem stems from oral health issues, timely adjustments can help improve the situation.
2. Facial Paralysis
Facial paralysis is a condition where the muscles on one side of the face become paralyzed, making it difficult to control saliva. If drooling is accompanied by a crooked mouth, immediate medical attention is needed.
3. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Abnormal stomach acid levels can trigger an increased saliva secretion reflex. People with GERD often experience drooling along with symptoms like acid reflux, heartburn, and chest pain.
4. Parkinson’s Disease
In Parkinson’s patients, swallowing function is impaired, causing saliva to accumulate rather than being swallowed in time. Additionally, nerve damage can stimulate excessive saliva production, leading to continuous drooling.
5. Cerebral Thrombosis (Stroke)
Blockages in cerebral blood vessels can impair the function of throat muscles, preventing the patient from controlling saliva while sleeping. If accompanied by symptoms such as a crooked mouth, saliva flowing in one direction, and difficulty closing the eyes, immediate medical attention is required.
6. Arteriosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis reduces blood flow to the brain, leading to oxygen deficiency and affecting facial muscle function. Middle-aged and elderly individuals with high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes should be particularly cautious.
How to Improve Drooling While Sleeping
1. Adjust Your Sleeping Position
Sleeping on your back can help reduce drooling, balance the development of different body organs, and support better breathing. Avoid sleeping on your stomach or staying in one position for too long. A U-shaped neck pillow can help support the neck and maintain a proper sleeping posture.
2. Maintain Oral Hygiene
Practice daily oral care by rinsing your mouth after meals, brushing your teeth in the morning and evening, using fluoride toothpaste, and flossing at least once a day to clean between teeth. If you have oral health issues, address them promptly to prevent long-term consequences.
3. Adjust Medications
If drooling is related to medications, consult your doctor to explore alternative options. However, do not change or stop taking prescribed medications without medical advice.
Drooling while sleeping may be normal in some cases, but if it persists, pay attention to warning signs of underlying health conditions and seek medical evaluation when necessary.
News in the same category


If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, Your Body Will Send You These 8 Signals — Don’t Ignore Them

The Surprising Effects of Avocado on Your Heart and Brain
Natural Remedy for Cataracts and Eye Inflammation: Restore Your Vision Naturally
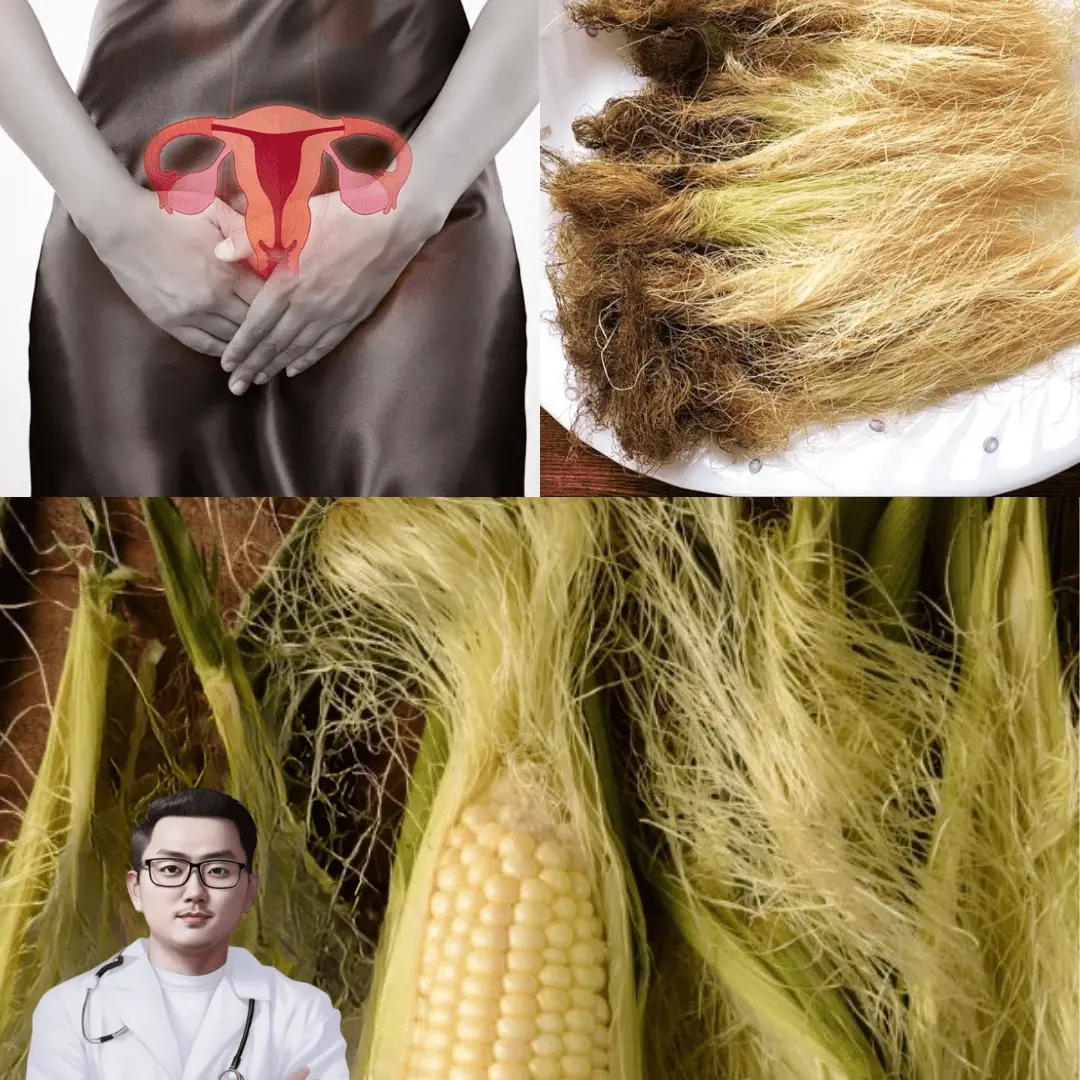

Unlock the Golden Magic of Corn Silk Tea
9 Powerful Home Remedies to Get Rid of Fungal Infection (Daad, Khaj, Khujli) Fast
7 Shocking Health Benefits Of Eating Sweet Potatoes Every Day — According To Science

About 15 Minutes Before a Stroke, the Body Often Sends 4 Clear Warning Signs — Call Your Loved Ones Immediately
Hidden Dangers in Your Mouth: Early Signs of Oral Cancer
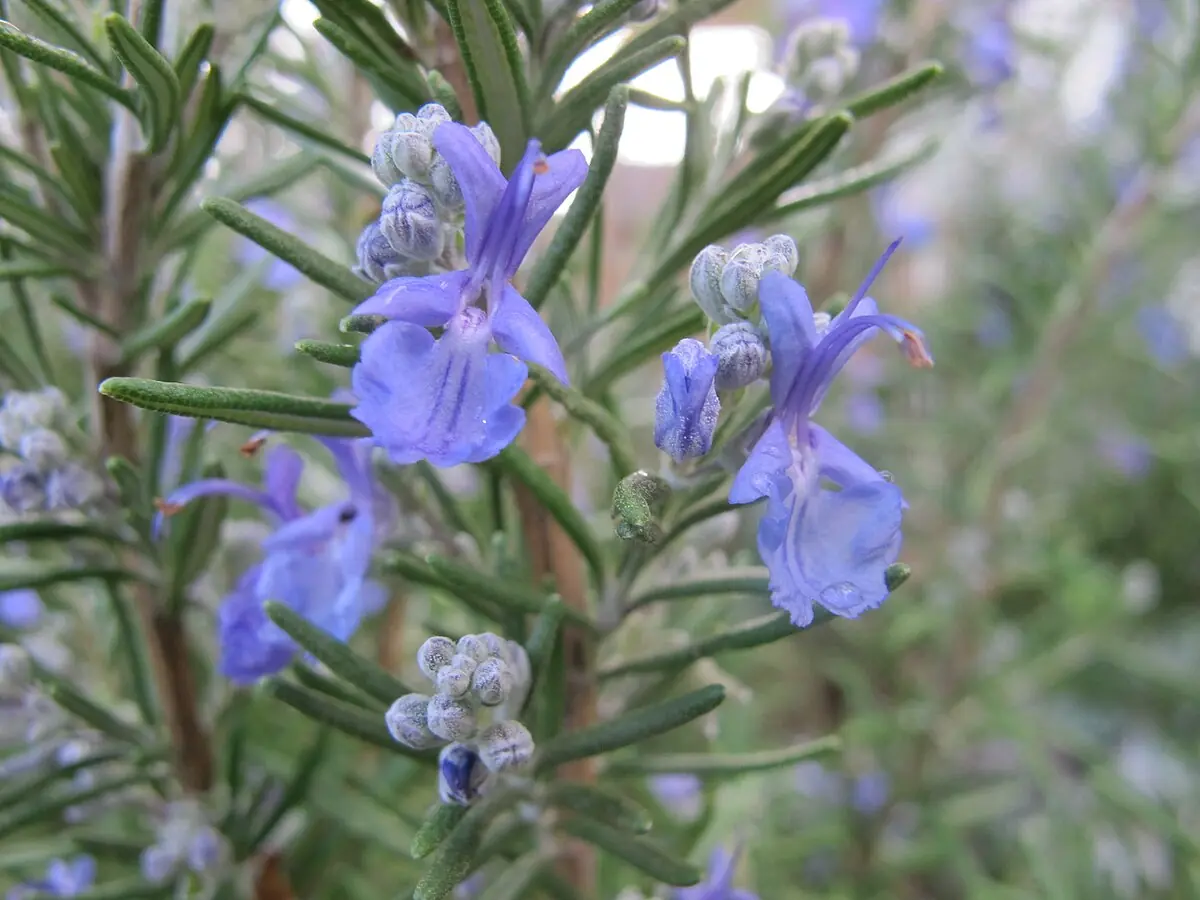

The Secret Power Of The Herb That Helps You Age Gracefully

The Unexpected Benefits of Eating Chicken Feet
If You See Someone with “Blue Veins,” Tell Them This — It Could Save Their Life
The Secret Power of Two Eggs a Day: Could This Simple Habit Transform Your Health? Buy vitamins and supplements

Man Passed Away After Eating Eggs — Stop Eating Eggs This Way Immediately
8 Foods That Fight Tumors — Eat Them Regularly

Does Eating Bananas Before Bed Have Any Benefits?

The Tongue as a Health Indicator: Meaning of a Whitish Color

Benefits of Boiled Eggs: Nutrition and Healthy Recipes
5 early warning signs of cervical cancer
7 Innocent Mistakes That Get Your Kidneys in Big Trouble
News Post
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN WE TONGUE KISS…See more

Nature’s Secret: 4 Healing Leaves That Support Metabolism, Immunity & Circulation Naturally

Don’t Drink Coconut Water Before You Know These 11 Secrets!

Pumpkin Seed Milk — The Natural Parasite Cleanser
Fast Rice Water Trick for a Brighter Smile
Morning Drink to Revive Your Kidneys Fast
The Onion Recipe That Could Transform Your Blood Sugar, Support Cleaner Arteries, and Protect Your Heart!

Top 4 Fruits That Help Your Kidneys Flush Out Toxins While You Sleep
Ginger, Clove, and Honey: The Natural Trio Your Body Will Thank You For

Heal 15 Years of Joint Pain Naturally with Turmeric and Honey Tea

This Juice Revived My Grandma’s Energy — Say Goodbye to Fatigue and Body Pain with This Natural Recipe

The Benefits of Eating 2 Boiled Eggs Every Morning: Transform Your Health!

If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, Your Body Will Send You These 8 Signals — Don’t Ignore Them

The Surprising Effects of Avocado on Your Heart and Brain

Ways to Get Over a Man Who Didn’t Value You
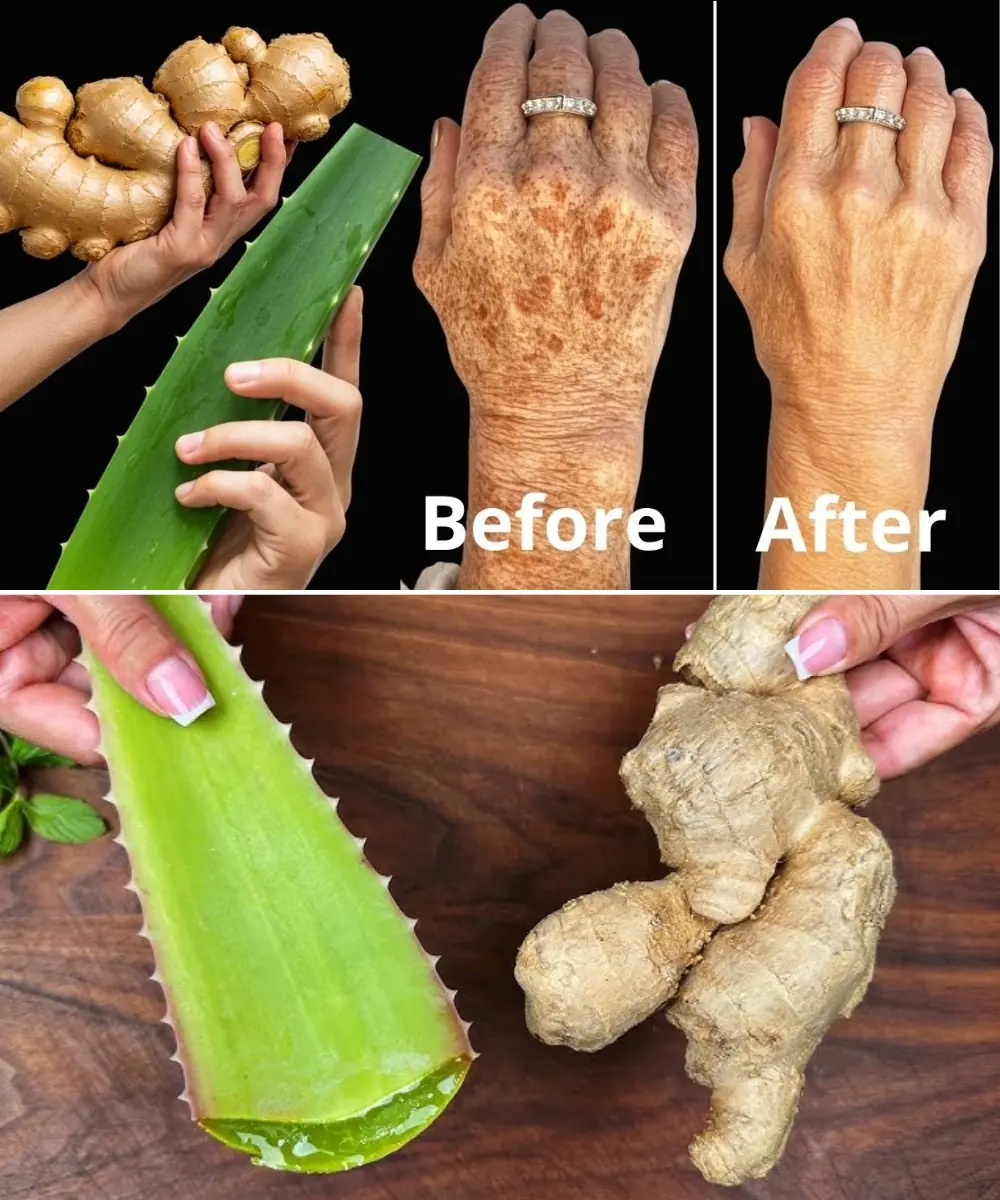

I’m 66 but Look 36 — My Secret? Aloe Vera & Ginger for Firm, Smooth Skin
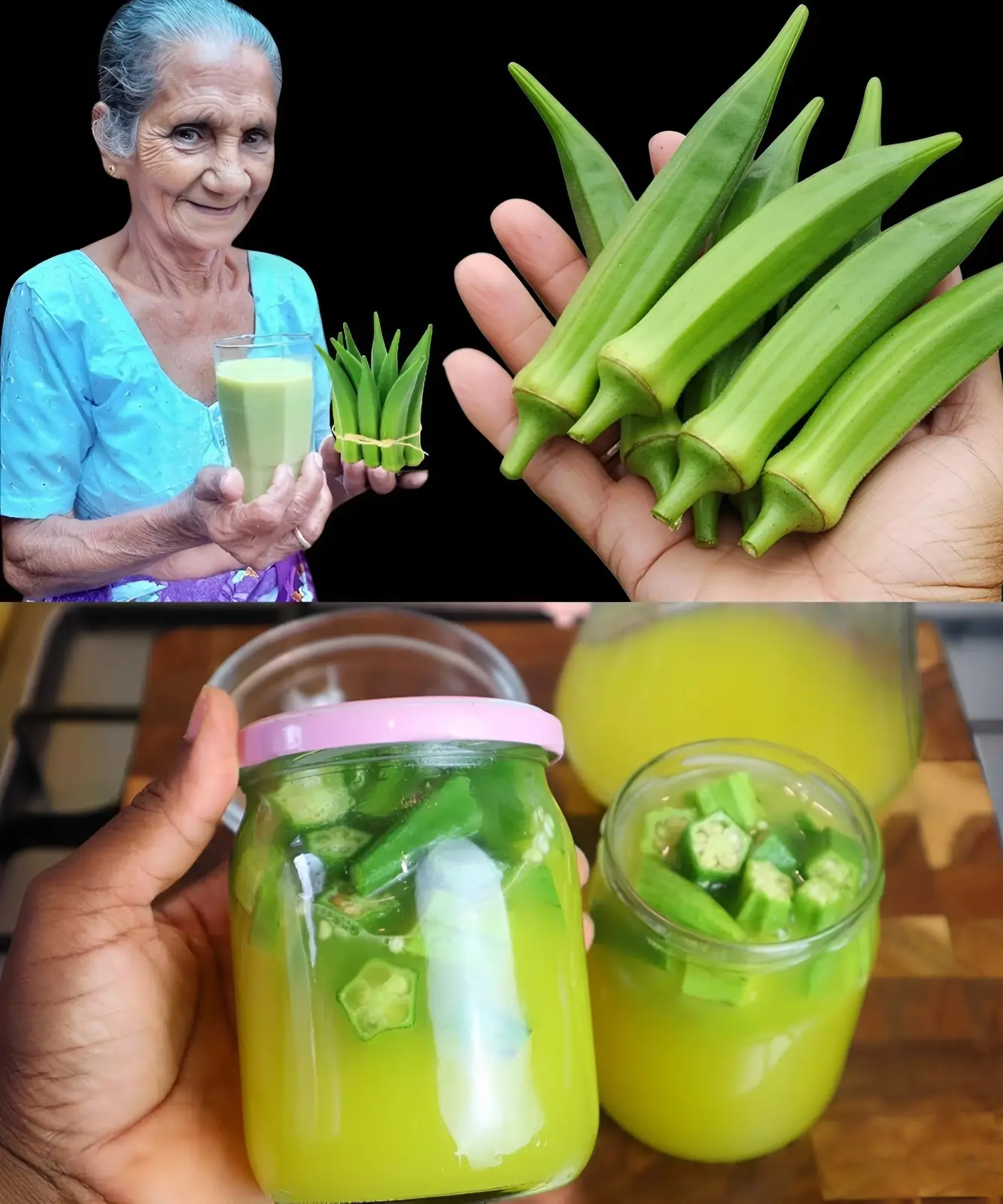

How to Make Okra Water to Treat 17 Health Problems Naturally
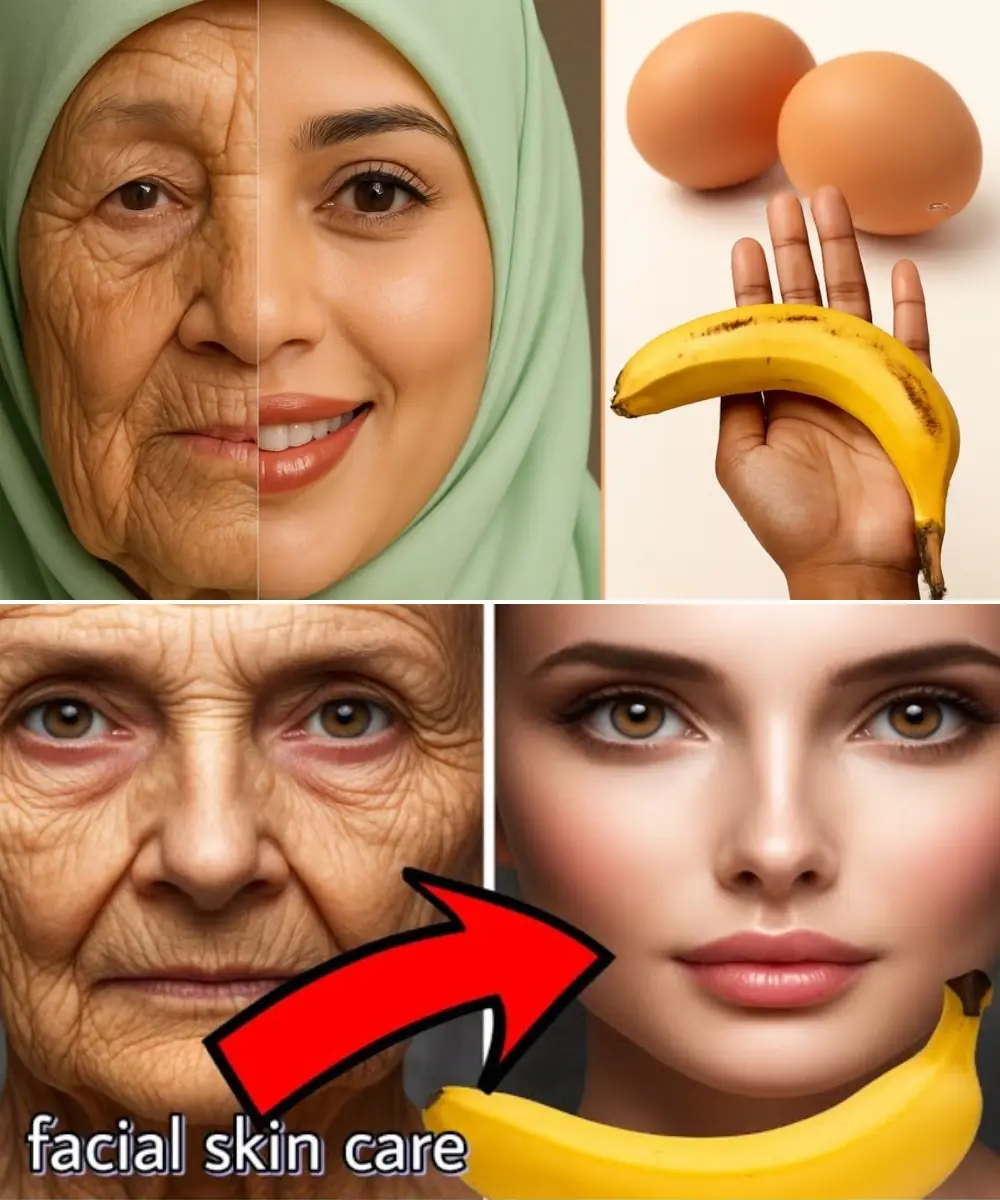

Banana and Egg Mask to Look Younger Even in Your 80s
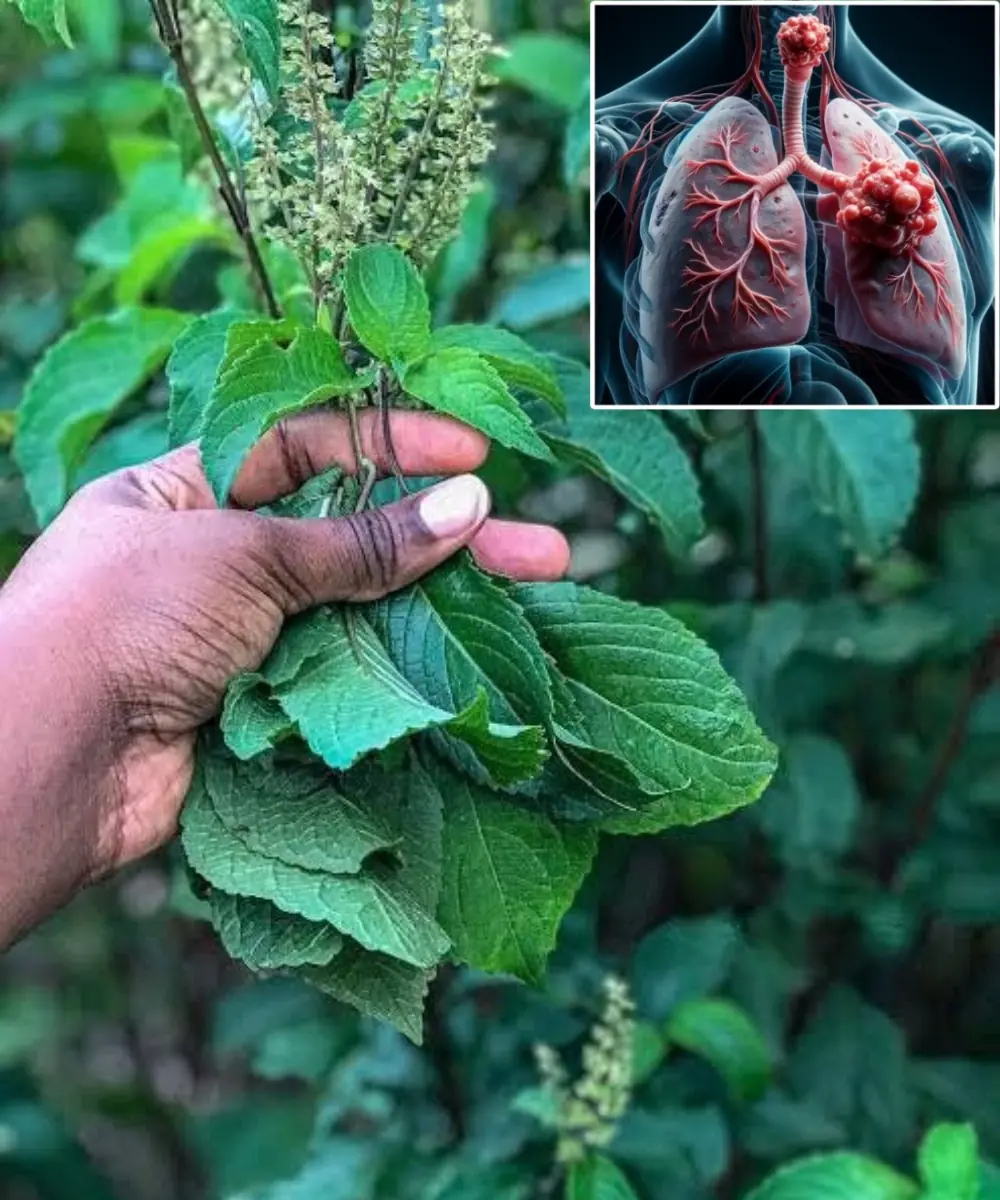

Scent Leaf Secrets Unveiled: 10 Surprising Health Benefits of This Miracle Herb
