
Scientists Successfully Rejuvenate a 53-Year-Old Woman’s Skin Cells by 30 Years
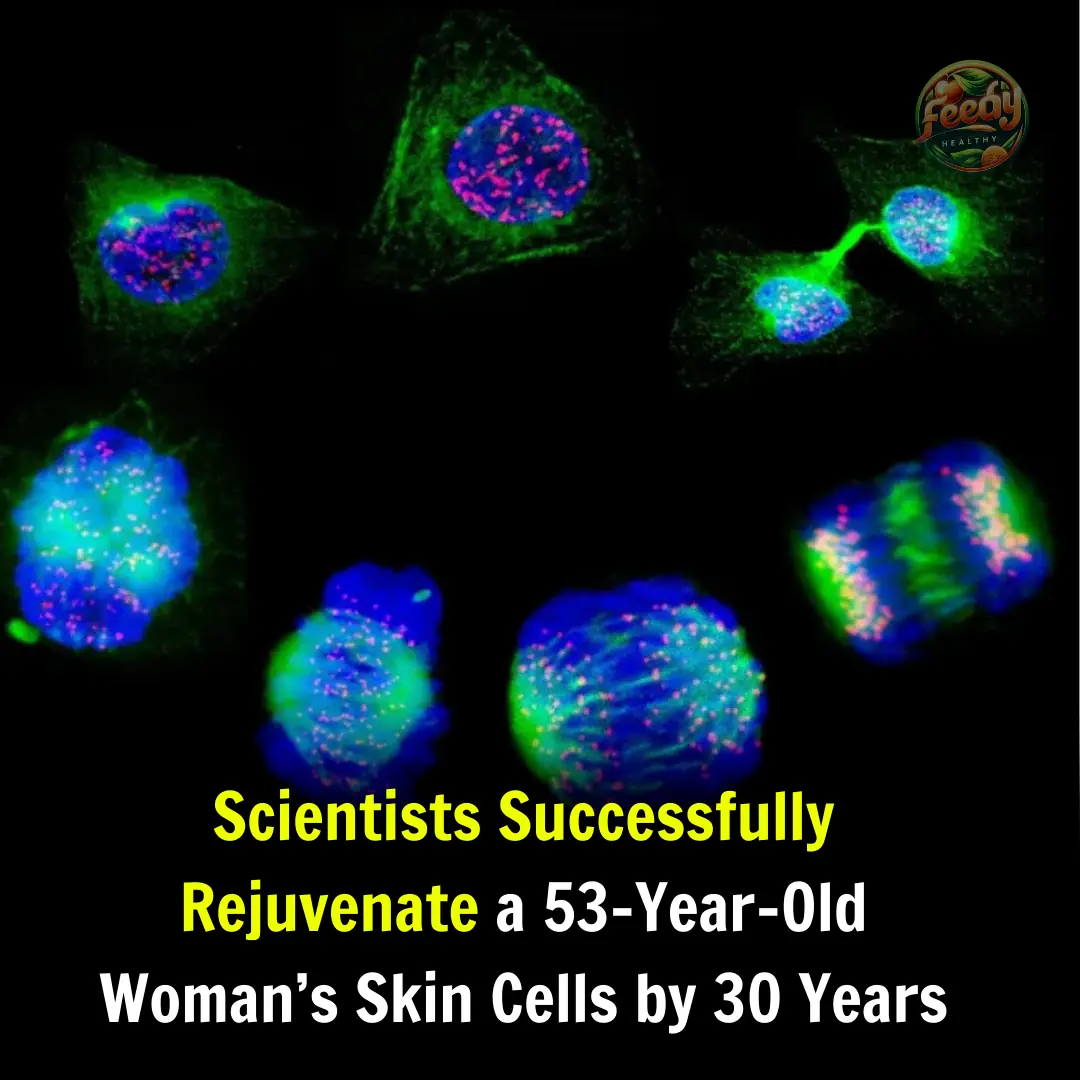
The fields of regenerative medicine and cellular biology are advancing rapidly, demonstrating that some aging-related processes may be more reversible than previously thought.
Recent research has shown that it is possible to rejuvenate the skin cells of a 53-year-old woman by 30 years, a groundbreaking scientific achievement that could redefine modern approaches to treating age-related diseases.
Understanding Cellular Aging
Cellular aging is a complex process marked by gradual changes in cell structure and function. Over time, alterations in gene expression, DNA damage accumulation, and reduced tissue regeneration capacity occur.
These changes increase susceptibility to chronic and degenerative diseases such as osteoarthritis and fibrosis. Scientific research aims to understand the underlying mechanisms of aging to develop interventions that slow down, stop, or even reverse some of its effects.
Cellular Reprogramming: A Key to Reversing Aging
In 2006, Nobel Prize-winning scientist Shinya Yamanaka revolutionized regenerative medicine by discovering that adult somatic cells could be reprogrammed into a state similar to embryonic stem cells. This was achieved by introducing four transcription factors—Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc—now known as Yamanaka factors.
Cells reprogrammed using this method, called induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), can differentiate into various cell types. However, this complete reprogramming erases a cell’s original identity, making therapeutic applications more challenging.
To overcome this limitation, researchers developed a method called Maturation Phase Transient Reprogramming (MPTR), which partially reverses aging without completely transforming cells into stem cells.
A study published in the journal eLife describes MPTR as a technique where cells are reprogrammed to an intermediate rejuvenation state before stopping the process, ensuring they retain their original function.
How Scientists Reversed 30 Years of Aging in Skin Cells
One of the most remarkable findings of the study is that fibroblast cells (skin cells) from a 53-year-old woman displayed gene expression and epigenetic markers similar to those of a 23-year-old person.
These results were assessed using epigenetic clocks, a method that estimates a cell’s biological age based on DNA methylation patterns.
Key Findings:
🔹 Reversal of Age-Associated DNA Methylation – During MPTR, certain DNA regions that were methylated in aged cells regained a pattern more similar to younger cells.
🔹 Increased Collagen Production – The rejuvenated cells boosted production of collagen types I and IV, essential proteins for maintaining skin structure and elasticity.
🔹 Preservation of Cell Identity – Once the reprogramming factors were removed, the fibroblasts retained their identity and did not transform into pluripotent stem cells, a crucial factor for safe therapeutic applications.
Clinical Implications and Potential Applications
The ability to reverse a cell’s biological age without erasing its identity lays the foundation for the development of age-reversal therapies, with potential applications in:
✔️ Dermatological Treatments – Rejuvenated skin cells could lead to new treatments for chronic wounds, ulcers, and premature aging.
✔️ Degenerative Disease Treatment – Conditions like arthritis and pulmonary fibrosis could benefit from restoring partial cell function, improving patients’ quality of life.
✔️ Preventive Medicine – Delaying or reversing cellular aging traits could reduce the incidence of chronic diseases, potentially extending healthy lifespan.
However, it is important to note that this technique is still in the experimental phase and must undergo rigorous clinical trials to confirm its effectiveness, safety, and feasibility in human applications.
The Role of Epigenetics in Anti-Aging Research
Epigenetics refers to chemical modifications that regulate gene activity without changing the DNA sequence. One of the most studied mechanisms is DNA methylation, which controls gene activation but undergoes alterations with age, contributing to aging-related changes.
MPTR’s ability to restore youthful epigenetic markers suggests that the biological clock can be reset, reversing age-related cellular characteristics. This approach provides significant advantages over other therapies by avoiding risks associated with complete dedifferentiation (losing a cell’s identity).
Final Thoughts
The study demonstrating the rejuvenation of a 53-year-old woman’s skin cells by 30 years represents a major breakthrough in anti-aging research. By allowing cells to retain their original function, the Maturation Phase Transient Reprogramming (MPTR) technique presents a safer and more effective foundation for future clinical applications.
The prospect of “resetting” the biological clock without permanently altering cellular function offers a unique opportunity to treat age-related diseases and, potentially, prevent them altogether.
News in the same category


If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, Your Body Will Send You These 8 Signals — Don’t Ignore Them

The Surprising Effects of Avocado on Your Heart and Brain
Natural Remedy for Cataracts and Eye Inflammation: Restore Your Vision Naturally

Unlock the Golden Magic of Corn Silk Tea
9 Powerful Home Remedies to Get Rid of Fungal Infection (Daad, Khaj, Khujli) Fast
7 Shocking Health Benefits Of Eating Sweet Potatoes Every Day — According To Science

About 15 Minutes Before a Stroke, the Body Often Sends 4 Clear Warning Signs — Call Your Loved Ones Immediately
Hidden Dangers in Your Mouth: Early Signs of Oral Cancer

The Secret Power Of The Herb That Helps You Age Gracefully

The Unexpected Benefits of Eating Chicken Feet
If You See Someone with “Blue Veins,” Tell Them This — It Could Save Their Life
The Secret Power of Two Eggs a Day: Could This Simple Habit Transform Your Health? Buy vitamins and supplements

Man Passed Away After Eating Eggs — Stop Eating Eggs This Way Immediately
8 Foods That Fight Tumors — Eat Them Regularly

Does Eating Bananas Before Bed Have Any Benefits?

The Tongue as a Health Indicator: Meaning of a Whitish Color

Benefits of Boiled Eggs: Nutrition and Healthy Recipes
5 early warning signs of cervical cancer
7 Innocent Mistakes That Get Your Kidneys in Big Trouble
News Post
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN WE TONGUE KISS…See more

Nature’s Secret: 4 Healing Leaves That Support Metabolism, Immunity & Circulation Naturally

Don’t Drink Coconut Water Before You Know These 11 Secrets!

Pumpkin Seed Milk — The Natural Parasite Cleanser
Fast Rice Water Trick for a Brighter Smile
Morning Drink to Revive Your Kidneys Fast
The Onion Recipe That Could Transform Your Blood Sugar, Support Cleaner Arteries, and Protect Your Heart!

Top 4 Fruits That Help Your Kidneys Flush Out Toxins While You Sleep
Ginger, Clove, and Honey: The Natural Trio Your Body Will Thank You For

Heal 15 Years of Joint Pain Naturally with Turmeric and Honey Tea

This Juice Revived My Grandma’s Energy — Say Goodbye to Fatigue and Body Pain with This Natural Recipe

The Benefits of Eating 2 Boiled Eggs Every Morning: Transform Your Health!

If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, Your Body Will Send You These 8 Signals — Don’t Ignore Them

The Surprising Effects of Avocado on Your Heart and Brain

Ways to Get Over a Man Who Didn’t Value You

I’m 66 but Look 36 — My Secret? Aloe Vera & Ginger for Firm, Smooth Skin

How to Make Okra Water to Treat 17 Health Problems Naturally

Banana and Egg Mask to Look Younger Even in Your 80s

Scent Leaf Secrets Unveiled: 10 Surprising Health Benefits of This Miracle Herb
