
Is Heart Failure Related to Cooking?
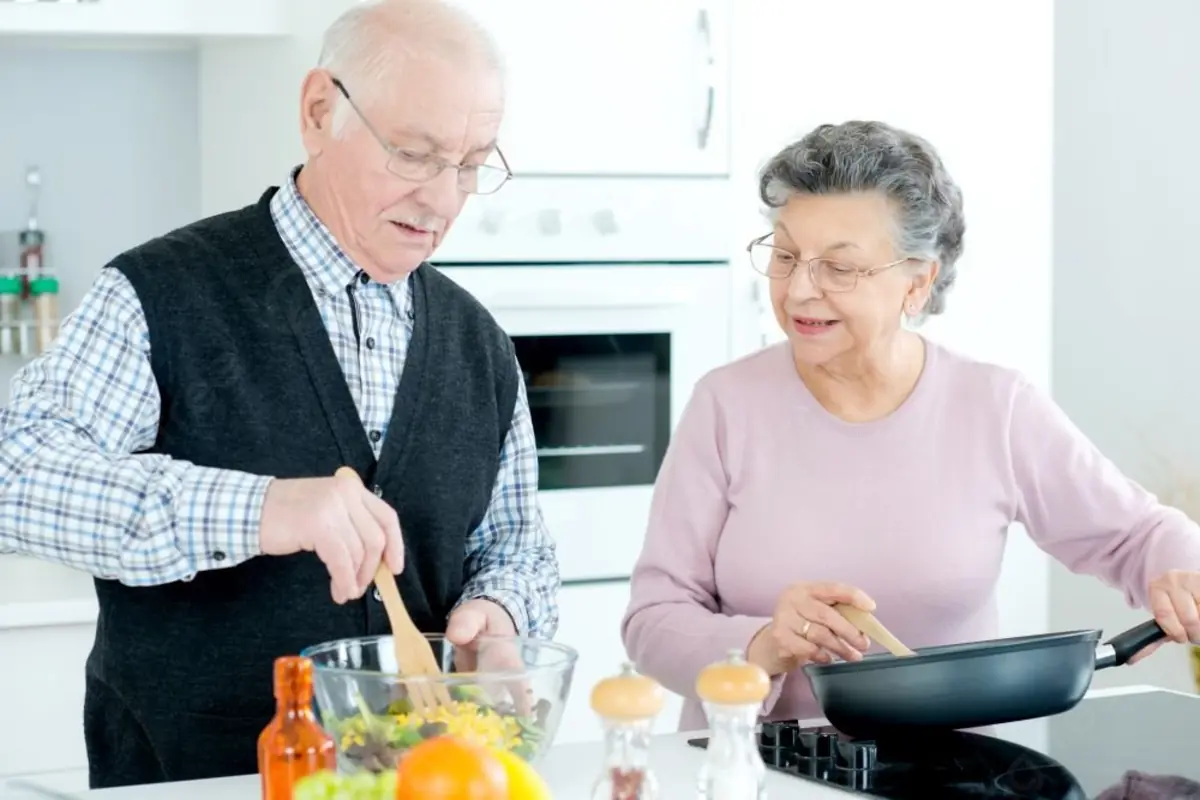

Doctor’s Advice: Important Considerations for Seniors with Cardiovascular Issues When Cooking
Have you ever thought that cooking could affect your heart health? Throughout my years working in the hospital, I have encountered many patients admitted due to cardiovascular issues. In cases of heart failure, some patients neglect certain lifestyle habits, which can worsen their condition.
Among these habits, cooking—an everyday activity that seems simple and necessary—can unexpectedly become a factor that aggravates heart disease.
Cooking – A Familiar but Not-so-Simple Task
At the hospital, I often meet elderly individuals who maintain their cooking habits. They take pride in being able to cook for themselves and enjoy the independence it brings.
However, for those with heart conditions, cooking is not just a routine task—it can put pressure on the heart and even worsen heart failure symptoms.
I once treated a man in his 60s with chronic heart failure. He regularly took medication to manage his condition. Despite my repeated advice to rest and limit physical exertion, he insisted on cooking daily.
He believed that cooking was an essential part of his life, and relying on his family made him feel too dependent.
Initially, his health remained stable. But over time, his heart endured increasing stress, leading to fatigue, shortness of breath, swollen legs, and ultimately, another hospital admission.
After a thorough examination, we discovered that prolonged cooking sessions, coupled with a hot kitchen environment, had placed excessive strain on his heart.
I always advise elderly heart patients that if they are not careful, cooking can negatively impact their cardiovascular health.
Today, I want to share the effects of cooking on heart health and some essential precautions to help heart patients avoid unnecessary health risks.
1. The Impact of High Temperatures
I once treated a 70-year-old woman with severe heart failure who relied on medication to maintain her heart function. Her health fluctuated, yet she remained determined to cook for herself.
Despite her family’s repeated pleas to avoid exertion, she considered cooking both a passion and a responsibility.
However, she began noticing that standing in the kitchen for too long left her breathless and with swollen limbs. After a medical checkup, we found that her heart condition had deteriorated, partly due to cooking in a high-temperature environment, which increased the strain on her heart.
High temperatures cause blood vessels to dilate, making the heart work harder to supply enough blood and oxygen. For those with heart disease, this adds an extra burden, worsening heart failure.
Additionally, heat from the stove, oil fumes, and steam can affect heart rhythm, making patients more prone to dizziness and fatigue.
Solutions:
- Avoid cooking during the hottest parts of the day; choose cooler times instead.
- Use an exhaust fan or ventilation system to reduce kitchen heat.
- If standing for too long feels exhausting, take breaks while cooking.
- Opt for meals that require less time in the kitchen, such as steaming or boiling instead of frying or stir-frying.
2. Be Mindful of Salt Intake

Beyond high kitchen temperatures, excessive salt consumption is a crucial concern for heart patients.
I once treated a 65-year-old man with hypertension and heart failure. He loved cooking and often added a lot of salt, believing that food had to be well-seasoned to taste good.
What he didn’t realize was that excessive salt intake leads to fluid retention, increasing blood volume and putting extra pressure on the heart. This can raise blood pressure and accelerate heart failure progression.
Initially, he didn’t notice any severe symptoms, but over time, his heart failure worsened, leading to another hospitalization.
Solutions:
- Reduce salt in meals and use natural seasonings like garlic, onion, ginger, pepper, or lemon to enhance flavor.
- Opt for low-sodium soy sauce or fish sauce.
- Avoid processed foods (pickles, cured meats, sausages), as they often contain high sodium levels.
- Consult a doctor for a low-sodium diet plan tailored to the patient’s condition.
3. Minimize Physical Strain While Cooking
Many elderly patients believe that as long as they are not too weak, cooking will not harm their health. However, this is not always the case.
I once met a 70-year-old man with chronic heart failure who insisted on preparing three meals a day, often cooking elaborate dishes that required significant effort.
One day, while cooking, he experienced severe chest pain and had to be rushed to the hospital. Tests revealed that his heart had weakened further, partly due to the physical strain of cooking.
Solutions:
- Avoid standing for too long while cooking; sit down when preparing ingredients.
- Minimize heavy lifting—ask family members for help when needed.
- Use kitchen appliances like rice cookers, microwaves, and pressure cookers to reduce effort and cooking time.
- Prepare ingredients in advance to avoid prolonged standing or multitasking too much at once.
Conclusion
Cooking may seem like a simple task, but it can significantly impact heart health.
- A high-temperature kitchen can cause blood vessels to expand, forcing the heart to work harder.
- Excessive salt consumption can increase blood pressure and strain the heart.
- Overexertion while cooking can worsen heart failure symptoms.
Therefore, elderly individuals with heart conditions should take these factors into account while cooking to protect their health. If any unusual symptoms arise, seeking medical attention promptly is essential.
News in the same category


Is Heart Failure Related to Cooking?
More and More People Are Dying from Liver Cancer!

Flu Season is Approaching? Doctors Warn: "2 Things to Avoid, 2 Foods to Eat More" – Knowing Early Will Benefit You!

Doctor’s Reminder: Elderly People Eating Chili Every Day May Experience These 3 Changes

More and More People Are Dying from Gallbladder Cancer!

Is Walking Linked to Stroke?

Are Peanuts a "Trigger" for Diabetes?

Eating an Egg Every Day: Health Boost or Heart Risk? Research Findings Provide the Answer

7 Symptoms Caused by Stress and Anxiety

China to Build a Giant Space Solar Panel That Could Harvest More Energy in One Year Than All the Oil on Earth

Scientists Reveal That Alzheimer’s May Be Linked to Chronic Periodontitis
Blood Sugar Fluctuations Over 24 Hours – How Does It Work at Different Times of the Day?

Blood Sugar Fluctuations Over 24 Hours – How Does It Work at Different Times of the Day?

What Are the Effects of Sleeping After 11 PM for a Long Time? The Consequences May Only Be Felt by Yourself!

Doctors Successfully Cure a Fatal Genetic Disease in a Fetus for the First Time

Useful aspirin tricks that every woman should know

7 Red Flags That Show Your Body Lacks Essential Nutrients

Foods That Are Unsuitable for People with High Blood Pressure – Avoid These Now!

Can Eating Walnuts Clean Your Blood Vessels? Reminder: Protect Your Blood Vessels – Don’t Overlook These Foods!
News Post

Boost Your Energy Like an 18-Year-Old! The Powerful Remedy 🐝🍋

The Healing Power of Mimosa Pudica: 10 Incredible Health Benefits of the Sensitive Plant

Revitalize Your Energy with This Potent Ginger, Garlic, Lemon, and Honey Drink

I Haven’t Been Sick for 35 Years! Clear Vision, Sharp Mind & Normal Blood Pressure – The Power of Ginger & Red Onion!
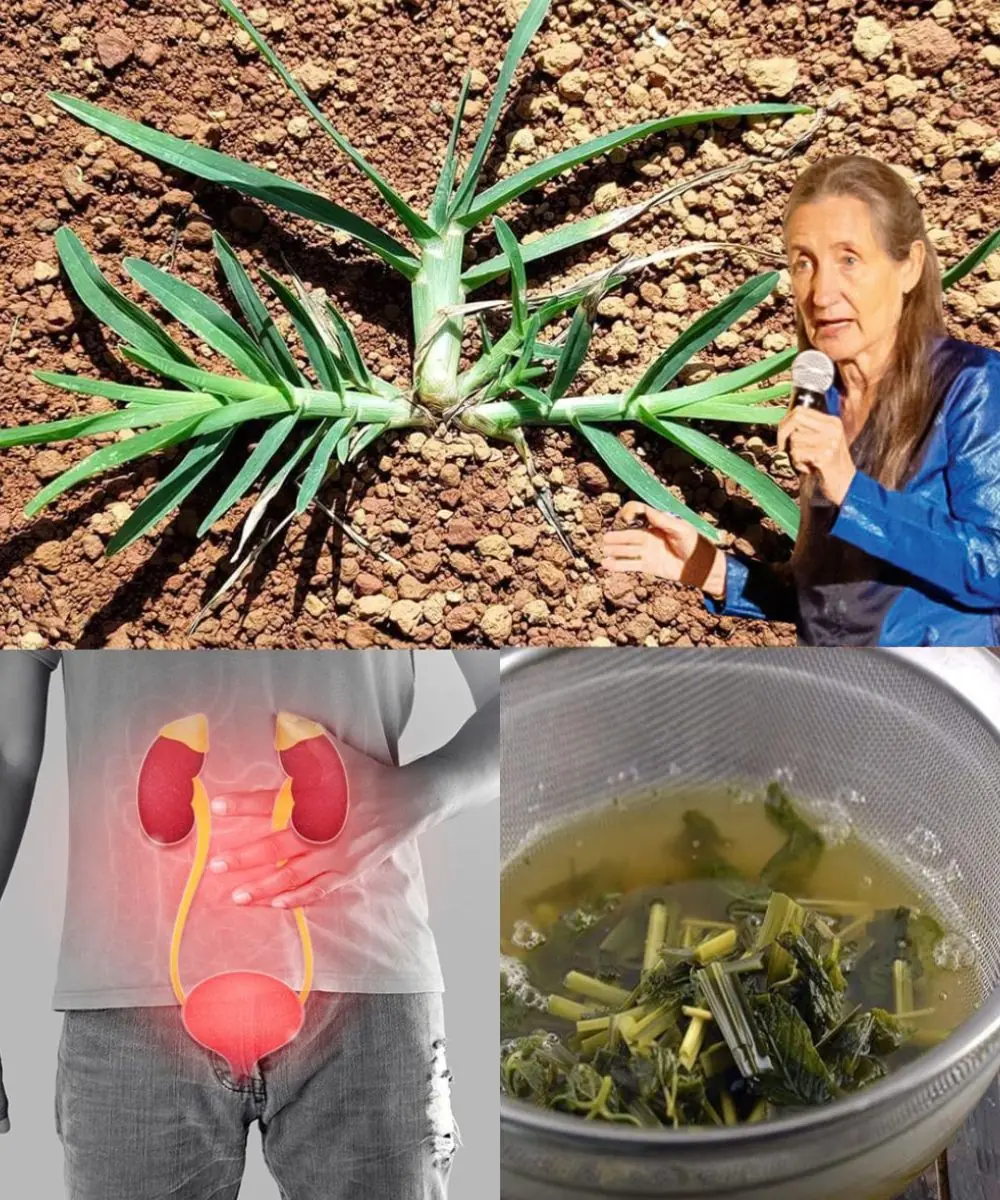

Goosegrass (Eleusine indica): A Natural Ally for Kidney Health
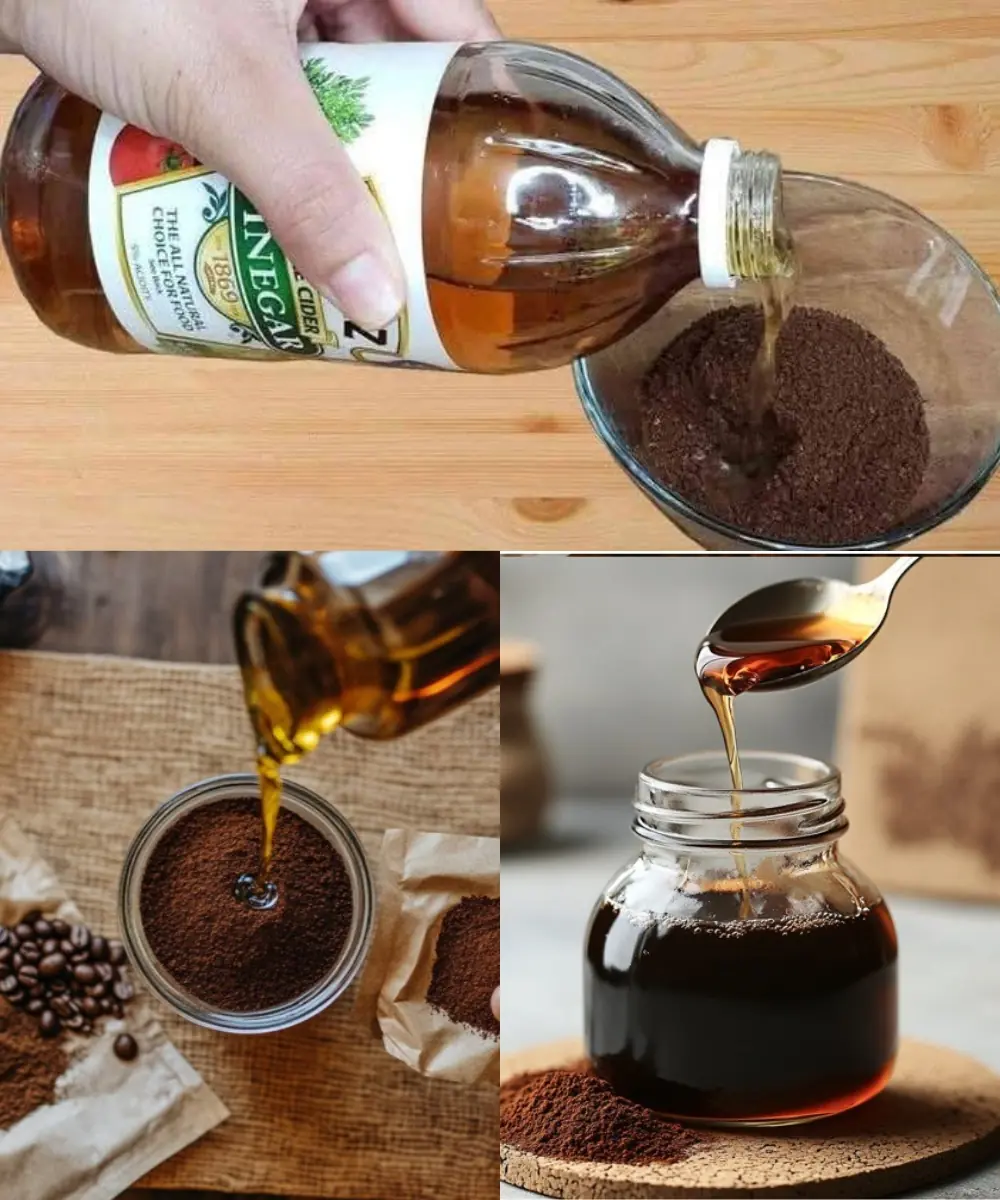

French Beauty Secret: How Coffee and Vinegar Can Transform Your Skin & Health

Don’t Discard the Flowers on Your Basil: Here are 8 Ways How to Use Them

This is How to Correctly Plant Tomatoes to Grow 5–8 ft Plants
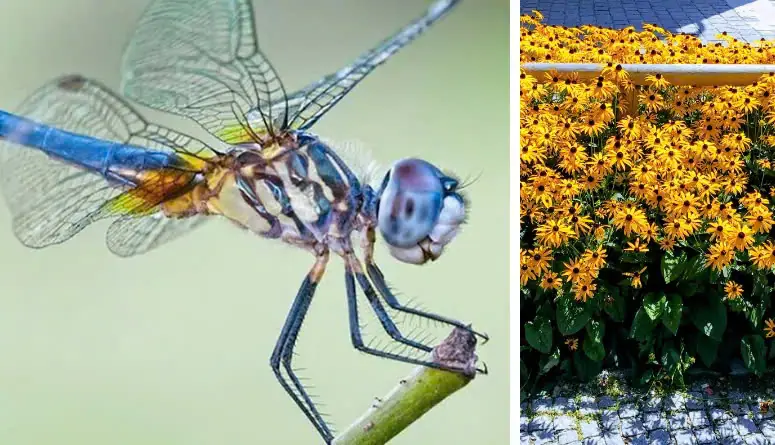

One Dragonfly Can Eat 100s of Mosquitoes per Day: Keep These Plants in Your Yard to Attract Dragonflies!
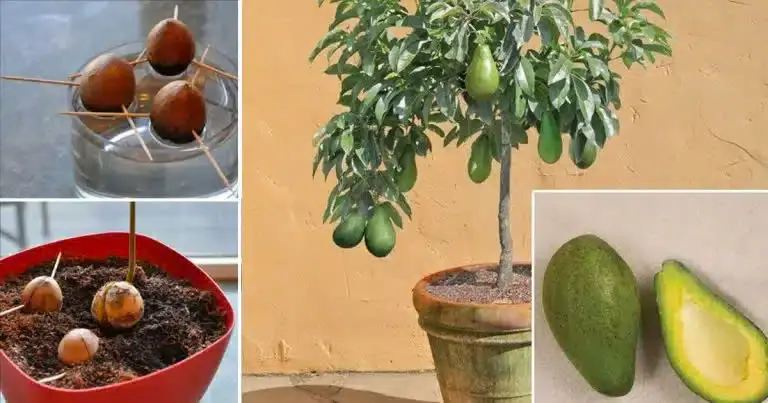

Stop Buying Avocados. Here’s How You Can Grow an Avocado Tree in a Small Pot at Home

12 Beautiful Houseplants That Will Help You Sleep Better

4 Heartwrenching Stories of Newborns Caught in Family Drama from Day One

Delving into the Wonders of Prickly Lettuce – Medicinal Miracles and Culinary Creations

Pierce Brosnan shares the truth about his marriage to Keely after 22 years of marriage

Taking Blood Thinners Like This Will Exhaust Your Liver!

More and More People Are Dying from Liver Cancer!

Flu Season is Approaching? Doctors Warn: "2 Things to Avoid, 2 Foods to Eat More" – Knowing Early Will Benefit You!

Doctor’s Reminder: Elderly People Eating Chili Every Day May Experience These 3 Changes
