
Colon Cancer in Young Adults Is on the Rise: Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore

Colon cancer, traditionally considered a disease that primarily affects people over 50, has been showing a worrying increase among younger adults. Recent studies report a significant rise in cases among individuals under 50, raising alarms within the medical and scientific communities.
While classic risk factors—such as obesity, family history, and certain inflammatory bowel diseases—are still relevant, the growing number of diagnoses in younger populations suggests the need for greater awareness of early symptoms.
This article will explore why colon cancer in young adults is increasing, the key warning signs to watch for, and the importance of early detection and healthy lifestyle choices.
The Rising Cases of Colon Cancer in Young Adults
Over the past few years, colorectal cancer incidence has been increasing in young adults, particularly between the ages of 20 and 40.
In middle- and high-income regions, the decline in cases among older adults contrasts sharply with the rise in younger populations, indicating a possible shift in tumor biology or environmental factors influencing its development.
This trend has led health organizations to reconsider the recommended age for colorectal cancer screenings. While there is no global standard, many medical societies now suggest starting screenings before age 45, especially for individuals with a family history of the disease or concerning symptoms.
Possible Contributing Factors
There is no single cause that fully explains the increase in colon cancer cases among young adults. However, certain factors may contribute, including:
🍔 Dietary Changes: Increased consumption of ultra-processed foods and low-fiber diets.
🏃 Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of regular physical activity.
⚖️ Obesity: Excess body weight is linked to a higher risk.
🚬 Smoking & Alcohol: Both increase inflammation and cancer risk.
🦠 Gut Microbiome Imbalances: Disruptions in gut bacteria may play a role.
🧬 Genetic Predisposition: Conditions like Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) and Lynch syndrome can increase susceptibility.
🚨 Key Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore
Early diagnosis greatly improves survival rates, but young patients are often diagnosed in later stages because symptoms are misattributed to other conditions or ignored. Recognizing early warning signs is crucial for timely intervention.
1. Persistent Abdominal Pain
🔹 Recurring or persistent stomach pain that worsens over time.
🔹 May be accompanied by bloating, cramping, or irregular bowel movements.
🔹 If the pain has no clear cause, a medical evaluation is recommended.
2. Rectal Bleeding or Blood in Stool
🔹 Bright red blood in stool or rectal bleeding should never be ignored.
🔹 While hemorrhoids are common, persistent bleeding requires medical attention.
🔹 Dark stools (melena) may indicate hidden internal bleeding.
3. Changes in Bowel Habits
🔹 Long-lasting changes in stool frequency or consistency—chronic diarrhea, constipation, or alternating between both.
🔹 If accompanied by pain, discomfort, or straining, it could be a red flag.
4. Unexplained Fatigue & Anemia
🔹 Iron-deficiency anemia may result from chronic intestinal bleeding.
🔹 Symptoms include extreme fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and pale skin.
5. Unintentional Weight Loss
🔹 Rapid weight loss without a clear reason should be investigated.
🔹 If combined with digestive symptoms or rectal bleeding, the risk of an underlying tumor increases.
6. Recurring Digestive Issues
🔹 Persistent bloating, gas, or feeling full quickly.
🔹 If these symptoms don’t improve with dietary changes or common treatments, consult a specialist.
🔬 Early Detection & Diagnosis
Early detection can drastically improve outcomes. The gold standard diagnostic test is a colonoscopy, but other options include:
✔ Sigmoidoscopy – Examining the lower part of the colon.
✔ Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT) – Detecting hidden blood in stool.
✔ Genetic Testing – Recommended for individuals with a family history of colon cancer.
📌 Advanced screening programs now use electronic health records to identify high-risk individuals.
If a suspicious lesion is found, a biopsy is performed to confirm malignancy. Once diagnosed, staging tests help determine the spread of cancer and guide treatment planning.
🩺 Treatment Options for Young Adults
Treatment for colon cancer in younger patients is similar to that in older adults but may require specific considerations.
✔ Surgery – Removal of the affected section of the colon and nearby lymph nodes.
✔ Chemotherapy – Used before or after surgery to target cancer cells.
✔ Targeted Therapy – Medications like EGFR inhibitors or anti-angiogenic drugs.
✔ Immunotherapy – Beneficial for cases with high microsatellite instability (MSI-H).
📌 A multidisciplinary approach, including psychological and physical rehabilitation support, is crucial for young patients.
🛡 Prevention & Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopting healthy habits can reduce the risk of colon cancer, even at a young age.
🥦 Balanced Diet – Eat more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, limit red and processed meats.
🏃 Regular Exercise – Aim for at least 150 minutes per week of moderate activity.
🚭 Avoid Smoking & Excess Alcohol – Both increase inflammation and cancer risk.
⚖️ Maintain a Healthy Weight – Obesity is a significant risk factor.
🩺 Regular Check-Ups – Especially for those with a family history of colon cancer.
Conclusion
The rise of colon cancer in young adults is an emerging health challenge. Recognizing early warning signs—persistent abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, bowel habit changes, anemia, and unexplained weight loss—is key to early diagnosis and better survival rates.
While the exact reasons behind this increase remain unclear, a combination of genetic, dietary, and environmental factors likely plays a role.
📌 Being proactive, staying informed, and prioritizing preventive healthcare can save lives! 💙
News in the same category


If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, Your Body Will Send You These 8 Signals — Don’t Ignore Them

The Surprising Effects of Avocado on Your Heart and Brain
Natural Remedy for Cataracts and Eye Inflammation: Restore Your Vision Naturally

Unlock the Golden Magic of Corn Silk Tea
9 Powerful Home Remedies to Get Rid of Fungal Infection (Daad, Khaj, Khujli) Fast
7 Shocking Health Benefits Of Eating Sweet Potatoes Every Day — According To Science

About 15 Minutes Before a Stroke, the Body Often Sends 4 Clear Warning Signs — Call Your Loved Ones Immediately
Hidden Dangers in Your Mouth: Early Signs of Oral Cancer

The Secret Power Of The Herb That Helps You Age Gracefully

The Unexpected Benefits of Eating Chicken Feet
If You See Someone with “Blue Veins,” Tell Them This — It Could Save Their Life
The Secret Power of Two Eggs a Day: Could This Simple Habit Transform Your Health? Buy vitamins and supplements

Man Passed Away After Eating Eggs — Stop Eating Eggs This Way Immediately
8 Foods That Fight Tumors — Eat Them Regularly

Does Eating Bananas Before Bed Have Any Benefits?

The Tongue as a Health Indicator: Meaning of a Whitish Color

Benefits of Boiled Eggs: Nutrition and Healthy Recipes
5 early warning signs of cervical cancer
7 Innocent Mistakes That Get Your Kidneys in Big Trouble
News Post
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN WE TONGUE KISS…See more

Nature’s Secret: 4 Healing Leaves That Support Metabolism, Immunity & Circulation Naturally

Don’t Drink Coconut Water Before You Know These 11 Secrets!

Pumpkin Seed Milk — The Natural Parasite Cleanser
Fast Rice Water Trick for a Brighter Smile
Morning Drink to Revive Your Kidneys Fast
The Onion Recipe That Could Transform Your Blood Sugar, Support Cleaner Arteries, and Protect Your Heart!

Top 4 Fruits That Help Your Kidneys Flush Out Toxins While You Sleep
Ginger, Clove, and Honey: The Natural Trio Your Body Will Thank You For

Heal 15 Years of Joint Pain Naturally with Turmeric and Honey Tea

This Juice Revived My Grandma’s Energy — Say Goodbye to Fatigue and Body Pain with This Natural Recipe

The Benefits of Eating 2 Boiled Eggs Every Morning: Transform Your Health!

If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, Your Body Will Send You These 8 Signals — Don’t Ignore Them

The Surprising Effects of Avocado on Your Heart and Brain

Ways to Get Over a Man Who Didn’t Value You
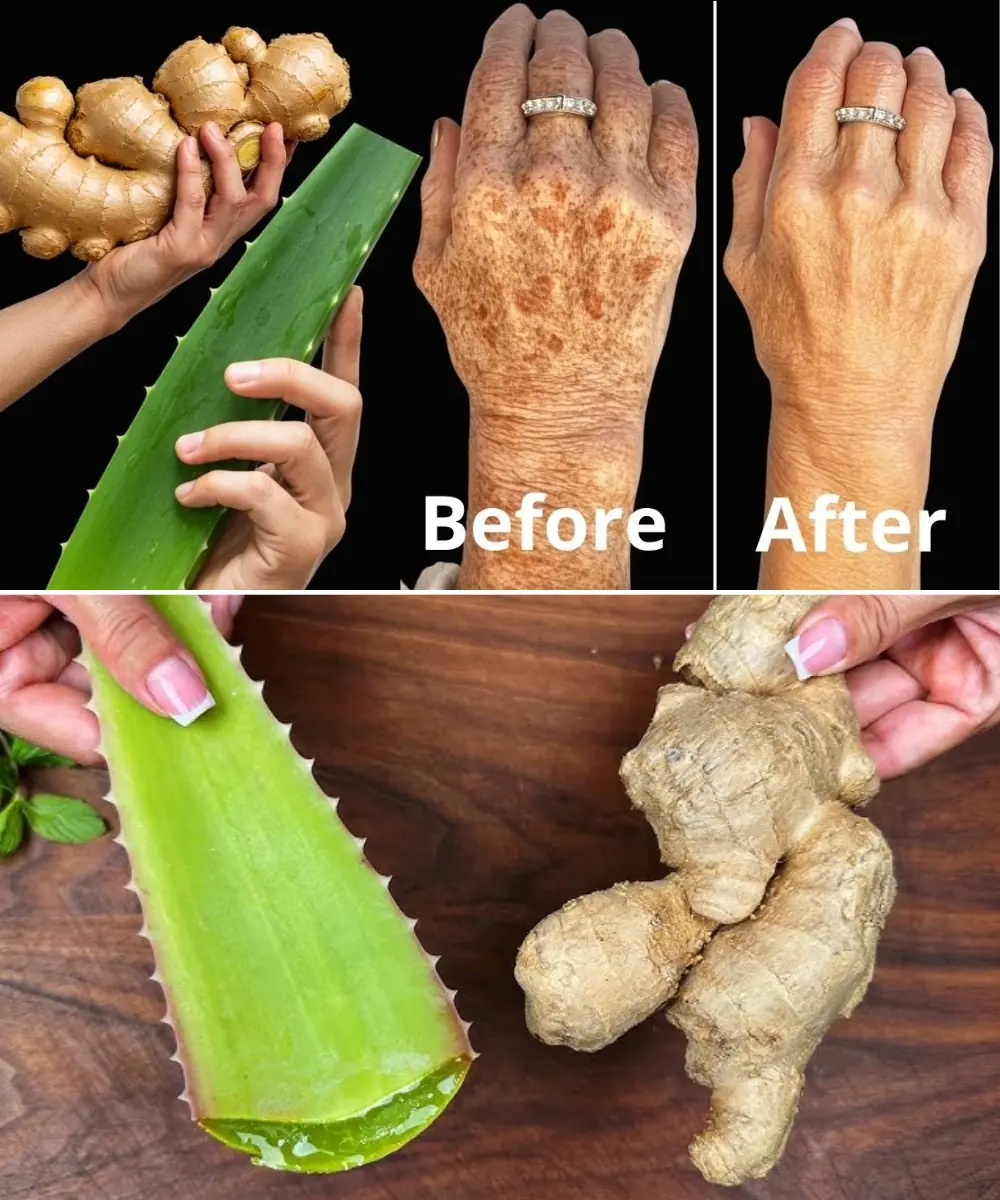

I’m 66 but Look 36 — My Secret? Aloe Vera & Ginger for Firm, Smooth Skin
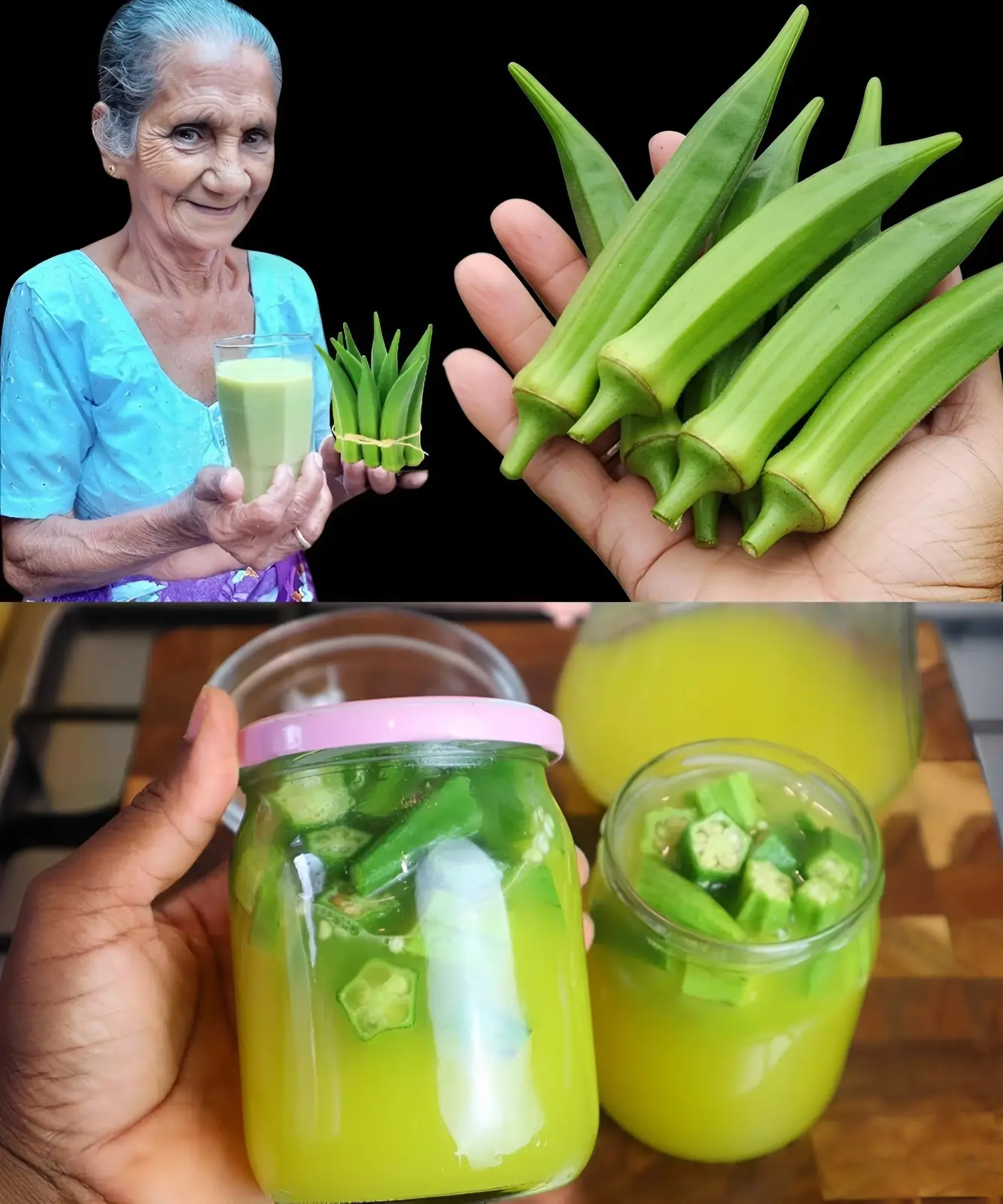

How to Make Okra Water to Treat 17 Health Problems Naturally
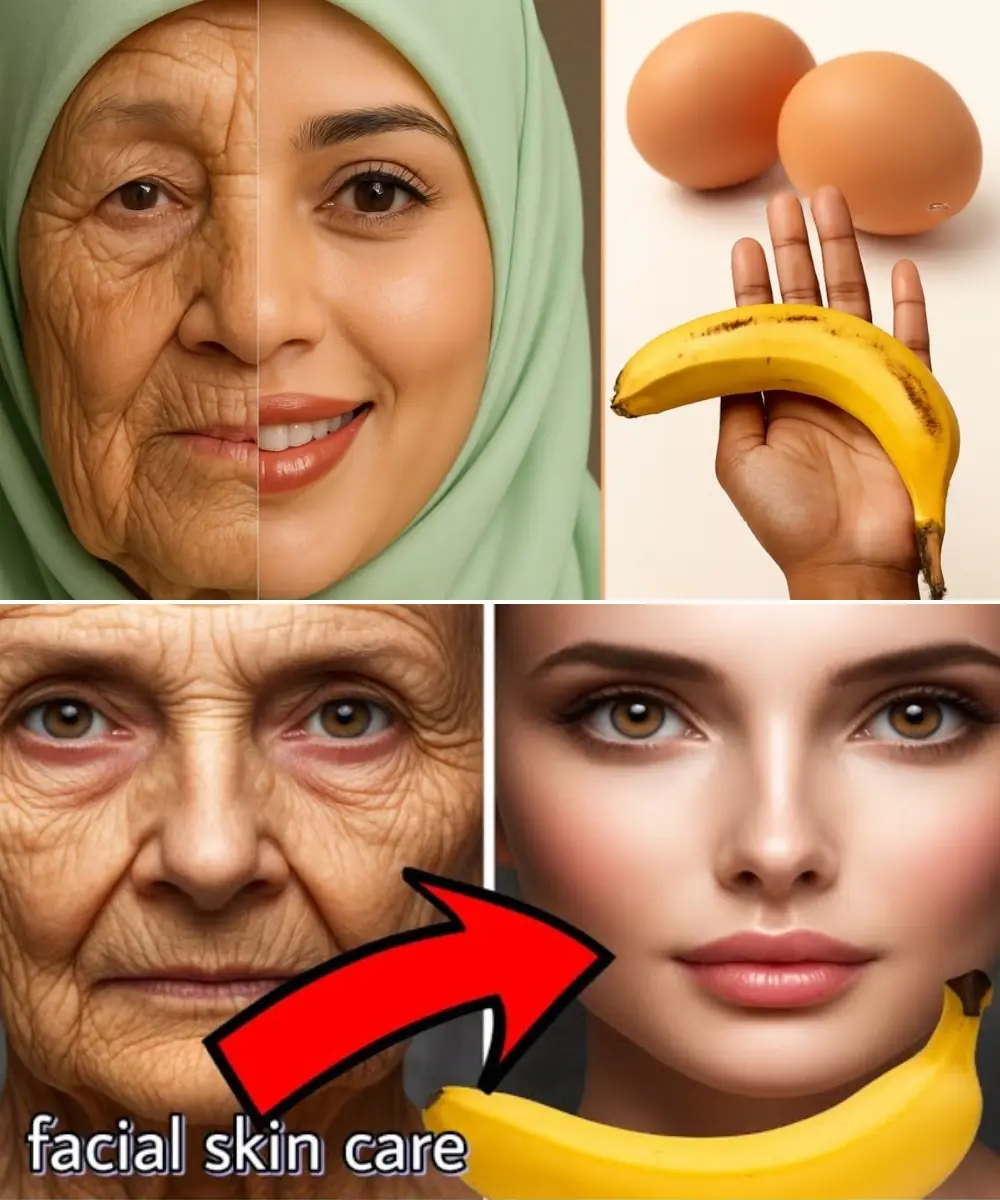

Banana and Egg Mask to Look Younger Even in Your 80s
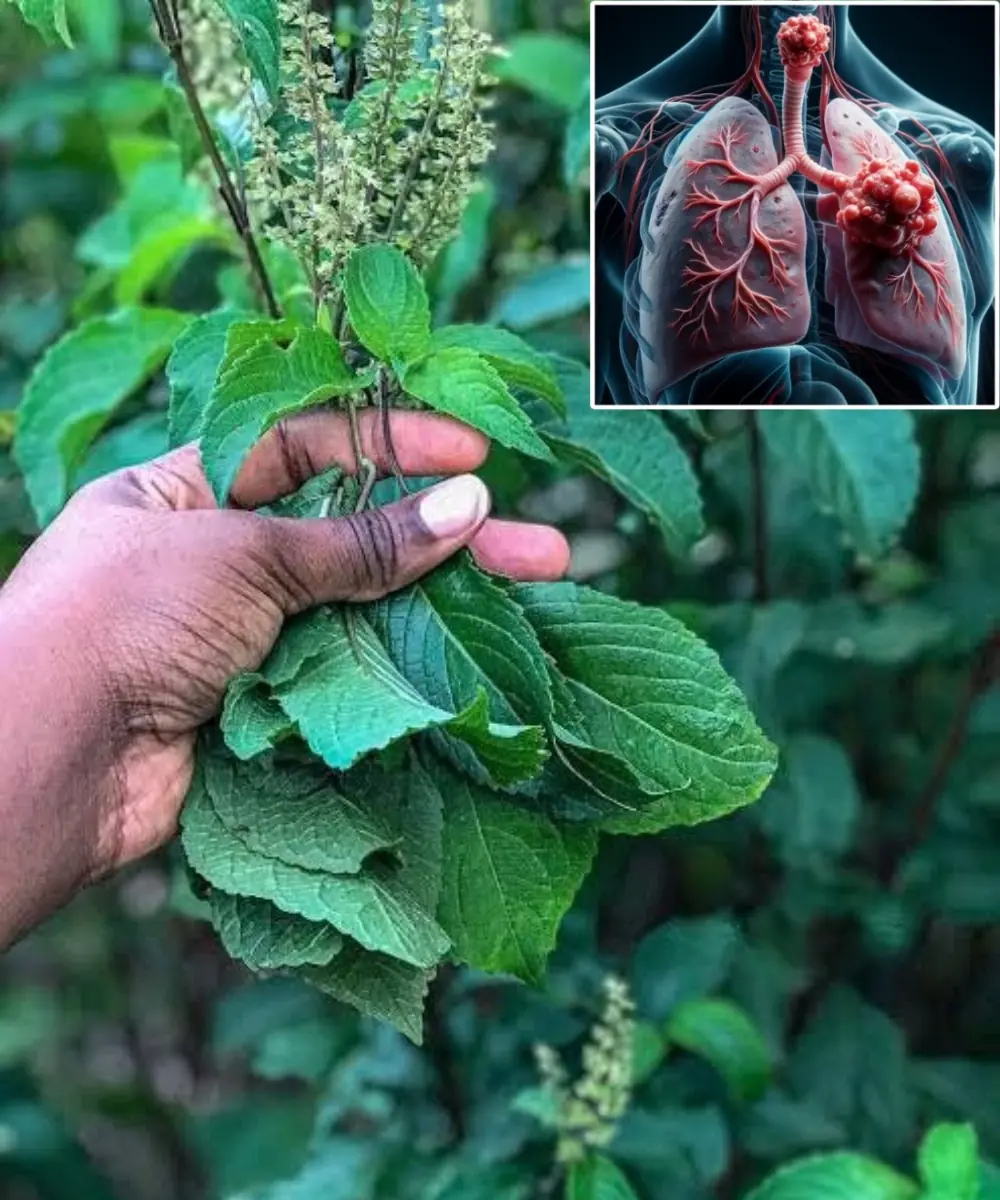

Scent Leaf Secrets Unveiled: 10 Surprising Health Benefits of This Miracle Herb
