
Hidden Dangers in Your Mouth: Early Signs of Oral Cancer
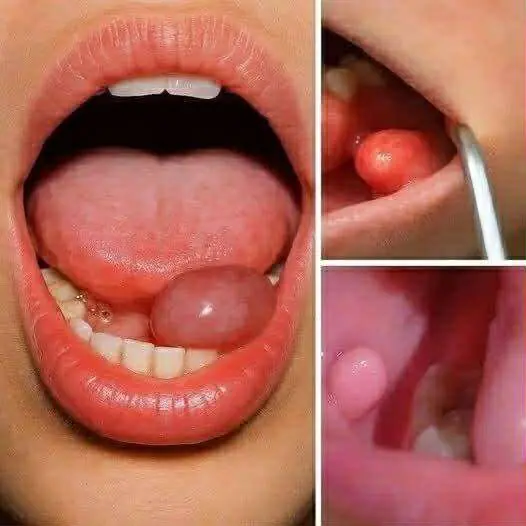
Many people ignore small changes in their mouths — a sore, patch, or bit of discoloration — assuming they’re harmless. However, these minor issues can sometimes signal something much more serious: oral cancer. This form of cancer often develops silently, showing few symptoms in its early stages but progressing rapidly if untreated. People over 40, smokers, and frequent alcohol consumers are at greater risk. Recognizing early warning signs such as persistent sores, numbness, or discoloration can make a life-saving difference.
Understanding Oral Cancer
Oral cancer affects the mouth, lips, tongue, gums, and nearby tissues. It is more common in men over the age of 40 and is frequently detected only after spreading to the lymph nodes in the neck. Early diagnosis, however, greatly improves survival rates.
Common Types of Oral Cancer
-
Lip cancer
-
Tongue cancer
-
Inner cheek cancer
-
Gum cancer
-
Cancer of the floor of the mouth
If any unusual symptoms appear, it’s important to consult a dentist or specialist immediately. Regular dental check-ups — ideally twice a year — can help detect early warning signs before the disease progresses.
Warning Signs and Symptoms
In its early stages, oral cancer may not cause noticeable discomfort, but certain symptoms warrant attention, including:
-
Mouth sores or ulcers that do not heal
-
Swelling inside the mouth
-
Loose teeth
-
Unexplained bleeding
-
Pain or difficulty swallowing
-
Lumps in the neck
-
Ear pain or persistent sore throat
-
Numbness in the lips, chin, or face
-
Red or white patches in the mouth
-
Jaw stiffness or tongue pain
-
Unexplained weight loss
These symptoms don’t always indicate cancer, but professional evaluation is essential if they persist for more than two weeks.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several behaviors and exposures significantly raise the risk of developing oral cancer:
-
Smoking: Cigarettes, cigars, and pipes are major contributors.
-
Tobacco chewing: Smokeless tobacco products can directly damage oral tissues.
-
Excessive alcohol use: Chronic drinking increases susceptibility.
-
HPV infection: Certain strains of human papillomavirus are linked to oral cancers.
-
Poor oral hygiene and chronic irritation may also play a role.
Stages of Oral Cancer
Understanding the stage of cancer helps determine the best treatment plan:
-
Stage 1: Tumor is less than 1 inch and hasn’t spread to lymph nodes.
-
Stage 2: Tumor is 1–2 inches, still without lymph node involvement.
-
Stage 3: Tumor is larger or has reached nearby lymph nodes.
-
Stage 4: Advanced stage involving deeper tissues or distant spread.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the cancer’s stage and location:
-
Surgery: Removal of the tumor; sometimes includes reconstructive procedures.
-
Radiation therapy: High-energy beams destroy cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue.
-
Chemotherapy: Anti-cancer drugs used alone or alongside radiation.
-
Targeted therapy: Focuses on specific cancer cell mechanisms to prevent further growth.
Key Facts to Know
-
Around 80% of oral cancer cases are linked to tobacco use.
-
The average age of diagnosis is approximately 50 years.
-
Men are more commonly affected than women.
-
Early detection raises survival rates to about 82%, while late detection reduces it to around 27%.
Why Early Detection Matters
Regular dental visits and self-monitoring for unusual changes are vital. Neglecting oral health often leads to delayed diagnosis and poorer outcomes. Detecting the disease early can prevent complications, improve treatment success, and save lives.
Final Thoughts
Oral cancer may start quietly, but its consequences can be devastating. Pay attention to persistent sores, patches, or numbness in your mouth. Seek medical evaluation for any lasting or unusual symptoms. Staying alert, avoiding tobacco and alcohol, and scheduling routine dental check-ups are your best defenses against this silent but serious disease.
This information is intended for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice or diagnosis.
News in the same category


If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, Your Body Will Send You These 8 Signals — Don’t Ignore Them

The Surprising Effects of Avocado on Your Heart and Brain
Natural Remedy for Cataracts and Eye Inflammation: Restore Your Vision Naturally

Unlock the Golden Magic of Corn Silk Tea
9 Powerful Home Remedies to Get Rid of Fungal Infection (Daad, Khaj, Khujli) Fast
7 Shocking Health Benefits Of Eating Sweet Potatoes Every Day — According To Science

About 15 Minutes Before a Stroke, the Body Often Sends 4 Clear Warning Signs — Call Your Loved Ones Immediately

The Secret Power Of The Herb That Helps You Age Gracefully

The Unexpected Benefits of Eating Chicken Feet
If You See Someone with “Blue Veins,” Tell Them This — It Could Save Their Life
The Secret Power of Two Eggs a Day: Could This Simple Habit Transform Your Health? Buy vitamins and supplements

Man Passed Away After Eating Eggs — Stop Eating Eggs This Way Immediately
8 Foods That Fight Tumors — Eat Them Regularly

Does Eating Bananas Before Bed Have Any Benefits?

The Tongue as a Health Indicator: Meaning of a Whitish Color

Benefits of Boiled Eggs: Nutrition and Healthy Recipes
5 early warning signs of cervical cancer
7 Innocent Mistakes That Get Your Kidneys in Big Trouble
News Post
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN WE TONGUE KISS…See more

Nature’s Secret: 4 Healing Leaves That Support Metabolism, Immunity & Circulation Naturally

Don’t Drink Coconut Water Before You Know These 11 Secrets!

Pumpkin Seed Milk — The Natural Parasite Cleanser
Fast Rice Water Trick for a Brighter Smile
Morning Drink to Revive Your Kidneys Fast
The Onion Recipe That Could Transform Your Blood Sugar, Support Cleaner Arteries, and Protect Your Heart!

Top 4 Fruits That Help Your Kidneys Flush Out Toxins While You Sleep
Ginger, Clove, and Honey: The Natural Trio Your Body Will Thank You For

Heal 15 Years of Joint Pain Naturally with Turmeric and Honey Tea

This Juice Revived My Grandma’s Energy — Say Goodbye to Fatigue and Body Pain with This Natural Recipe

The Benefits of Eating 2 Boiled Eggs Every Morning: Transform Your Health!

If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, Your Body Will Send You These 8 Signals — Don’t Ignore Them

The Surprising Effects of Avocado on Your Heart and Brain

Ways to Get Over a Man Who Didn’t Value You

I’m 66 but Look 36 — My Secret? Aloe Vera & Ginger for Firm, Smooth Skin

How to Make Okra Water to Treat 17 Health Problems Naturally

Banana and Egg Mask to Look Younger Even in Your 80s

Scent Leaf Secrets Unveiled: 10 Surprising Health Benefits of This Miracle Herb
