
Health News 2025-02-25 23:41:29
Are Your Legs a Warning Sign of Cervical Cancer? Don’t Ignore These 4 Symptoms!
News in the same category


If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, Your Body Will Send You These 8 Signals — Don’t Ignore Them

The Surprising Effects of Avocado on Your Heart and Brain
Natural Remedy for Cataracts and Eye Inflammation: Restore Your Vision Naturally
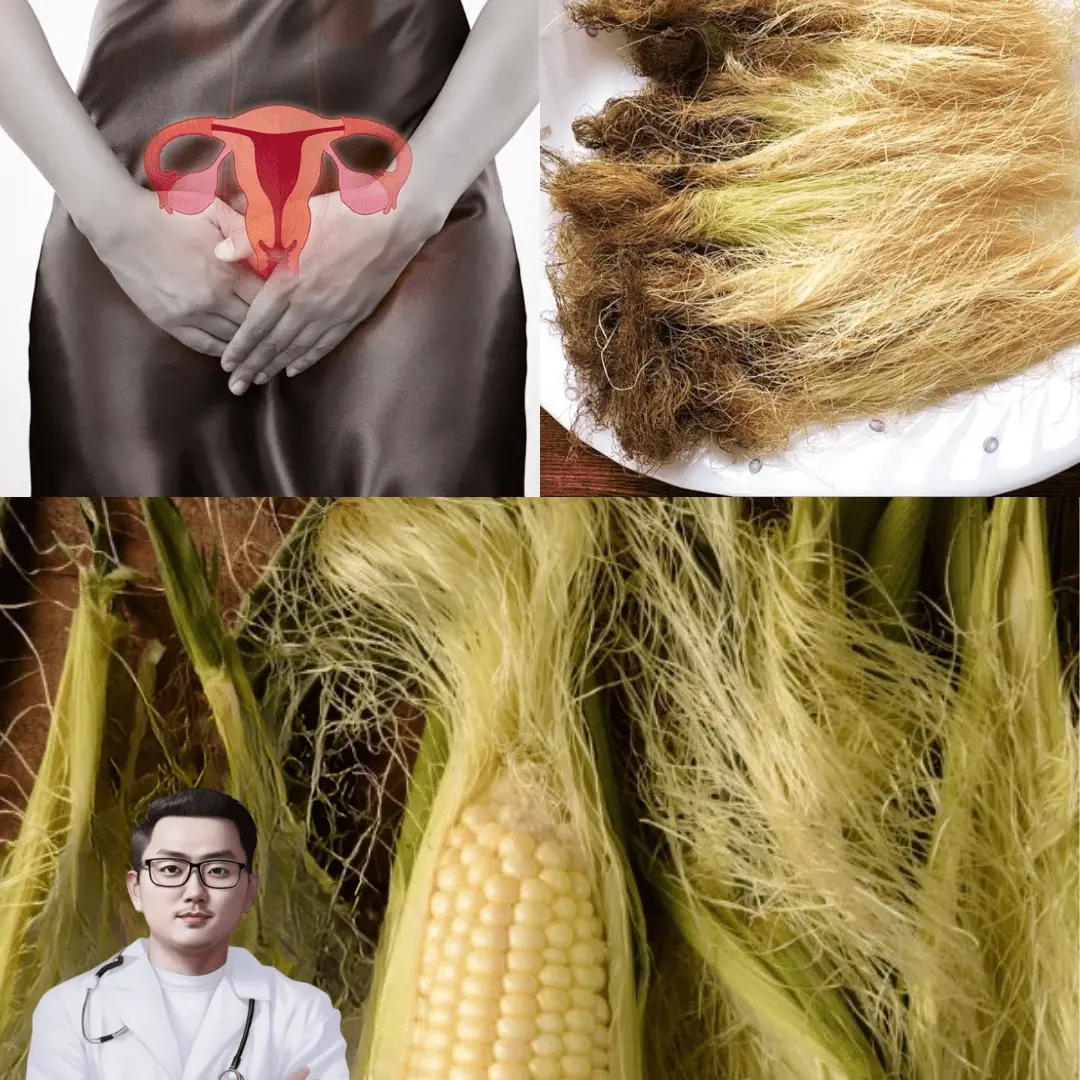

Unlock the Golden Magic of Corn Silk Tea
9 Powerful Home Remedies to Get Rid of Fungal Infection (Daad, Khaj, Khujli) Fast
7 Shocking Health Benefits Of Eating Sweet Potatoes Every Day — According To Science

About 15 Minutes Before a Stroke, the Body Often Sends 4 Clear Warning Signs — Call Your Loved Ones Immediately
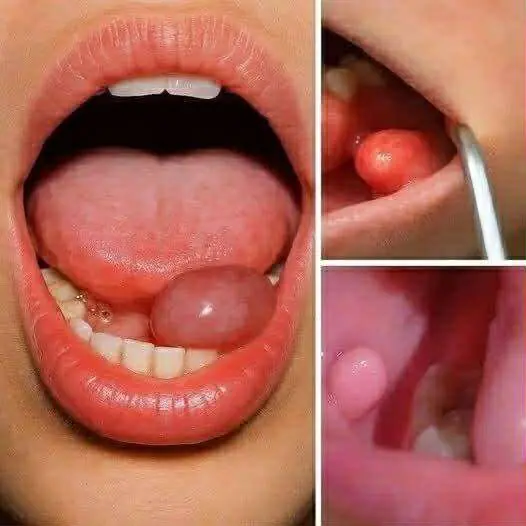
Hidden Dangers in Your Mouth: Early Signs of Oral Cancer
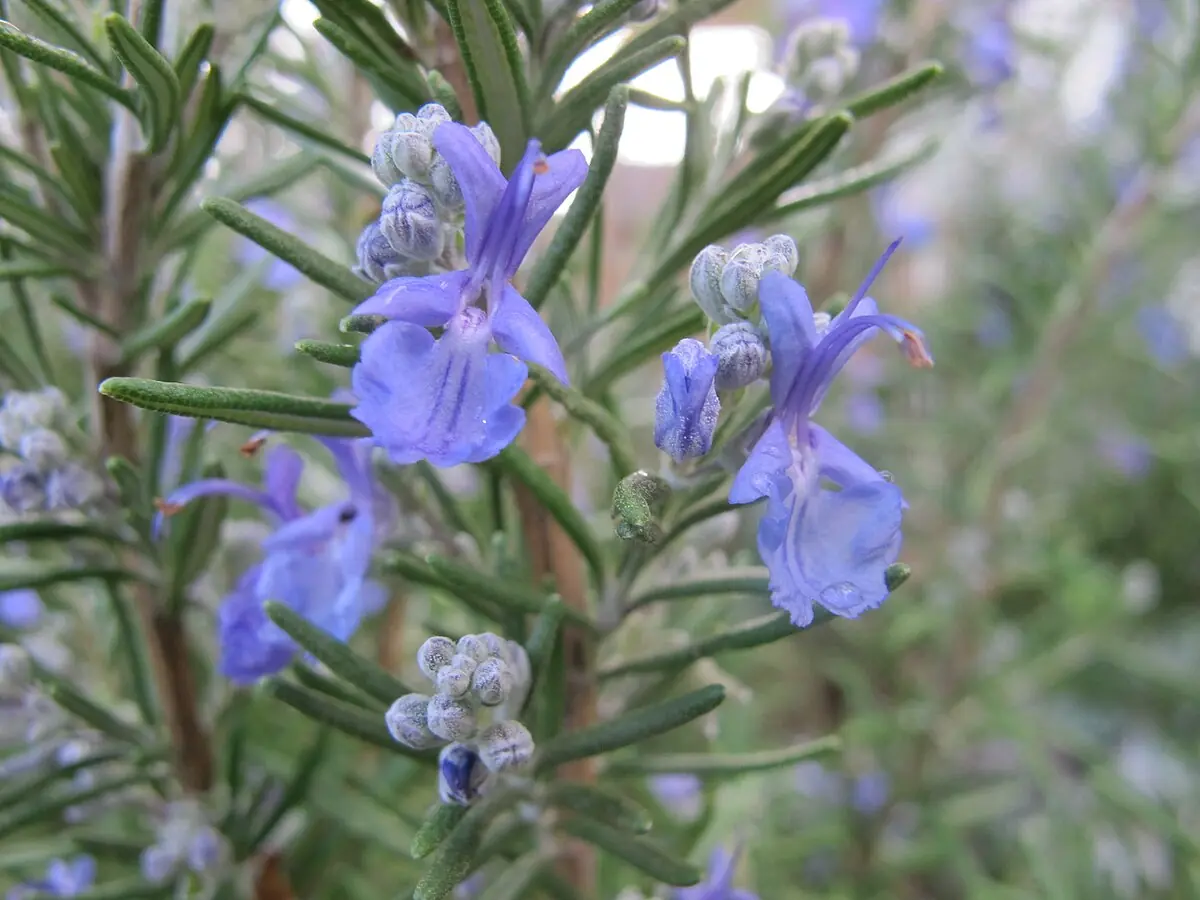

The Secret Power Of The Herb That Helps You Age Gracefully
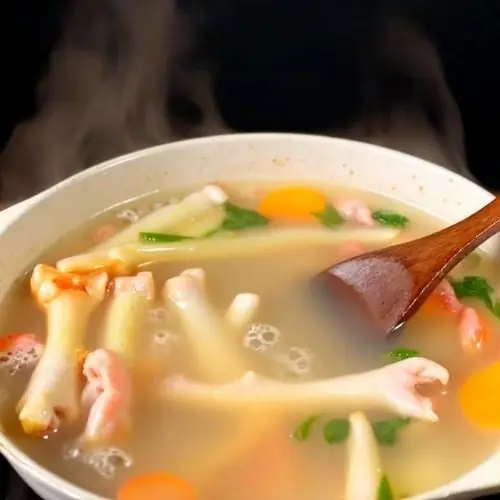

The Unexpected Benefits of Eating Chicken Feet
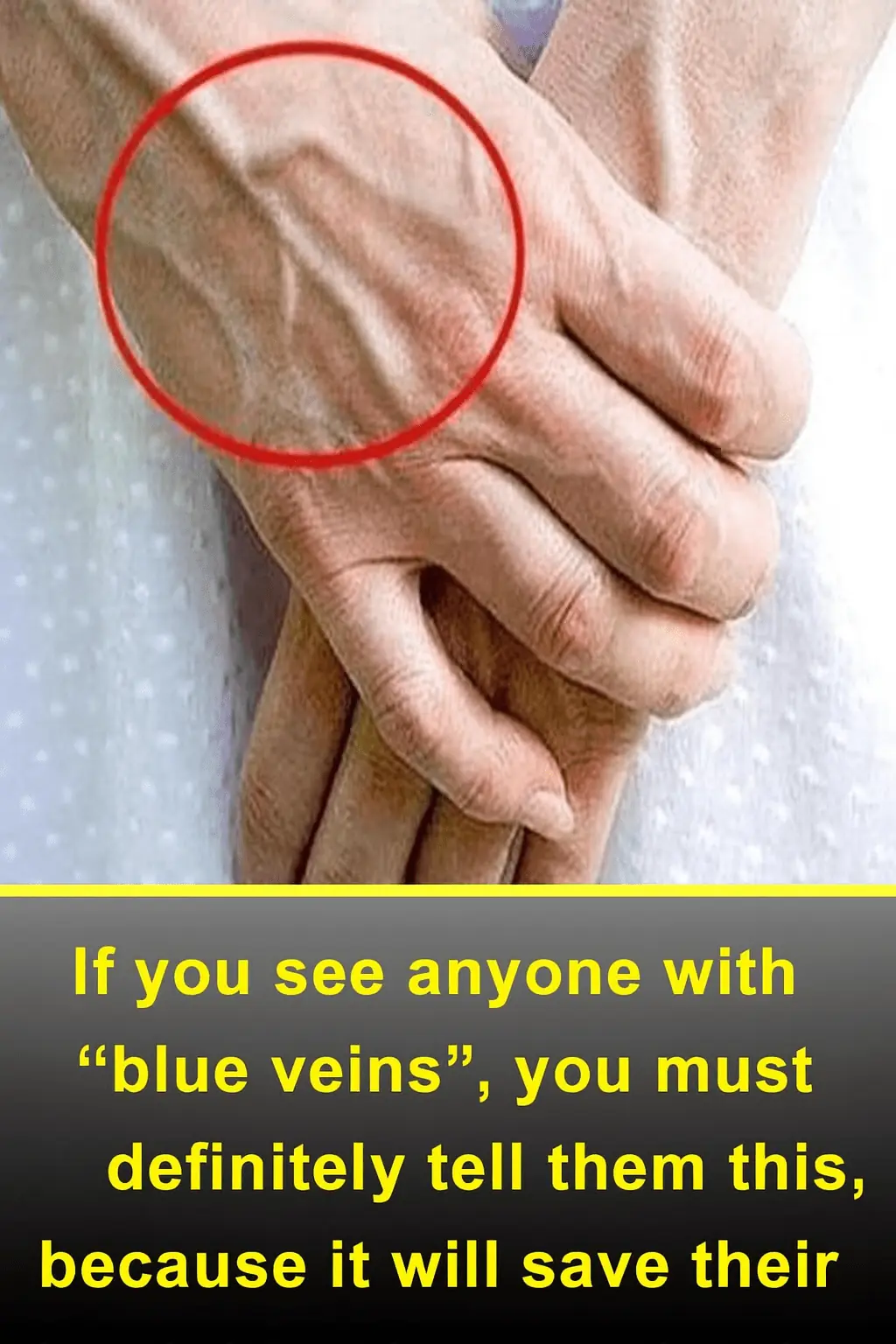
If You See Someone with “Blue Veins,” Tell Them This — It Could Save Their Life
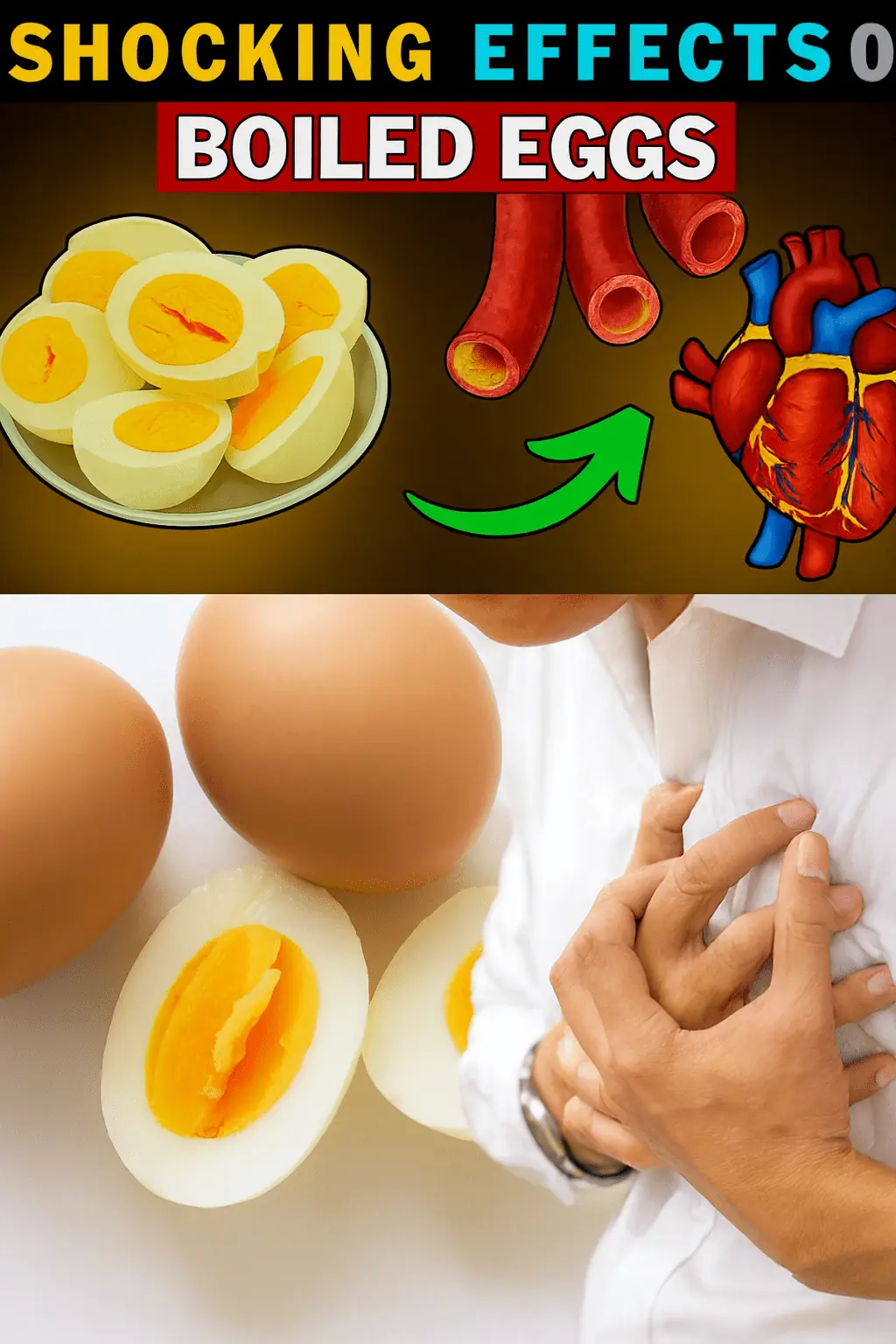
The Secret Power of Two Eggs a Day: Could This Simple Habit Transform Your Health? Buy vitamins and supplements

Man Passed Away After Eating Eggs — Stop Eating Eggs This Way Immediately
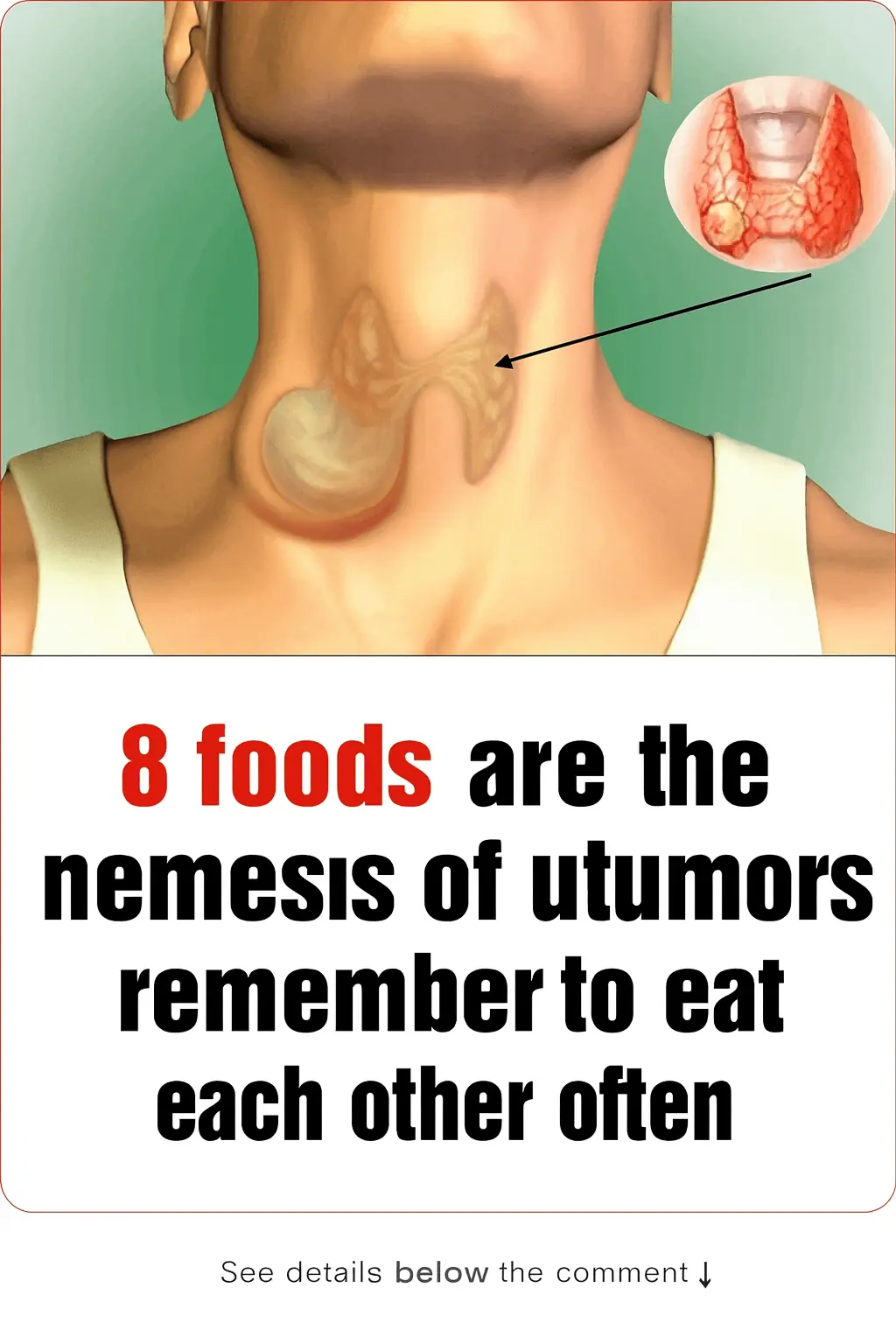
8 Foods That Fight Tumors — Eat Them Regularly

Does Eating Bananas Before Bed Have Any Benefits?

The Tongue as a Health Indicator: Meaning of a Whitish Color

Benefits of Boiled Eggs: Nutrition and Healthy Recipes
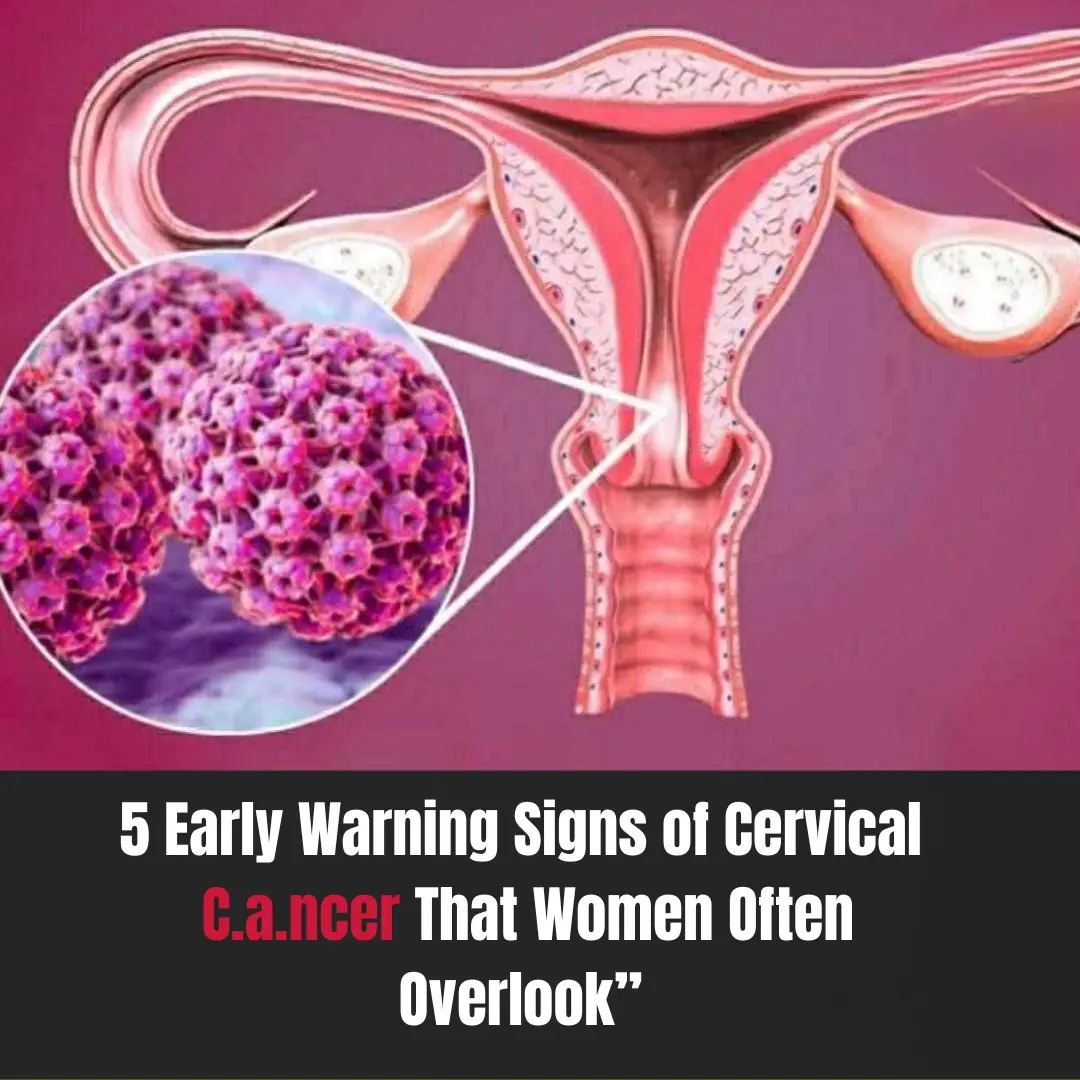
5 early warning signs of cervical cancer
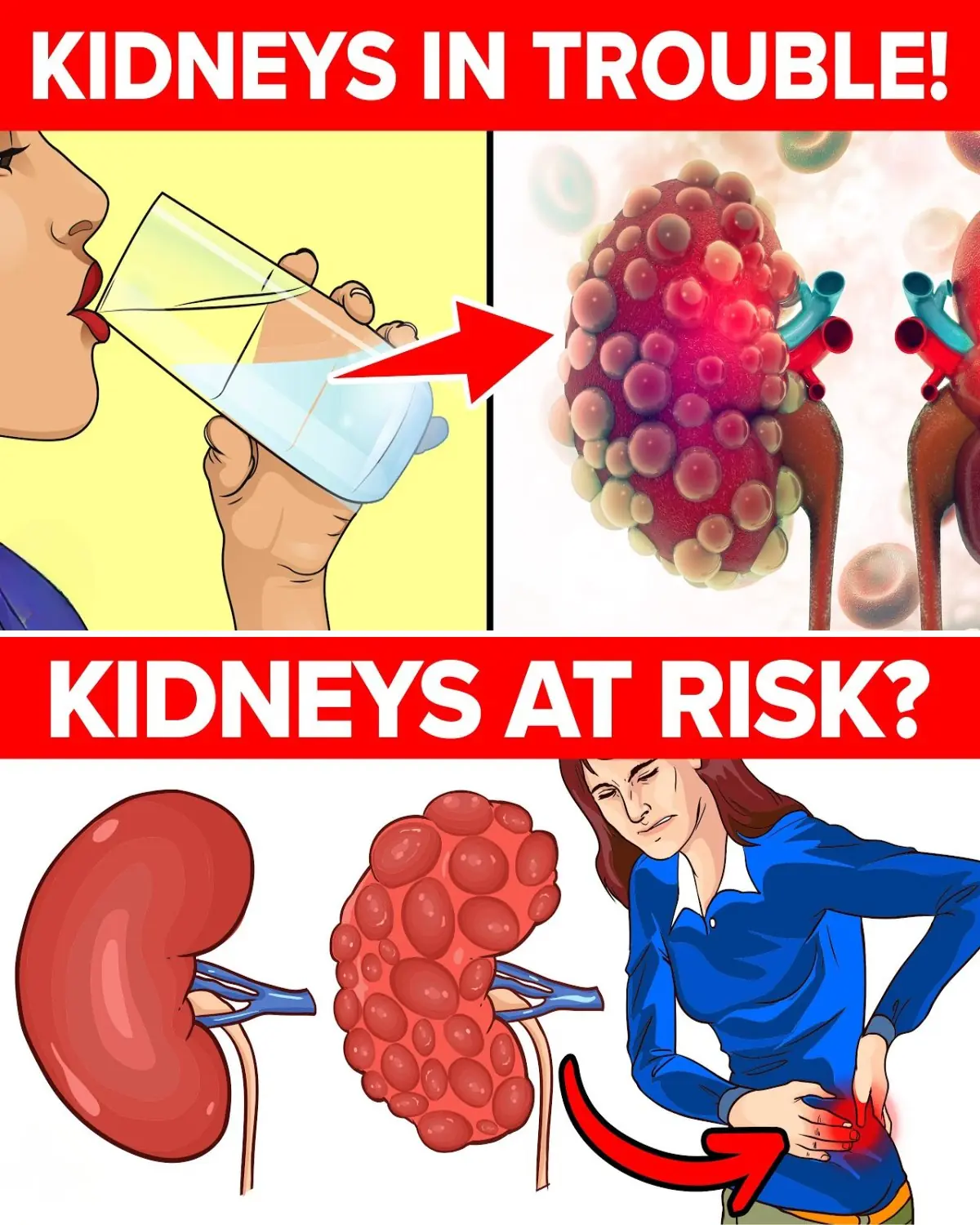
7 Innocent Mistakes That Get Your Kidneys in Big Trouble
News Post
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN WE TONGUE KISS…See more
Fitness 30/10/2025 13:23
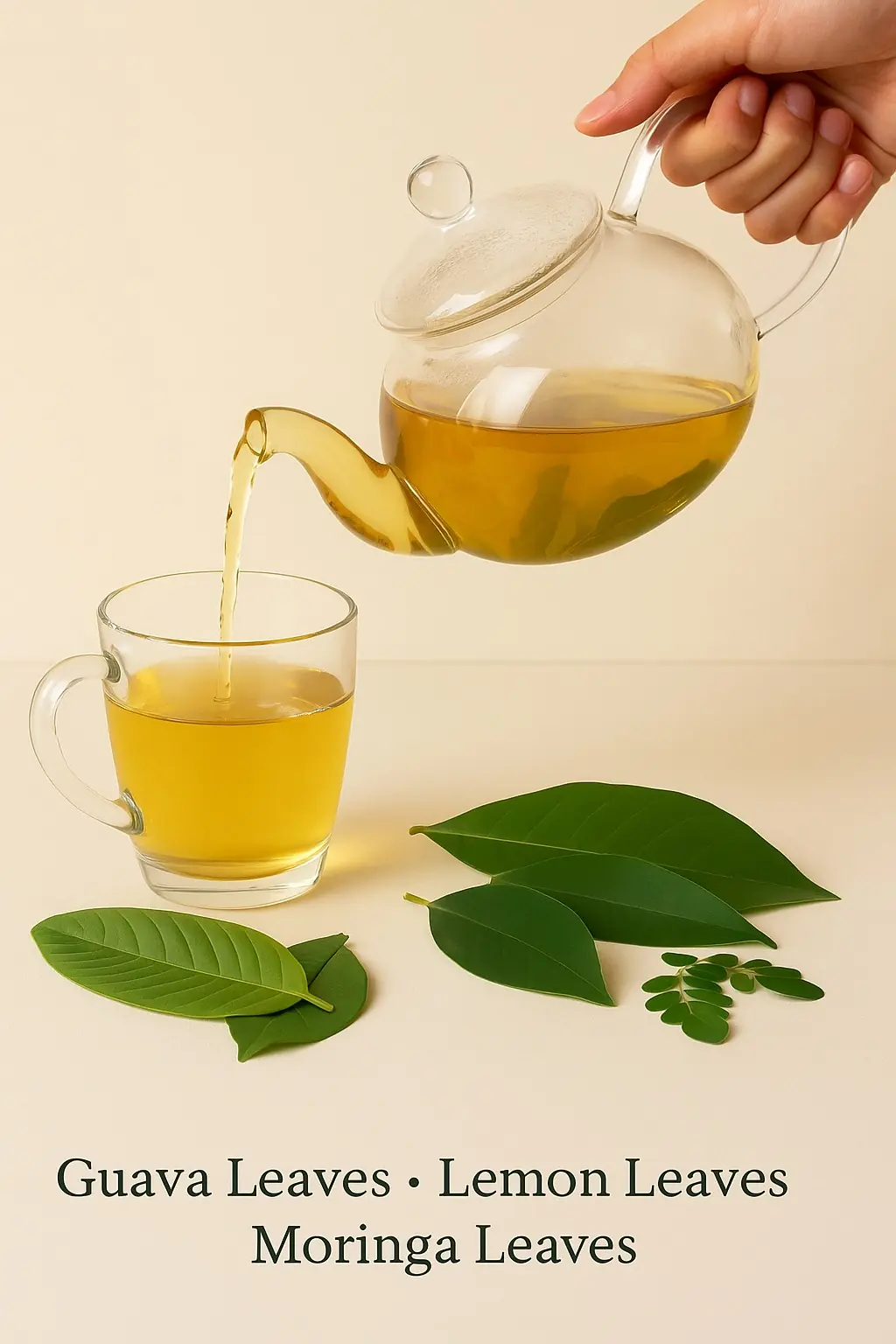

Nature’s Secret: 4 Healing Leaves That Support Metabolism, Immunity & Circulation Naturally
Healthy 27/10/2025 19:23
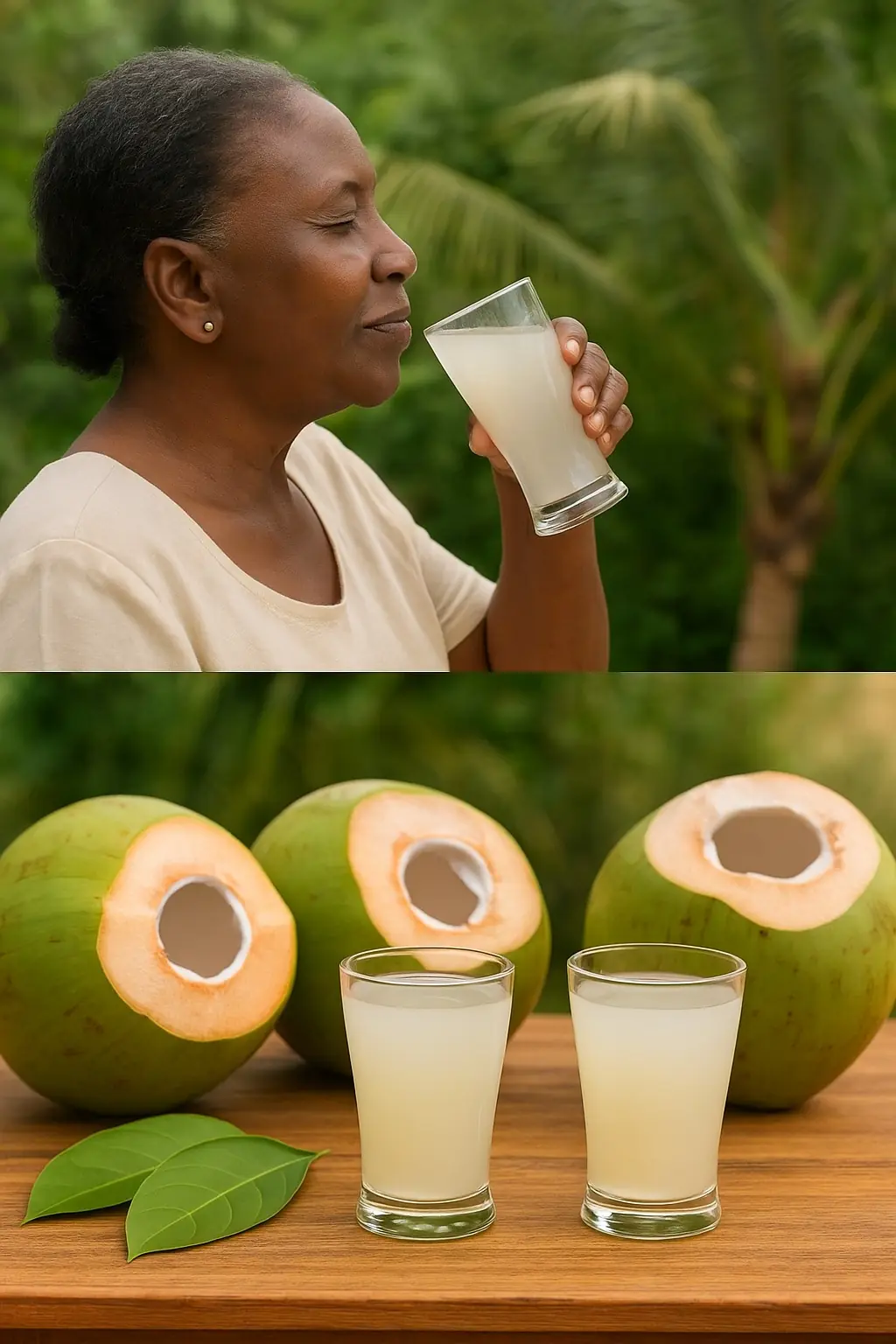

Don’t Drink Coconut Water Before You Know These 11 Secrets!
Healthy 27/10/2025 19:21
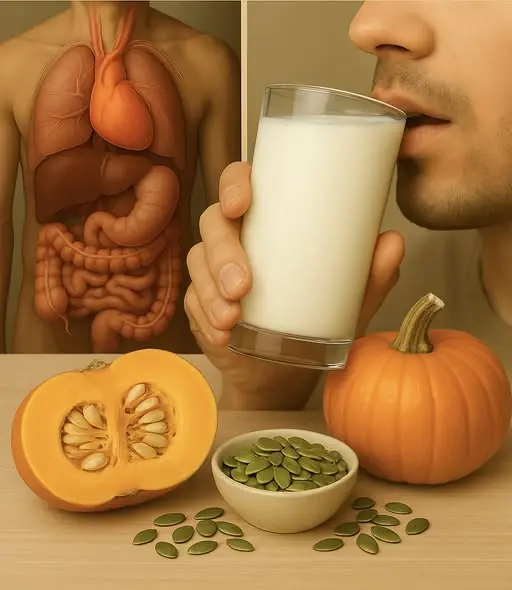

Pumpkin Seed Milk — The Natural Parasite Cleanser
Healthy 27/10/2025 19:19
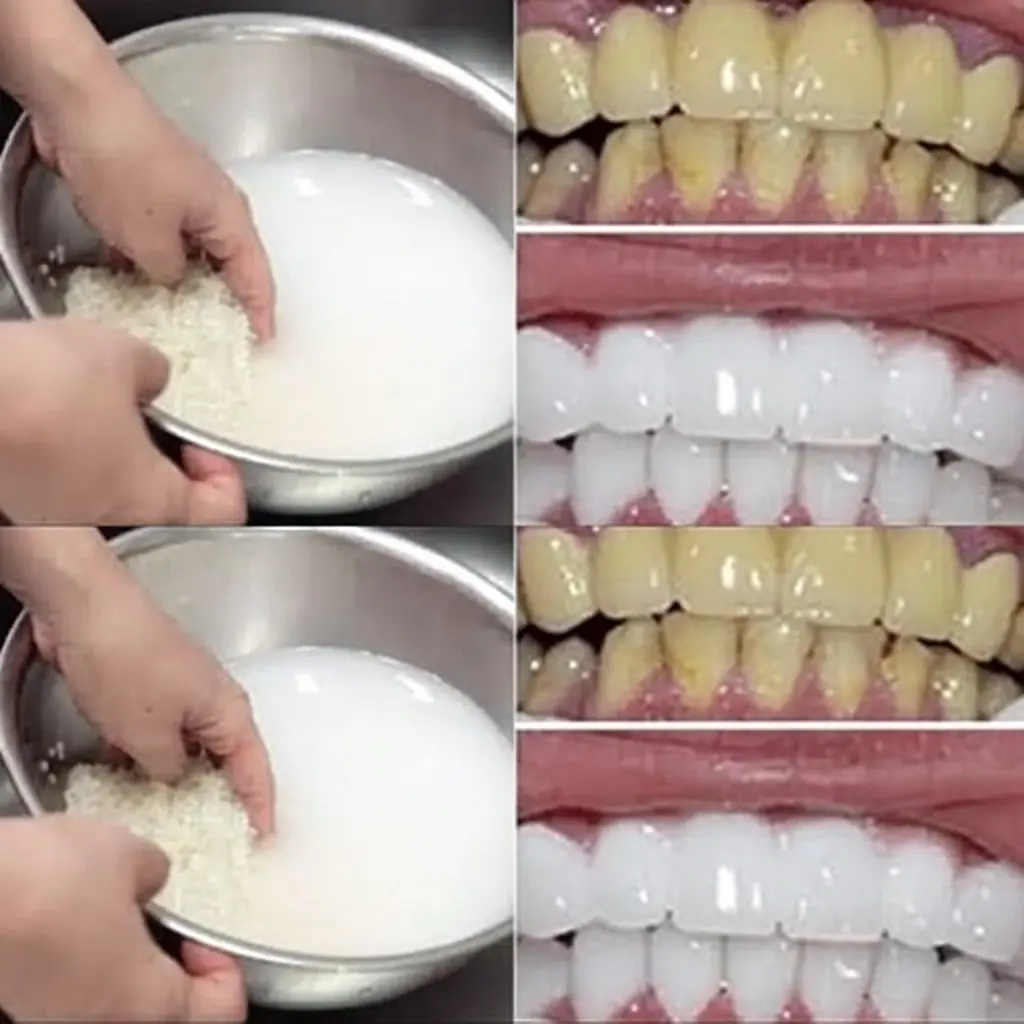
Fast Rice Water Trick for a Brighter Smile
Healthy 26/10/2025 22:42
Morning Drink to Revive Your Kidneys Fast
Healthy 26/10/2025 22:38
The Onion Recipe That Could Transform Your Blood Sugar, Support Cleaner Arteries, and Protect Your Heart!
Healthy 26/10/2025 22:37

Top 4 Fruits That Help Your Kidneys Flush Out Toxins While You Sleep
Healthy 26/10/2025 22:35
Ginger, Clove, and Honey: The Natural Trio Your Body Will Thank You For
Healthy 26/10/2025 19:06
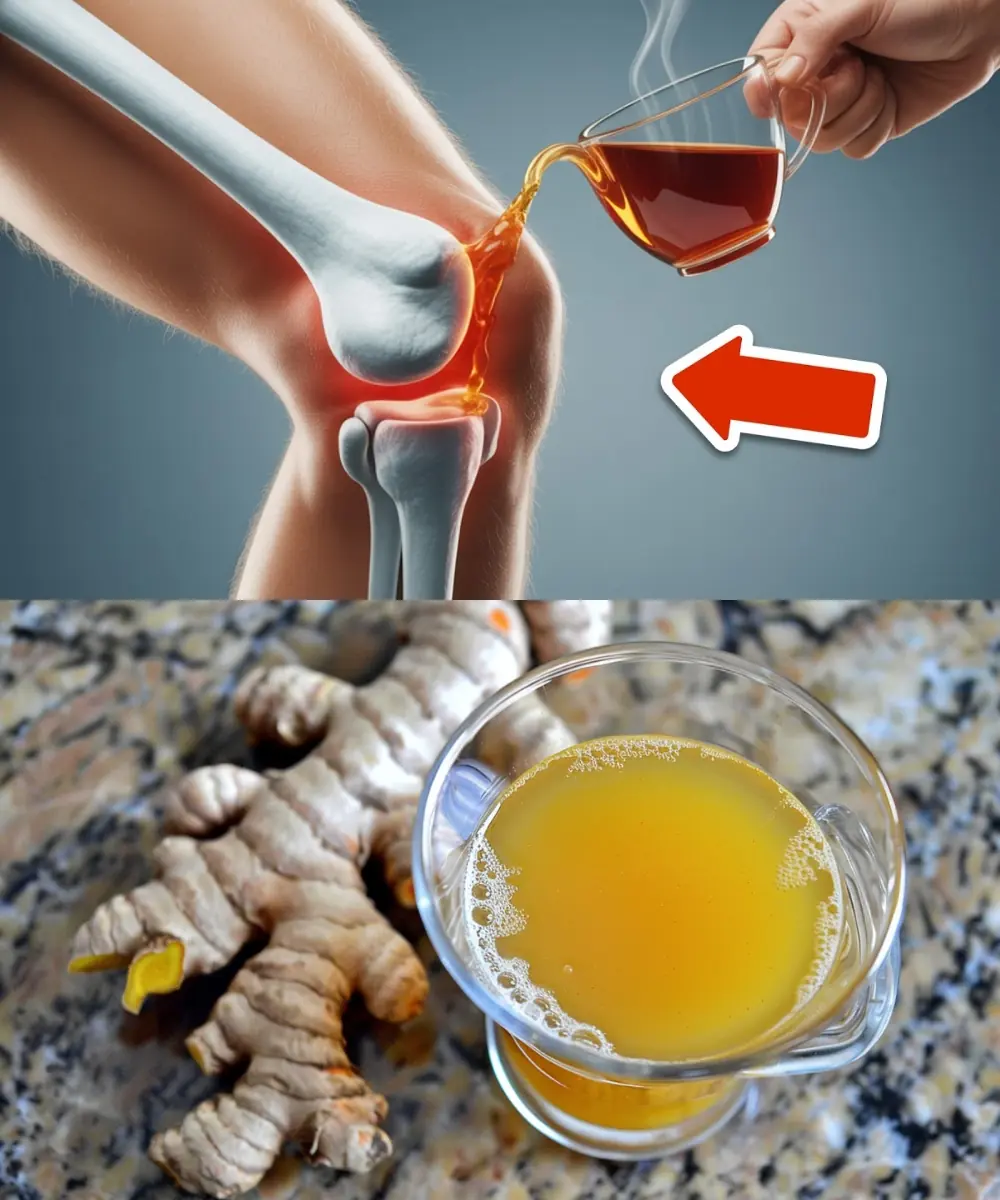

Heal 15 Years of Joint Pain Naturally with Turmeric and Honey Tea
Healthy 26/10/2025 19:04

This Juice Revived My Grandma’s Energy — Say Goodbye to Fatigue and Body Pain with This Natural Recipe
Healthy 26/10/2025 19:02

The Benefits of Eating 2 Boiled Eggs Every Morning: Transform Your Health!
Health News 26/10/2025 01:57

If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, Your Body Will Send You These 8 Signals — Don’t Ignore Them
Health News 26/10/2025 01:54

The Surprising Effects of Avocado on Your Heart and Brain
Health News 26/10/2025 01:44

Ways to Get Over a Man Who Didn’t Value You
Fun Fact 26/10/2025 01:36
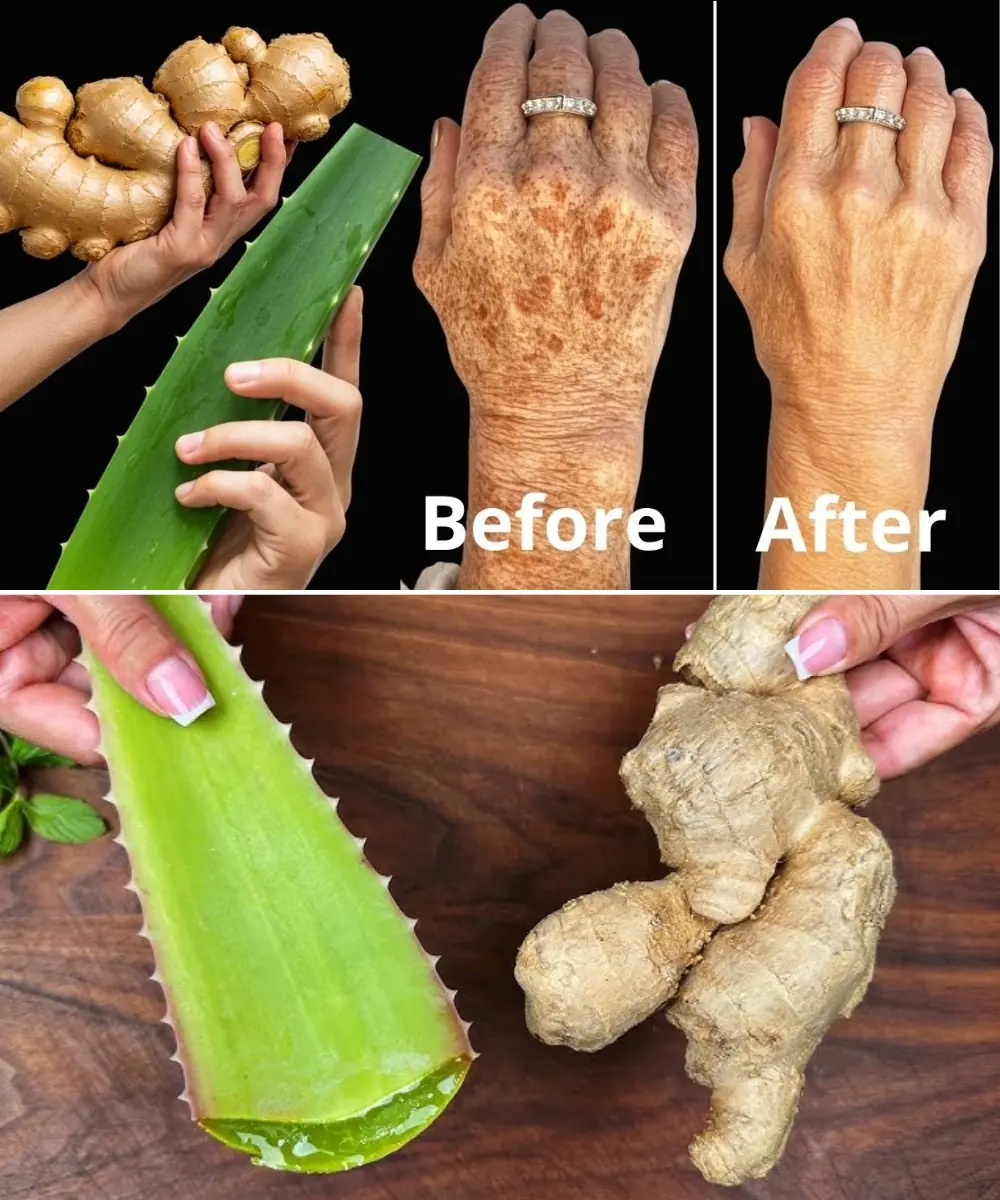

I’m 66 but Look 36 — My Secret? Aloe Vera & Ginger for Firm, Smooth Skin
Healthy 25/10/2025 19:44
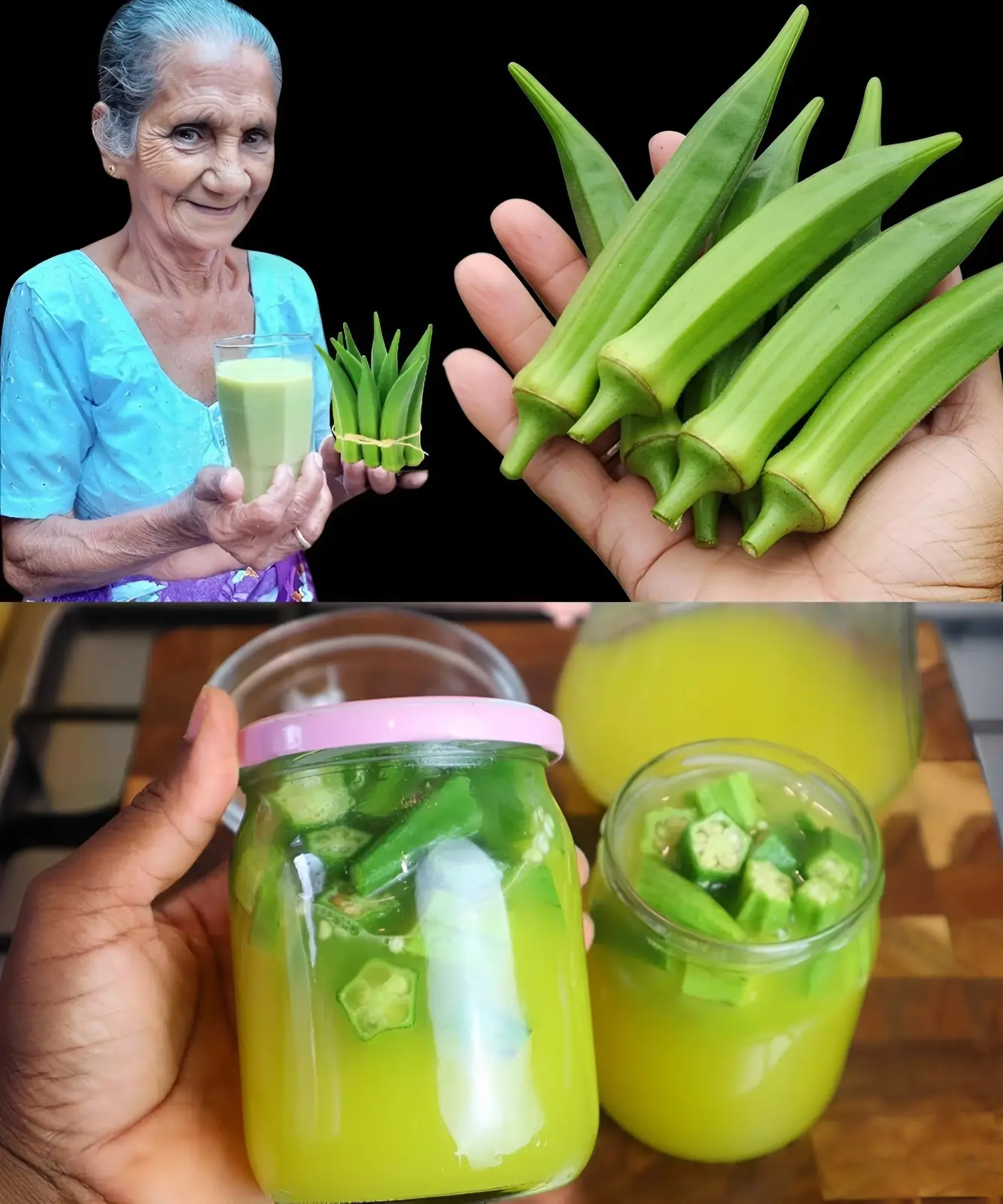

How to Make Okra Water to Treat 17 Health Problems Naturally
Healthy 25/10/2025 19:42
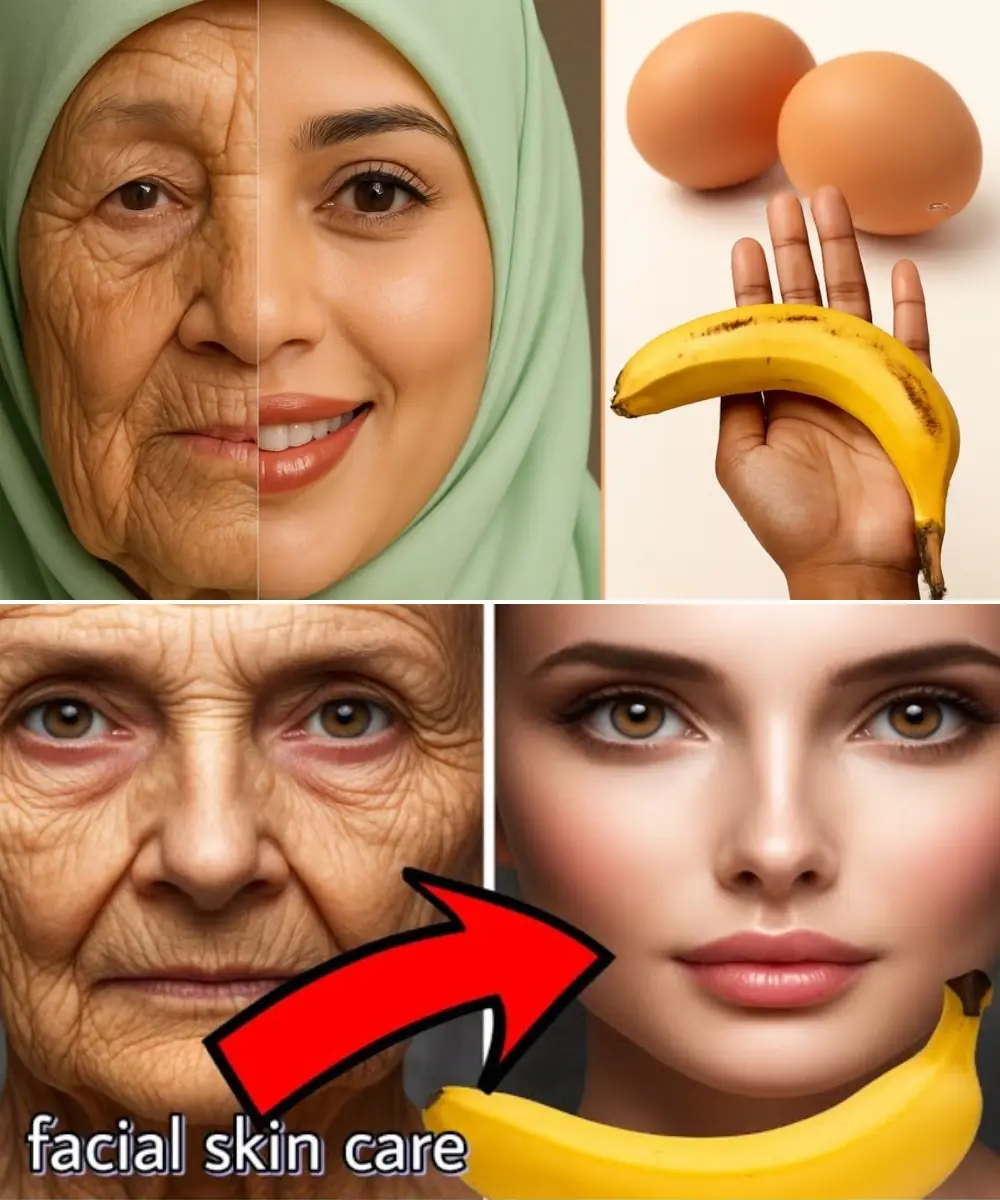

Banana and Egg Mask to Look Younger Even in Your 80s
Healthy 25/10/2025 19:29
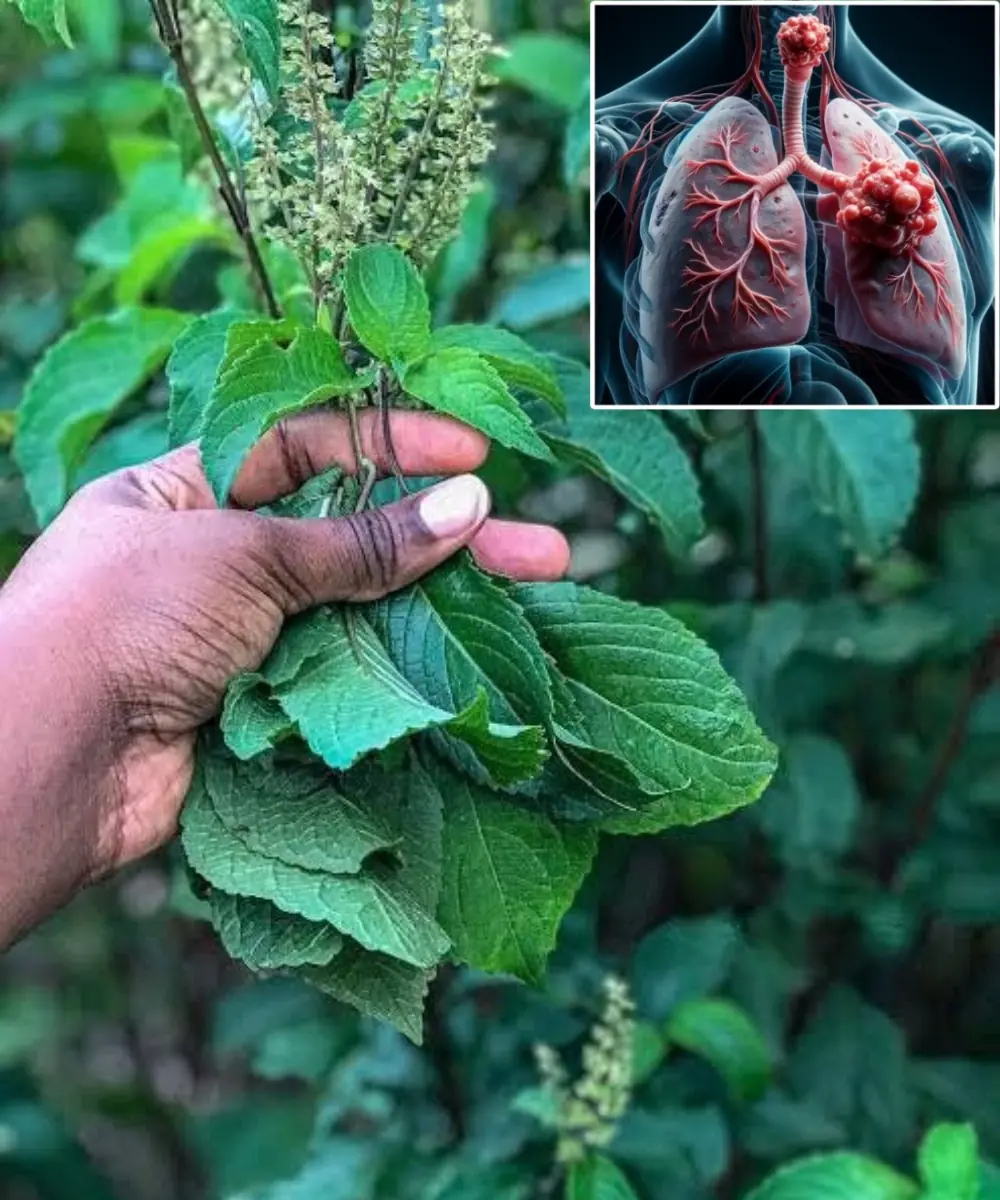

Scent Leaf Secrets Unveiled: 10 Surprising Health Benefits of This Miracle Herb
Healthy 25/10/2025 19:24

From White Hair to Black Hair Naturally in Just 5 Minutes — Fast Hair Growth Remedy
Healthy 25/10/2025 19:22