
Scientists Create a Stem Cell Patch Capable of Regenerating Damaged Hearts
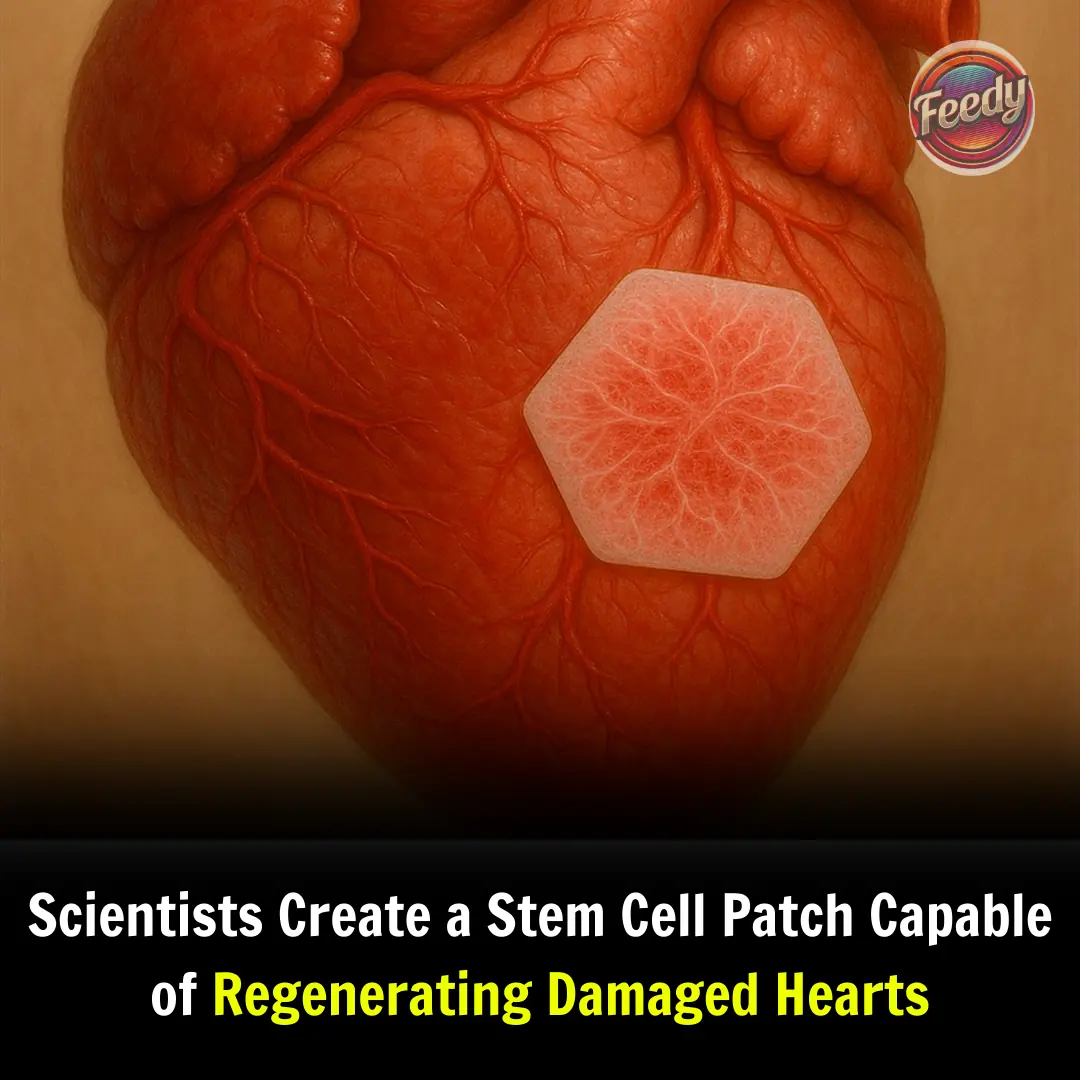
Cardiovascular disease remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Among these, heart failure—often a result of heart attacks and other cardiac conditions—is a devastating condition with limited treatment options.
Recently, a team of scientists developed a stem cell patch capable of regenerating damaged hearts, marking a major milestone in regenerative medicine.
This breakthrough could revolutionize how heart disease is treated and offer new hope to millions of patients around the world.
Read more: Scientists develop a new biomaterial that can regenerate damaged cartilage in joints.
How Does the Stem Cell Patch Work?
The stem cell patch is a bioengineered tissue structure implanted directly onto the surface of the affected heart. It is composed of cardiomyocytes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and supportive cells. These cells are programmed to differentiate into functional heart tissue, promoting myocardial regeneration.
Researchers have demonstrated that the patch integrates effectively with existing heart tissue, stimulates cellular repair, and improves heart function. Over time, the graft develops blood vessels, allowing for stable connection and normal interaction with the patient’s circulatory system.
A key aspect of this technology is that, unlike traditional implants, the transplanted cells establish biochemical communication with the host tissue, facilitating a more effective regenerative process.
Research Results in Primates and Humans
To evaluate the safety and efficacy of the patch, scientists conducted tests on non-human primates and later on a patient with end-stage heart failure. In preclinical studies, the patches showed long-term cell retention and improved contractility of the heart wall. An increase in the heart’s ejection fraction was also observed, indicating better overall organ function.
MRI scans using gadolinium contrast confirmed sufficient blood vessel formation within the graft, ensuring oxygen and nutrient delivery to the regenerating tissue. Similarly, the human patient who received the treatment showed promising initial results.
Effective graft integration was achieved without serious side effects such as arrhythmias or tumor formation. Continuous electrocardiogram monitoring revealed that the graft’s electrical activity was synchronized with the patient’s heart rhythm—an important finding indicating successful functional integration.
Benefits of the Stem Cell Patch
The development of this technology brings numerous advantages for heart disease treatment:
-
Myocardial regeneration: Unlike conventional therapies, the patch can restore damaged heart tissue.
-
Improved cell integration: The graft merges effectively with the patient's heart, enhancing function.
-
Reduced complications: No significant side effects, such as immune rejection or dangerous arrhythmias, have been reported.
-
Better tissue perfusion: The patch develops functional blood vessels, ensuring efficient delivery of oxygen and nutrients.
-
Potential clinical application: This breakthrough is a major step toward regenerative therapy for heart failure patients.
Challenges and Next Steps
Despite the encouraging results, challenges remain before widespread implementation. One major hurdle is ensuring the patches can be manufactured under Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) standards. Additionally, larger-scale clinical trials are needed to assess the treatment’s effectiveness in a broader patient population.
Another crucial aspect is developing appropriate immunosuppression strategies to prevent graft rejection without compromising the patient’s immune system. Advanced gene-editing techniques are being explored to reduce the immunogenicity of the implanted cells, potentially minimizing the need for long-term immunosuppression.
Efforts are also being made to enhance the biomaterials that form the patch matrix, aiming to optimize interactions between the cells and their environment.
Conclusion
The stem cell patch represents a remarkable innovation in the field of regenerative medicine and cardiovascular treatment. With its ability to restore heart function without causing serious side effects, this development could transform the way heart failure is treated and offer new hope to millions around the globe.
While challenges remain, scientific evidence suggests we are getting closer to finding an effective and lasting solution for cardiac regeneration. The convergence of tissue engineering, biotechnology, and personalized medicine is paving the way toward a future where regenerative therapy becomes a viable and accessible option for those suffering from severe heart conditions.
News in the same category


Doctors Gave Up, But a Woman Recovered from Cancer by Drinking Ginger and Honey

Panic Attacks And Anxiety Have Been Linked To Certain Vitamin And Mineral Deficiencies
The Hidden Link Between Air Pollution, Alzheimer’s, and Cancer — And the Dust in Your Home
The Hidden Danger in Your Pork: What You Need to Know Before You Eat!
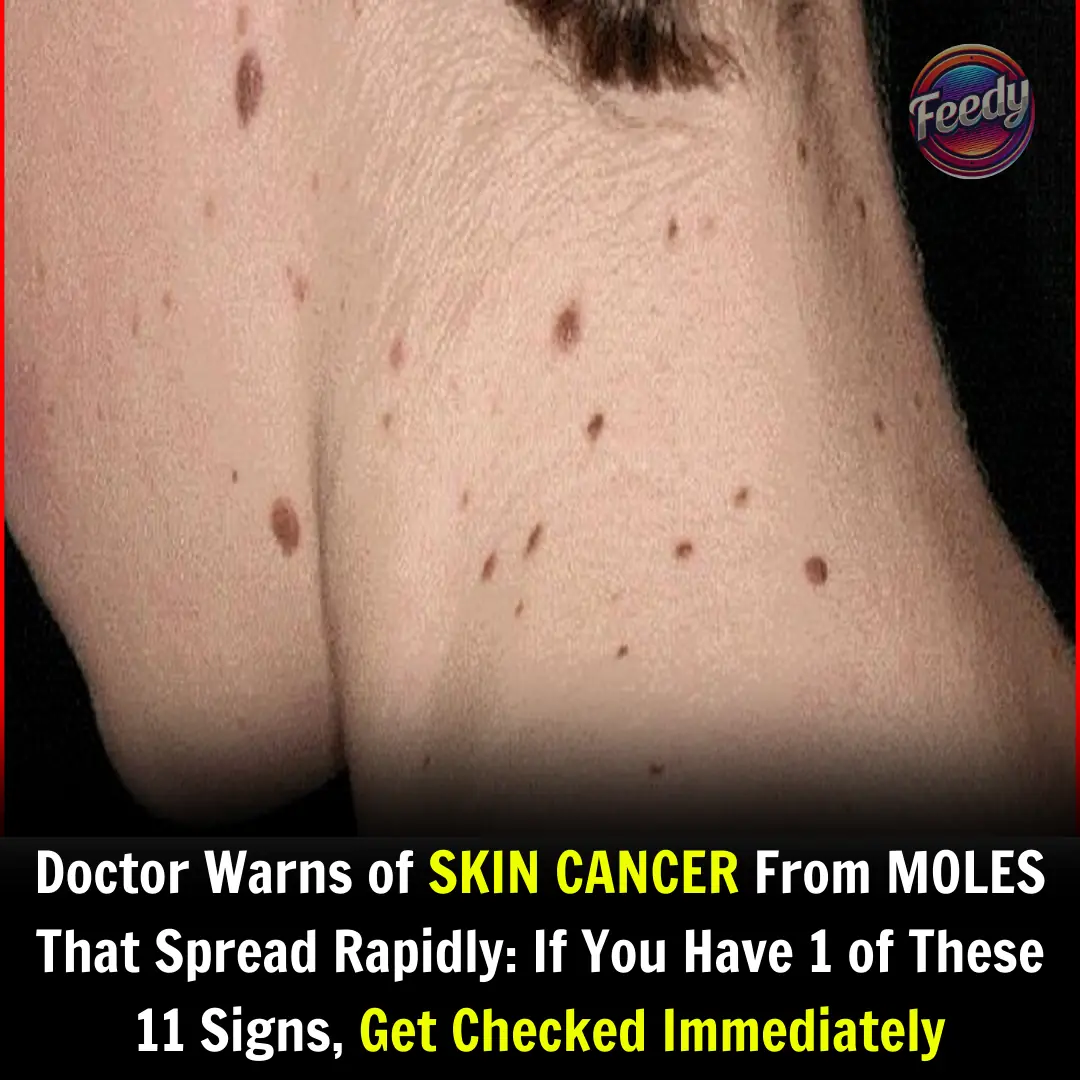
Doctor Warns of SKIN CANCER From MOLES That Spread Rapidly: If You Have 1 of These 11 Signs, Get Checked Immediately

8 Unexpected Signs You Could Be Lactose Intolerant

Is Drinking Water First Thing in the Morning Beneficial?

Don’t Throw Away Damaged Tomatoes

Remember: The kitchen is closely linked to your health!

17-Year-Old Girl Hospitalized with Kidney Failure, Must Undergo Dialysis for Life: Doctors Warn Against 3 Common Habits Among Youth

Plant in the Bible Said to Heal All Ailments

A Vegetable as Powerful as a "Miracle Herb" — A Natural Enemy of Cancer That Grows Freely in Gardens, Yet Many Overlook It

A 36-year-old teacher passed away from diabetes despite not liking sweets — doctor says it's due to 4 of her favorite foods.

Doctor issues urgent vape warning after 17-year-old develops irreversible 'popcorn lung' from popular habit

46-Year-Old Star Shares a Super Easy Anti-Aging Meal: “I’ve Maintained It for 19 Years”

This One Superfood Could Tackle Major Health Issues—Here’s What You Need To Know
Most are missing out. 10 top apple cider vinegar hacks
Shingles Vaccine Guards Against Dementia, Study Reveals
News Post

Game Challenge: Find 15 Differences in 30 SECONDS!

Understanding a Cat’s Behavior: Why Does It Rub and Scratch Against You?

These 5 Popular Drinks Are Slowly Damaging Your Kidneys — Are You Still Drinking Them?

California Authorities Identify Human Remains As A 13-Year-Old Girl Who Vanished 50 Years Ago

Stephen Hawking said he had a simple answer when asked whether he believed in god

Find Pizza, Comb, Fork, Ice Cream...😊

I Meticulously Saved Every Penny for Our Dream Home—Only for My Husband’s Parents to Try and Claim It.
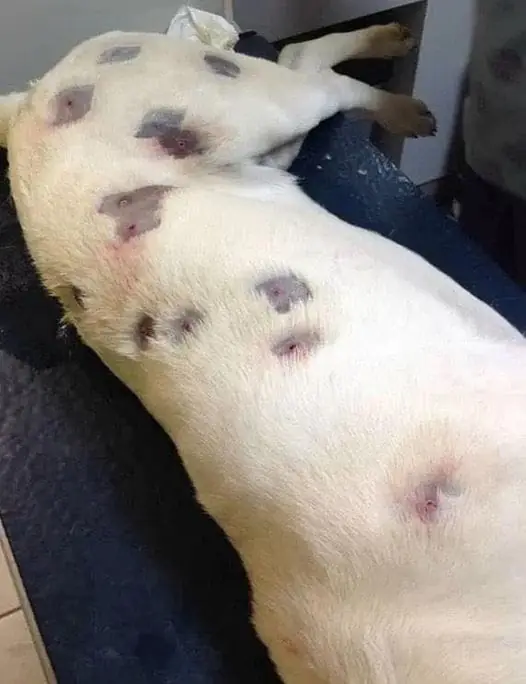
She Believed The Dog Had Numerous Bites, But The Doctor Examined It More Closely And Called The Police

My Ex-husband Got Our House, Car and All Our Money After Divorce – I Laughed Because That Was Exactly What I Planned

Can You Spot All 12 Differences? Let’s Find Out!

Homemade Korean Rice Face Cream For Wrinkle Free, Young Skin

Use This To Reverse Your Premature Grey Hair With Home Remedies

Woman Humiliated Me at a Restaurant, but the Next Day, She Appeared at My Door as My DIL…

The only drink you need for glowing skin

Pope Francis is back at the Vatican after a five-week hospital

Homemade Tonic For Thick Hair Growth
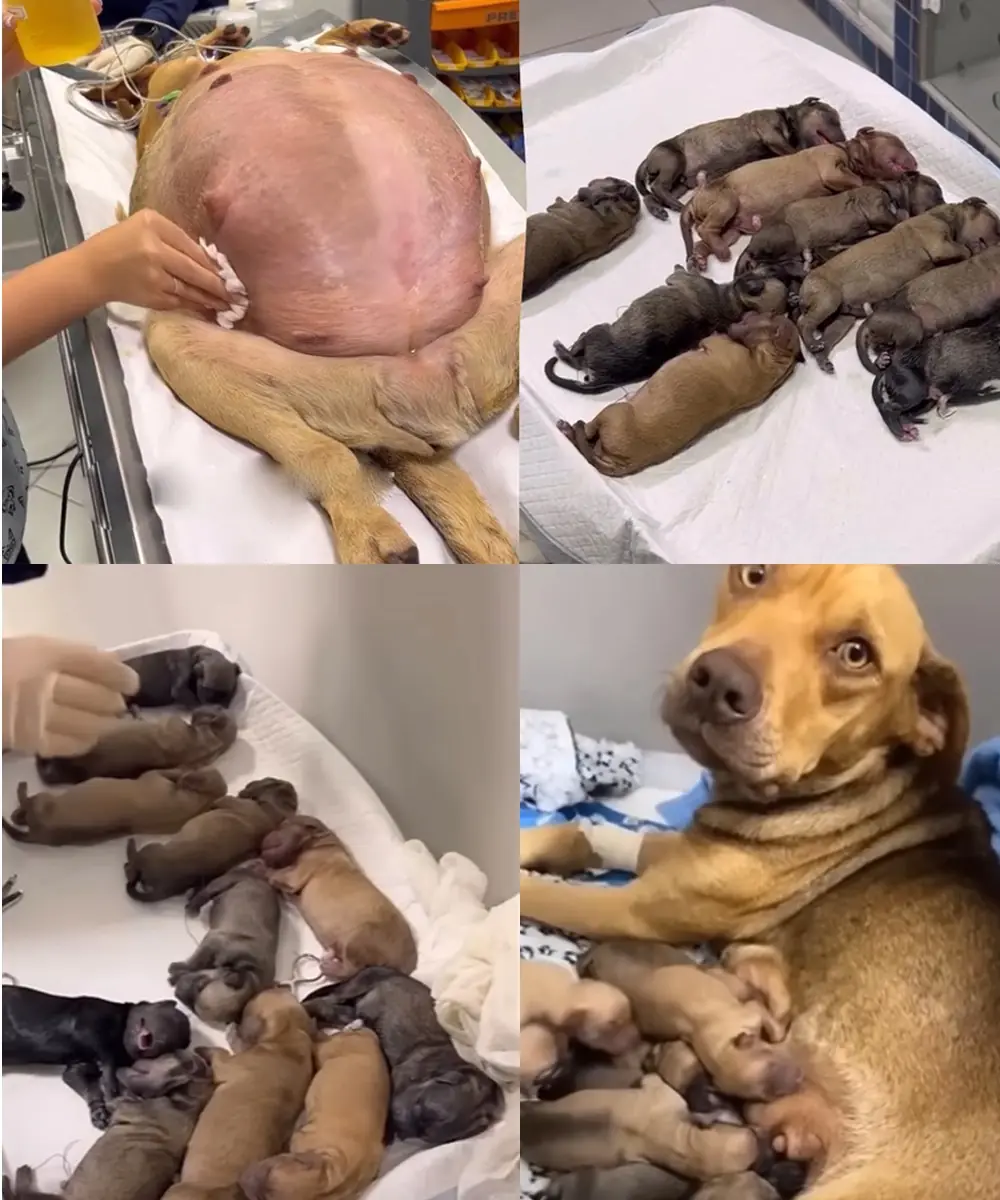
A Pregnant Dog’s Miraculous Journey: How She Found Help at My Gate…

The Black Serum To Get Long, Black Hair

Transform your skin with vaseline and milk
