Meet Helicobacter pylori: A Dangerous Bacteria That Can Cause Deadly Cancer

Helicobacter pylori is a bacteria that has drawn significant attention from the scientific community due to its involvement in various digestive diseases, including gastritis, peptic ulcers, and, in severe cases, gastric cancer. It is estimated that half of the world’s population is infected with this bacteria, though not everyone develops related diseases.
Its discovery in 1982 by Barry Marshall and Robin Warren revolutionized gastroenterology. They proved that many stomach ulcers were not caused by stress but by this bacteria. Their groundbreaking work earned them the 2005 Nobel Prize in Medicine for their contribution to understanding and treating these conditions.
What Is Helicobacter pylori and How Is It Transmitted?
Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped, Gram-negative bacteria with high motility due to its flagella, which help it move in the acidic environment of the stomach. This adaptability allows it to neutralize stomach acid by producing urease, an enzyme that breaks down urea into ammonia and bicarbonate, creating a less acidic area where the bacteria can thrive.
How It Spreads:
📌 Oral-oral or fecal-oral transmission – Common in areas with poor sanitation and close human contact.
📌 Contaminated food and water – Drinking unclean water or eating contaminated food can spread the bacteria.
📌 Medical equipment – Poorly sterilized endoscopes may contribute to transmission.
📌 Contact with animals – Some studies suggest potential transmission through pets or livestock.
Read More: Foods That Help Combat Helicobacter pylori from Day One
Health Impact: Diseases Linked to H. pylori Infection
H. pylori infections can have serious consequences for digestive health, and in some cases, may even affect other organs. It is responsible for chronic inflammation in the stomach lining and contributes to various serious health conditions.
1. Gastritis and Peptic Ulcers
One of the most common effects of H. pylori is chronic gastritis, a persistent inflammation of the stomach lining that can lead to stomach or duodenal ulcers over time.
🔹 Symptoms:
✅ Abdominal pain
✅ Heartburn
✅ Nausea
✅ Digestive bleeding in severe cases
These ulcers can disrupt digestion, reducing the absorption of iron and vitamin B12, leading to anemia and nutritional deficiencies.
2. Link to Gastric Cancer
One of the most concerning aspects of H. pylori is its connection to gastric cancer. The bacteria induce chronic inflammation, which can cause abnormal cell changes in the stomach lining, leading to gastric adenocarcinoma and MALT lymphoma (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue).
🔴 The World Health Organization (WHO) has classified H. pylori as a Group 1 carcinogen, meaning there is strong evidence of its role in causing stomach cancer. It is estimated that H. pylori is present in at least 80% of gastric cancer cases worldwide, highlighting the urgent need for early detection and treatment.
How Is Helicobacter pylori Diagnosed?
Diagnosing H. pylori can be done using invasive and non-invasive tests.
Non-Invasive Tests:
🔹 Urea Breath Test – The patient ingests a urea solution. If H. pylori is present, it produces marked CO2, which can be detected in exhaled breath.
🔹 Stool Antigen Test – Detects H. pylori antigens in stool samples.
🔹 Serological Tests – Detects antibodies in the blood but cannot distinguish between past and current infections.
Invasive Tests:
🔹 Endoscopy with Biopsy – A tissue sample is collected from the stomach lining to detect H. pylori through histological analysis, culture, or urease tests.
🔹 Bacterial Culture – Helps determine antibiotic resistance but is rarely used due to complexity.
🔹 PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) Test – A highly accurate test that detects H. pylori DNA, though it is not widely used in routine diagnosis.
Treatment Options & Antibiotic Resistance
The standard treatment for H. pylori involves a combination of antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) to reduce stomach acid.
Common Treatment Protocols:
✔️ Triple Therapy – PPI + Two antibiotics (Amoxicillin + Clarithromycin or Metronidazole) for 10–14 days.
✔️ Bismuth-Based Quadruple Therapy – Used for antibiotic-resistant infections, adding bismuth to increase effectiveness.
✔️ Tailored Antibiotic Therapy – In some cases, bacterial culture tests help select antibiotics based on resistance patterns.
The Growing Problem of Antibiotic Resistance
🚨 H. pylori is becoming increasingly resistant to Clarithromycin and Metronidazole, making standard treatments less effective. This has led researchers to explore:
🔹 Probiotics
🔹 Bacteriophage therapy
🔹 New antibiotic regimens
🔹 Potential vaccines (still in development)
Prevention Strategies
Since H. pylori infection is typically acquired in childhood, improving hygiene and ensuring access to clean water are key to preventing its spread.
How to Reduce Your Risk:
✔️ Practice Good Hygiene – Wash hands thoroughly before eating and after using the restroom.
✔️ Drink Safe Water – Avoid consuming unfiltered or unsafe water, especially in areas with poor sanitation.
✔️ Ensure Food Safety – Eat well-cooked foods and avoid contamination.
✔️ Avoid Sharing Utensils – Oral-oral transmission is possible, so avoid sharing cups, spoons, and cutlery.
✔️ Regular Check-Ups – People with a family history of stomach diseases should undergo periodic screenings.
Ongoing Research in Vaccines
Although there is currently no approved vaccine for H. pylori, scientists are actively working on developing effective immunizations to prevent infection in the future.
Conclusion
Helicobacter pylori is a highly adaptable stomach bacteria capable of causing a range of diseases, from gastritis and ulcers to gastric cancer. Its high global prevalence and growing antibiotic resistance make research into new treatments and prevention strategies crucial.
✔️ Early detection and treatment are essential to prevent severe complications.
✔️ Improving hygiene and food safety can significantly reduce infection risks.
✔️ New therapies and vaccines may provide future solutions to combat this silent but dangerous bacteria.
Taking care of your digestive health today could help protect you from serious health complications in the future. 🛑🔬
News in the same category


Scandalous discovery of why intimate parts smell like fish

First childhood death from measles reported in the US amid active outbreak.
If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, the Body Will Show these 10 Signs
10 Foods That You Should Eat Daily For Clean Arteries

10+ Foods to Help Lower Your Blood Sugar

5 Types of Foods That Naturally Contain Progesterone – Doctor’s Advice: Women Over 45 Should Eat More
What Happens When Pancreatic Cancer Is Caused by Diet? Doctors Warn: People with a Weak Pancreas Should Avoid These Foods

Meet Helicobacter pylori: A Dangerous Bacteria That Can Cause Deadly Cancer
Scientists Successfully Rejuvenate a 53-Year-Old Woman’s Skin Cells by 30 Years

New Highly Contagious and Virulent HIV Variant Discovered
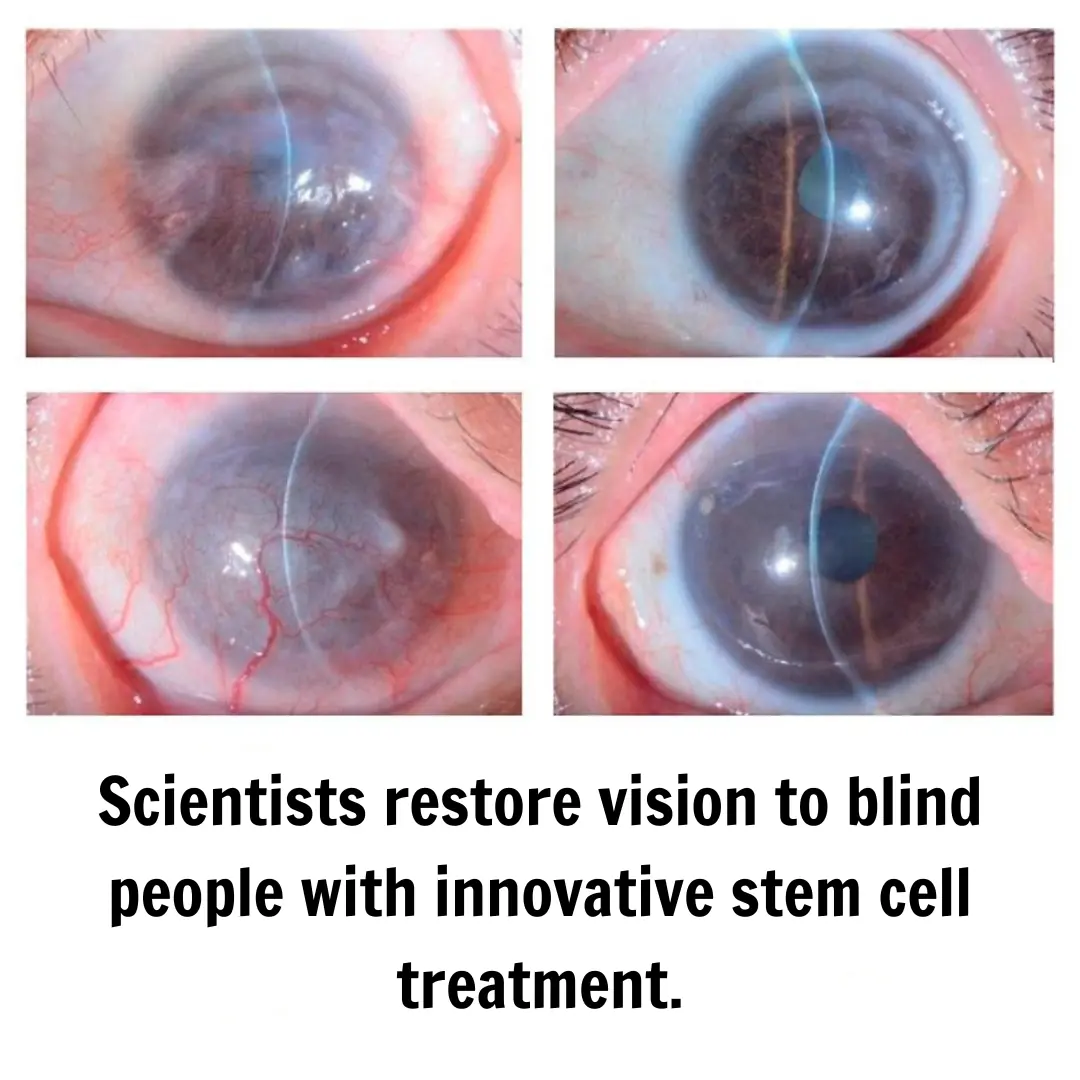
Japanese Scientists Restore Vision in Blind Individuals
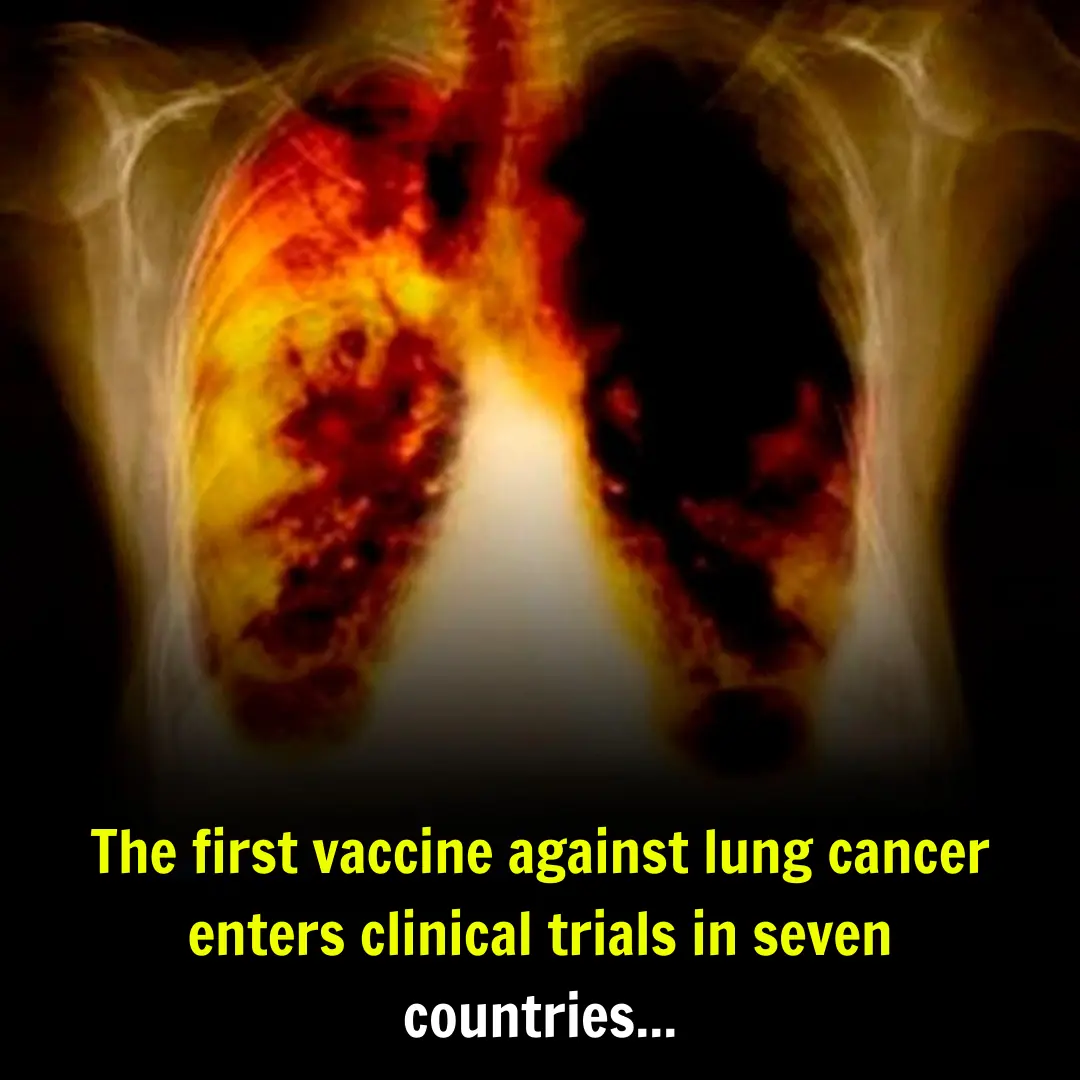
The First Lung Cancer Vaccine Enters Clinical Trial Phase in Seven Countries

Is Eating Sweet Potatoes “Anti-Cancer” or “Cancer-Promoting”? Research Findings Have Been Released
Can You Eat Onions If You Have High Blood Pressure? Doctor’s Advice: Avoid These 3 Foods for Better Blood Pressure Control
Are There Warning Signs in the Body Before Cancer Appears? Check Yourself and Get Screened as Soon as Possible
Kidney Cancer: Warning Signs You Should Not Ignore

🌿 Mimosa Pudica: The Mysterious Healing Plant of South America

Doctor's Warning: People Prone to Pancreatic Cancer Share These Common Traits – Be Careful!

Rain Water Solar Term: Remember to Eat These 2 Foods to Expel Dampness from Your Body
News Post

Excessive consumption of green juices can cause oxalate kidney injury.
10 Ways To Support Your Lymphatic System

Pure Magic: Burning a Clove of Garlic, What Happens After 15 Minutes at Home?
The Juice That Strengthens Bones and Soothes Knee Pain Naturally
Clean Your Kidneys, Liver & Lungs – Powerful Natural Detox! 🍊🌿

Euphorbia Hirta: Nature's Remedy for Respiratory and Immune Health

Why is it said that warm lemon juice can save a life: Drinking it at the right time will prevent cancer, filter blood, and remove belly fat

Scandalous discovery of why intimate parts smell like fish

First childhood death from measles reported in the US amid active outbreak.

If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, the Body Will Show these 10 Signs

10 Foods That You Should Eat Daily For Clean Arteries

Natural Recipe with Watermelon, Carrot, Beetroot, and Ginger

10+ Foods to Help Lower Your Blood Sugar

5 Types of Foods That Naturally Contain Progesterone – Doctor’s Advice: Women Over 45 Should Eat More
So useful! Gonna watch out for these Holly Owens Contributing Writer
9 Early Signs of Diabetes You May Not Be Noticing
How to Remove Blackheads and Whiteheads Naturally with Vaseline

What Happens When Pancreatic Cancer Is Caused by Diet? Doctors Warn: People with a Weak Pancreas Should Avoid These Foods
