12 Signs Your Body Could Be Sending About Lactose Intolerance

Have you ever dealt with stomach discomfort without knowing the cause? It could be your body’s way of signaling lactose intolerance. Millions of people suffer from it, yet many remain unaware that their symptoms stem from an inability to digest dairy properly.
Lactose intolerance occurs when the small intestine doesn’t produce enough lactase—the enzyme responsible for breaking down lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. This leads to digestive distress and other unexpected symptoms.
If you suspect lactose intolerance, recognizing the warning signs is the first step to managing your symptoms and improving your well-being.
1. Abdominal Pain and Cramping
One of the most common signs of lactose intolerance is stomach pain. If you experience cramps or discomfort after eating dairy, your body may be struggling to digest lactose. When undigested lactose reaches the colon, bacteria ferment it, creating gas and irritation that leads to bloating and pain.
2. Nausea or Vomiting
Feeling queasy after consuming dairy? Some people experience nausea, or in severe cases, vomiting. This happens because lactose intolerance can trigger irritation in the digestive tract, leading to discomfort.
3. Fatigue and Low Energy
Do you often feel drained despite getting enough rest? Digestive discomfort, gut inflammation, and improper nutrient absorption from dairy can contribute to fatigue. If dairy leaves you sluggish, it may be time to adjust your diet.
4. Brain Fog and Difficulty Concentrating
Have you ever felt mentally sluggish or had trouble focusing after consuming dairy? Some people report brain fog, forgetfulness, and difficulty thinking clearly. This may be linked to gut inflammation and the gut-brain connection.
5. Indigestion and Heartburn
Persistent bloating, acid reflux, or an upset stomach after meals could be linked to lactose intolerance. When lactose isn’t digested properly, it can cause irritation in the stomach lining, leading to discomfort and indigestion.
6. Mouth Ulcers
Though not a common symptom, some people with lactose intolerance report recurring mouth ulcers. While the exact cause remains unclear, it could be linked to underlying gut issues and food sensitivities.
7. Skin Issues and Swelling
Some individuals experience rashes, eczema, or even swelling after consuming dairy. While a milk allergy is different from lactose intolerance, both can cause skin reactions. In severe cases, allergic reactions may result in hives, facial swelling, and breathing difficulties.
8. Diarrhea or Constipation
Frequent diarrhea after eating dairy is a major sign of lactose intolerance. Undigested lactose pulls excess water into the intestines, causing loose stools. Conversely, some individuals experience constipation, as lactose intolerance can alter gut bacteria and slow digestion.
9. Bloating and Gas
Feeling like your stomach is about to burst after consuming dairy? The fermentation of lactose in the colon produces gas, leading to bloating and discomfort. The severity depends on the amount of lactose consumed and individual sensitivity.
10. Headaches and Migraines
If you frequently experience unexplained headaches or migraines after consuming dairy, it could be linked to lactose intolerance. Experts believe that gut inflammation and digestive stress may trigger headaches in sensitive individuals.
11. Excessive Gas
Lactose intolerance can cause embarrassing and uncomfortable flatulence. When bacteria break down lactose in the colon, they release hydrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide—leading to excessive gas and bloating.
12. Muscle and Joint Pain
Although rare, some people report muscle stiffness or joint pain after consuming dairy. While not widely recognized, researchers suggest that mild inflammation triggered by lactose intolerance could lead to aches and pains in certain individuals.
What Can You Do?
If you suspect you have lactose intolerance, try reducing or eliminating dairy from your diet to see if symptoms improve. You may also consider lactose-free dairy alternatives or digestive enzyme supplements to help break down lactose.
Additionally, symptoms of lactose intolerance can sometimes overlap with gluten sensitivity. If removing dairy doesn’t improve your symptoms, it may be worth exploring other dietary factors.
If symptoms persist or worsen, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
News in the same category

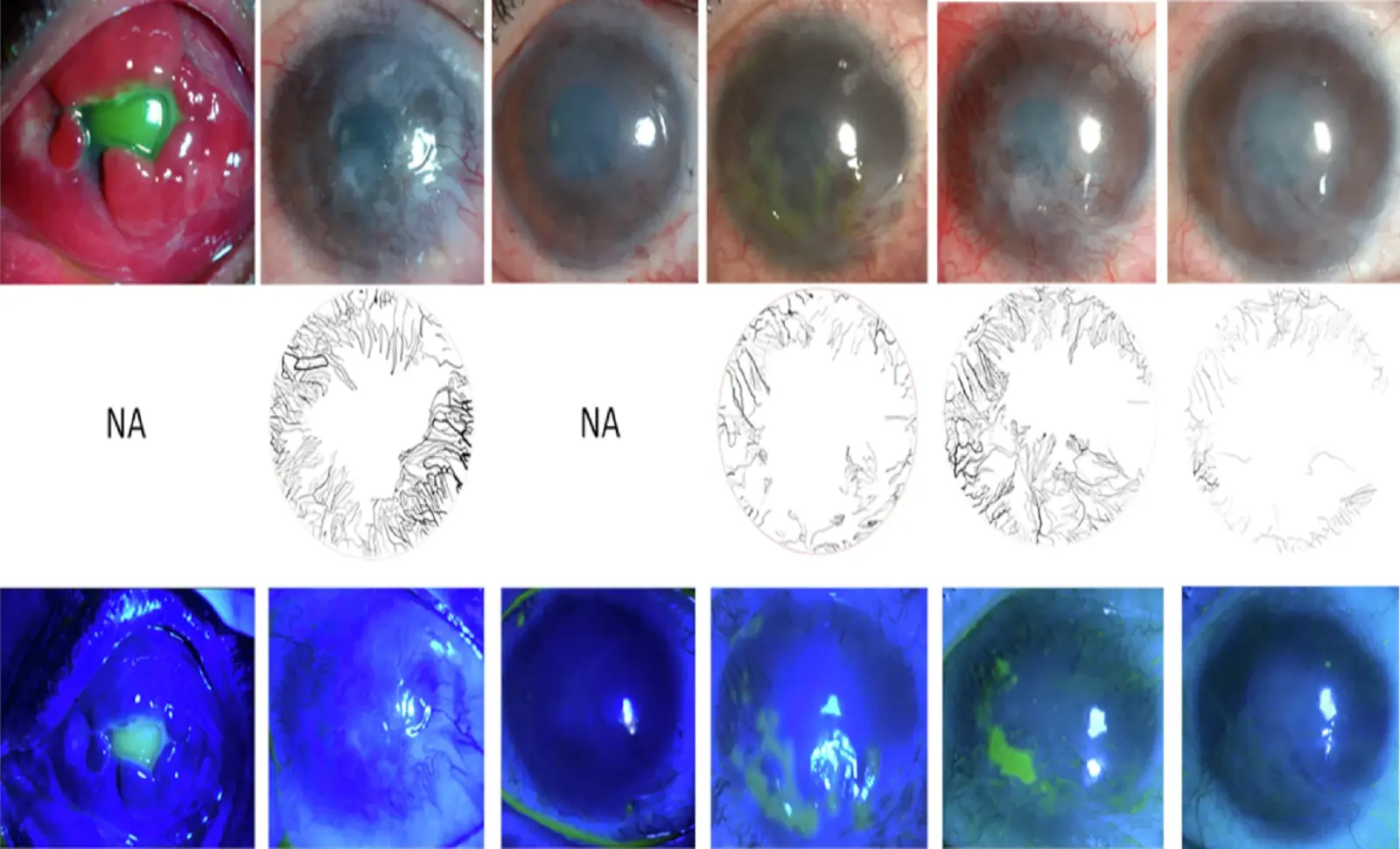
New Cellular Therapy Restores Damaged Cornea in 14 Blind Patients

10 Ways to Help Reduce Your Colon Cancer Risk

7 Signs Of Intestinal Parasites Living Inside Your Body
20 Cancer Signs People Ignore Until It’s Too Late

Doctor makes worrying claim that ‘every new patient’ at cancer clinic is under 45 and blames one thing

10 Alarming Signals Your Body Might Be Warning You About
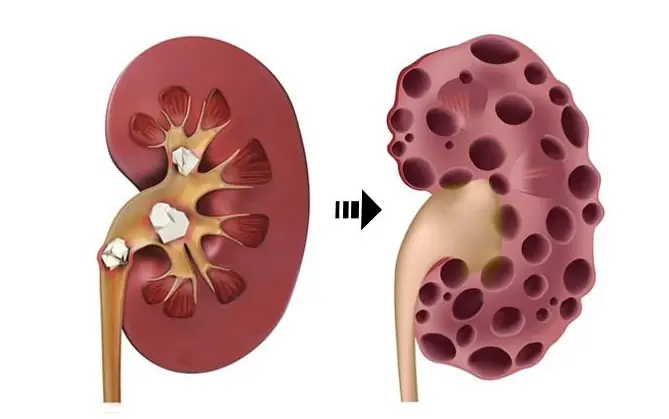
KIDNEY DISEASE SILENTLY CREEPS IN – IF YOU NOTICE THIS AT NIGHT, BEWARE!
5 Reasons to Have Protein Before Bed

The Tiger Spider: Nature’s Defense Against the Violin Spider

9 Foods to Consider Limit if You Have Hypothyroidism
Attention, Parents! You Might Want To Hold On To Your Kids’ Baby Teeth

10 Ways Baths Can Be Either Good and Bad for Your Body
10 Warning Signs Your Thyroid Might Not Be Working Properly
What Happens After 30 Days of Cold Showers

A Groundbreaking Medical Breakthrough Brings Hope for the End of HIV/AIDS
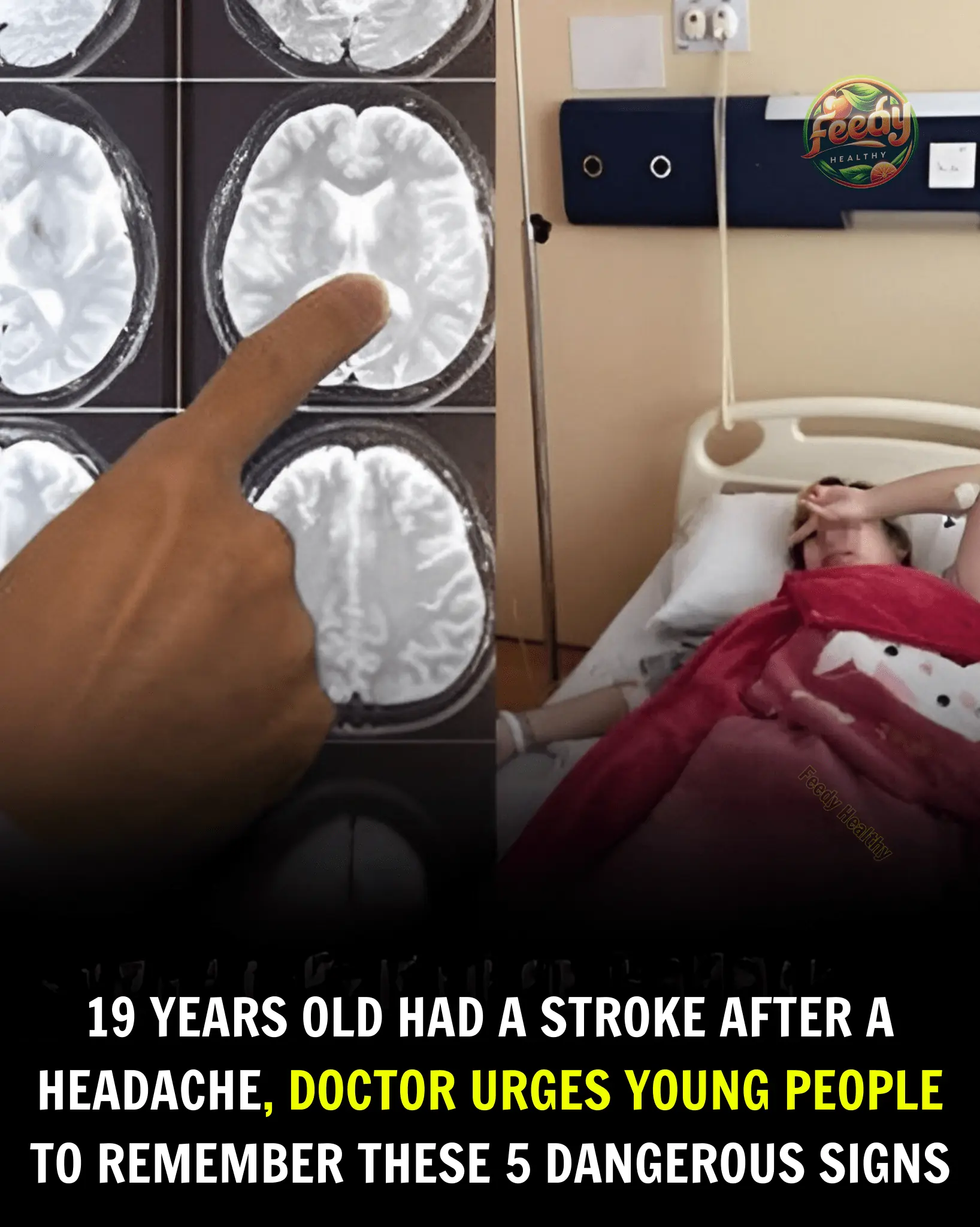
5 Alarming Stroke Warning Signs to Watch for in Young People

Peeing in the Shower, Doctor Explains Why Women Shouldn’t

A small trick that can save lives.
News Post

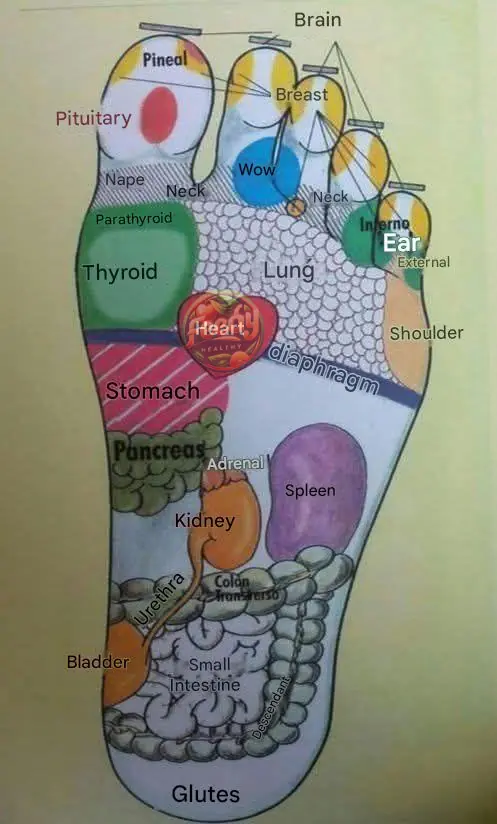
PUT OIL ON THE SOLES OF YOUR FEET

New Cellular Therapy Restores Damaged Cornea in 14 Blind Patients

10 Ways to Help Reduce Your Colon Cancer Risk

Persistent Symptoms After the COVID-19 Vaccine: New Study Reveals Unexpected Immune Effects

Secrets to Youthful, Radiant Skin for Women Over 40

Rosemary for Leg Pain: Natural Relief for Joints and Back

Mix Vaseline with Lemon – You’ll Be Amazed by the Results!

The conductor seated the pregnant stowaway in the compartment with the strange old man. At night, screams echoed through the car.

7 Signs Of Intestinal Parasites Living Inside Your Body
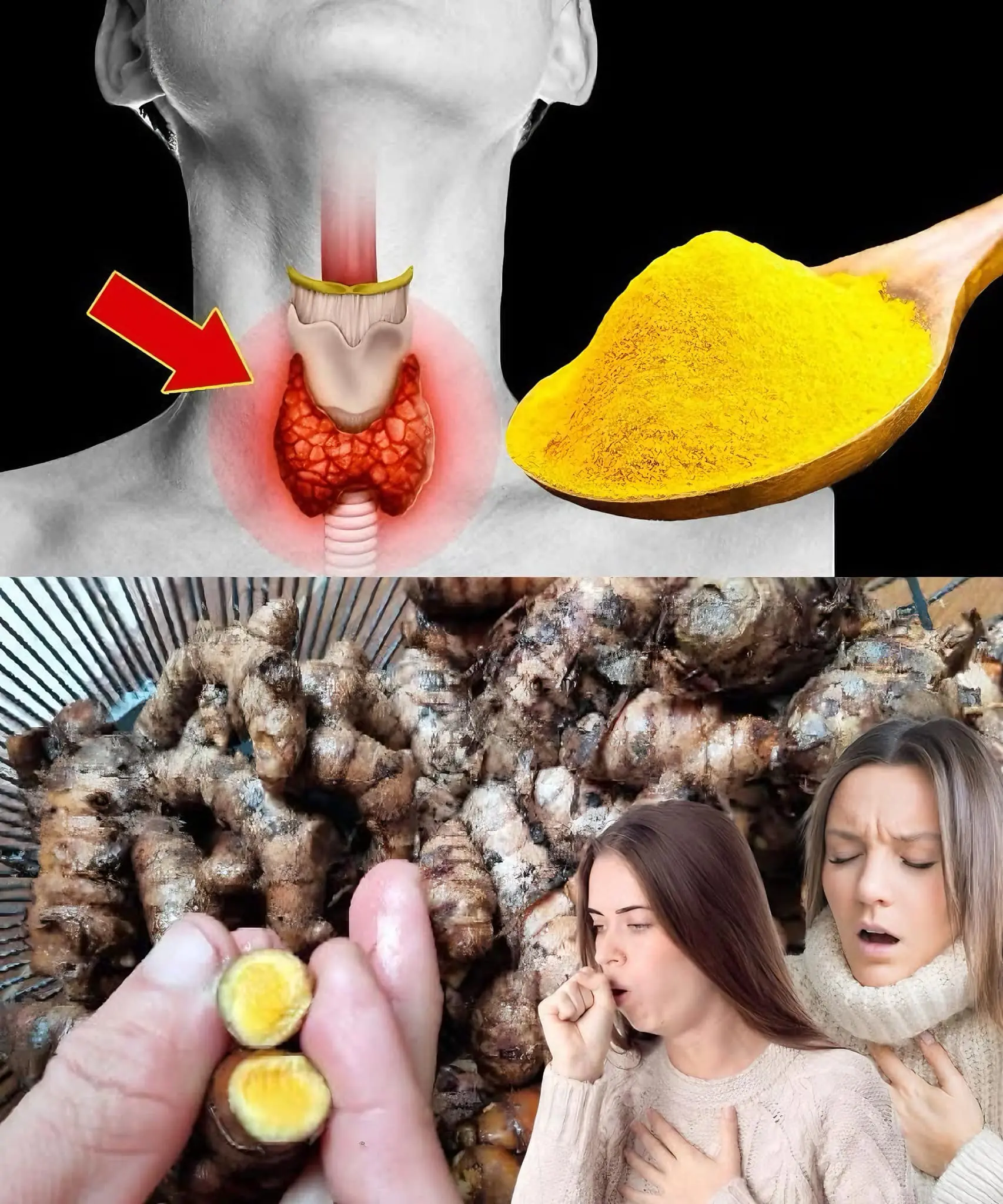
Forget Pills: Natural Remedies for Effectively Treating Thyroid Disorders

Why Do You Have Bleach Stains on Your Underwear? The Surprising Truth

Refreshing Carrot, Lemon/Lime, and Apple Juice Recipe

New Father Kicks Wife With Newborn Twins onto the Streets, Years Later He Begs Her for Help

20 Cancer Signs People Ignore Until It’s Too Late

Doctor makes worrying claim that ‘every new patient’ at cancer clinic is under 45 and blames one thing

Why hang a clothespin on the shower?

Effects of smartphone restriction on cue-related neural activity

10 Alarming Signals Your Body Might Be Warning You About

KIDNEY DISEASE SILENTLY CREEPS IN – IF YOU NOTICE THIS AT NIGHT, BEWARE!
