
If you have cirrhosis, you should pay more attention to your diet. Only by following these guidelines can you improve your condition.
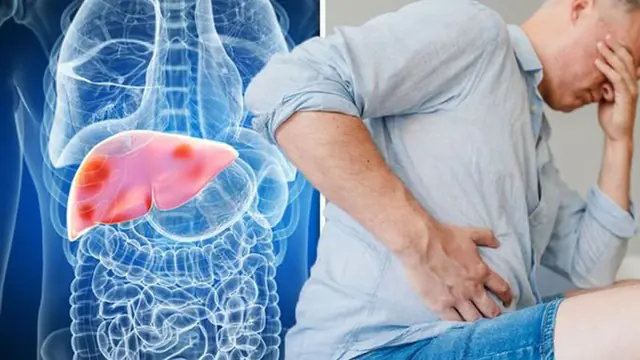
Cirrhosis is a common chronic liver disease that progresses silently but can have severe consequences if left uncontrolled. In its early stages, the disease often presents no obvious symptoms. However, as it advances, it can lead to serious complications such as gastrointestinal bleeding, ascites (fluid buildup in the abdomen), liver failure, and even hepatic encephalopathy, a life-threatening condition.
The primary causes of cirrhosis include viral hepatitis (Hepatitis B, C), excessive alcohol consumption, fatty liver disease, autoimmune disorders, and metabolic diseases. Once diagnosed, in addition to following medical treatments, patients must adopt a proper diet to support liver function, slow disease progression, and enhance their quality of life. Below are essential dietary guidelines to help protect your liver!
1. Prioritize High-Quality Protein Intake
The liver plays a crucial role in protein metabolism. In cirrhosis, this function weakens, leading to muscle loss, malnutrition, and edema. Thus, consuming high-quality protein is essential.
Best Sources of High-Quality Protein for Liver Health:
- Lean meats: Chicken breast, fish, shrimp
- Dairy products: Milk, yogurt, cheese
- Eggs: Especially egg whites
- Legumes and soy-based products: Tofu, soy milk
However, excessive animal protein intake can overburden the liver, so balancing it with plant-based proteins is recommended.
2. Include Essential Vitamins for Liver Protection
Vitamins are crucial for supporting liver function and enhancing the body's detoxification process. Key vitamins beneficial for cirrhosis patients include:
- Vitamin B complex: Helps protect liver cells and supports energy metabolism. Found in whole grains, beans, eggs, and animal liver.
- Vitamin C: Reduces inflammation, boosts immunity, and aids in liver detoxification. Rich sources include oranges, lemons, kiwis, strawberries, and bell peppers.
- Vitamins A, D, and E: Help maintain liver function and can be found in carrots, sweet potatoes, salmon, eggs, and nuts.
For best results, prioritize obtaining vitamins from natural food sources rather than over-relying on supplements unless prescribed by a doctor.
3. Limit Fat Intake to Reduce Liver Strain
Since the liver is responsible for fat metabolism, excessive fat consumption can overload the liver, leading to fatty liver disease and worsening cirrhosis.
Healthy Fat Consumption Guidelines:
✅ Choose healthy fats: Olive oil, fish oil, almond butter, and nuts.
❌ Avoid saturated and trans fats: Fast food, fried foods, processed meats, and organ meats.
4. Diversify Your Diet to Improve Appetite
Many cirrhosis patients experience loss of appetite, bloating, and indigestion, leading to nutrient deficiencies. Maintaining a varied diet can stimulate taste buds and ensure the body gets the necessary nutrients.
Suggested Meal Plan for Cirrhosis Patients:
- Breakfast: Oatmeal, boiled egg, low-fat milk
- Lunch: Steamed fish, boiled vegetables, brown rice
- Dinner: Vegetable soup, tofu with mushroom sauce
- Snacks: Yogurt, low-sugar fruits
Additionally, dividing meals into smaller portions throughout the day can ease digestion and reduce the burden on the liver.
5. Avoid Foods That Harm the Liver
Certain foods can damage liver cells, trigger inflammation, and worsen cirrhosis. Patients should strictly avoid:
❌ Alcohol: The leading cause of liver damage.
❌ Spicy and acidic foods: Such as chili, pepper, and mustard – they can irritate the stomach lining and increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
❌ Hard foods: Can be difficult to digest and may damage the digestive tract.
❌ Processed and canned foods: Contain preservatives and chemicals that are harmful to the liver.
6. Stay Hydrated to Support Detoxification
Water plays a crucial role in helping the liver flush out toxins, maintain metabolic functions, and prevent toxin buildup.
Hydration Guidelines:
✔ Drink 1.5 – 2 liters of water per day, including plain water, fresh fruit juices (without added sugar), and herbal teas.
✔ Avoid carbonated drinks, coffee, and strong tea, as they may lead to dehydration and negatively affect liver function.
7. Control Sodium Intake to Prevent Fluid Retention
Cirrhosis can cause swelling and fluid retention, which worsens with excessive salt consumption.
Tips to Reduce Sodium in Your Diet:
- Avoid processed and canned foods.
- Use alternatives like lemon, ginger, and herbs for seasoning.
- Cook at home to control sodium levels.
Conclusion
A well-balanced diet plays a vital role in managing and improving cirrhosis. By ensuring proper nutrition, avoiding harmful foods, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, patients can slow disease progression and enhance their well-being.
Remember, cirrhosis is not the end. With a proper diet and the right medical care, you can effectively manage the disease and live a healthier life!
News in the same category


Why is it said that warm lemon juice can save a life: Drinking it at the right time will prevent cancer, filter blood, and remove belly fat
Doing This for One Hour a Week Can Slow Cancer Progression
U.S. Develops "Smart Bomb" to Eliminate Metastatic Cancer
Discovery of a "Checkpoint" Affecting 70% of Cancer Types
Scientists Have Found an Effective Cancer Treatment Solution

6 Amazing Benefits of Drinking Okra Water with Lemon Every Morning

What Happens When You Drink Lemon Turmeric Water Every Morning?

9 Out of 10 People Suffer from Back Pain? These 3 Foods Can Help Detox Your Body and Relieve Discomfort

What Happens When You Stay Up Late Scrolling on Your Phone? The Harsh Truth: 4 Consequences Your Body Will Pay For
How to Prevent Angina? Three Key Factors to Keep in Mind, with Medication as the First Priority

Can Your Face Reveal Your Lifespan? Four Facial Features of Long-Lived People—Do You Have Them?
Let me make it clear: Cancer patients can boost their immune system through regular exercise, but there are six key points to keep in mind.
Uterine Fibroids: Four Key Symptoms Women Should Watch For
Why Some Doctors Advise Against Brain CT Scans? Essential Facts You Should Know

Why Are Heart Attacks Becoming More Common in Young People? Three Habits You Should Avoid
4 Signs Your Body May Be Lacking Vital Energy and Blood – Here’s What to Do About It
Osteoporosis Myths You Need to Stop Believing – Are You at Risk?

If you have cirrhosis, you should pay more attention to your diet. Only by following these guidelines can you improve your condition.
News Post

What Happens to Your Body If You Take an Aspirin Every Day? The Answer Is Revealed—Tell Your Parents!

Doctor explains why you should 'never' wash your chicken before cooking it

How Often Should You Wash Your Hair in Hot Weather? Does Washing Every Day Cause Hair Loss? Answering Your Long-Standing Questions

Should People with High Blood Lipids Avoid Tofu?

Does Chives Act as a "Catalyst" for Tumor Growth?
Don't Ignore Numbness in Your Hands and Feet! If You Notice These Signs, Get Checked Immediately
Research Finds: Heart Rate is Linked to Longevity – What is the Ideal Heart Rate? The Answer is Clear!

Is the High Cancer Rate in China Linked to Oyster Sauce?

What Does It Mean When a Man’s Nose Hair Frequently Sticks Out? Why Do Some People Have Gray Nose Hair?

Can Sleep Predict Cancer? If You Experience These 5 Unusual Signs at Night, Get Checked Immediately!

Scientists Successfully Remove the Extra Chromosome Responsible for Down Syndrome in Human Cells

Excessive consumption of green juices can cause oxalate kidney injury.
10 Ways To Support Your Lymphatic System

Pure Magic: Burning a Clove of Garlic, What Happens After 15 Minutes at Home?
The Juice That Strengthens Bones and Soothes Knee Pain Naturally
Clean Your Kidneys, Liver & Lungs – Powerful Natural Detox! 🍊🌿

Euphorbia Hirta: Nature's Remedy for Respiratory and Immune Health

Why is it said that warm lemon juice can save a life: Drinking it at the right time will prevent cancer, filter blood, and remove belly fat

Scandalous discovery of why intimate parts smell like fish
