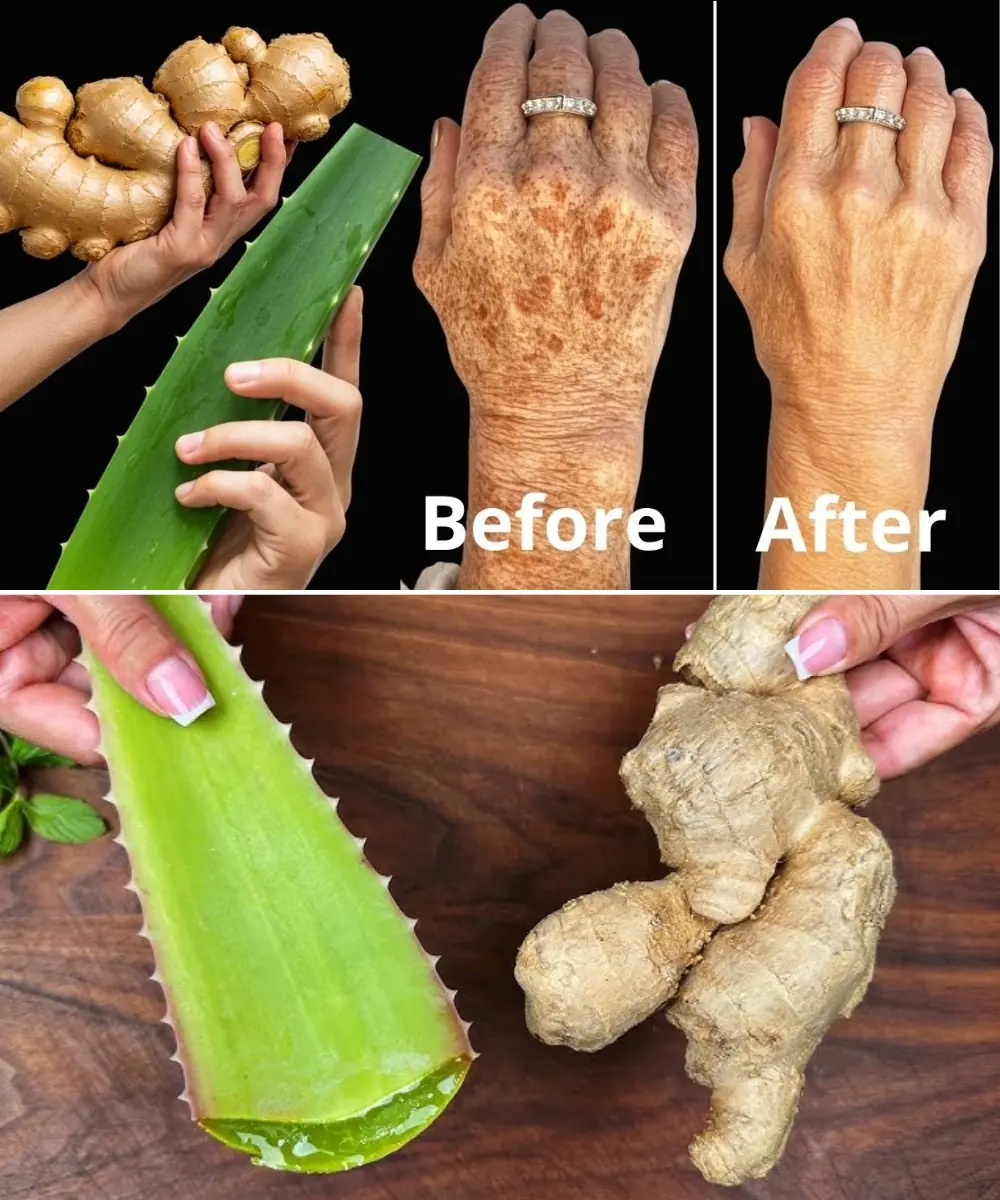
improve digestion, fight inflammation, and boost the immune system. But while it’s healthy for most people, ginger isn’t suitable for everyone. In certain health conditions, this spicy root can actually make things worse.
If you have any of the following issues, it’s best to be cautious before adding ginger to your daily routine.
1. Blood Disorders
Why to Avoid: Ginger naturally thins the blood. For people with bleeding disorders such as hemophilia, or those taking anticoagulant medications, this can increase the risk of bleeding.
Risk: Excessive or prolonged bleeding.
2. Gallstones
Why to Avoid: Ginger boosts bile production to aid digestion. For those with gallstones, this can cause pain or worsen existing blockages.
Risk: Increased gallbladder pain and digestive discomfort.
3. Low Blood Pressure
Why to Avoid: Ginger improves blood circulation and may lower blood pressure. While that’s good for most, it can cause dizziness or fainting in people who already have low blood pressure or take medication for it.
Risk: Blood pressure dropping too low.
4. Diabetes
Why to Avoid: Ginger helps lower blood sugar levels, but if you’re on diabetes medication, it can push your blood sugar too low.
Risk: Hypoglycemia (dangerously low blood sugar).
5. Pregnancy (When Consumed in Excess)
Why to Avoid: In small doses, ginger can reduce nausea during pregnancy. However, consuming too much might trigger uterine contractions, especially in the later months.
Risk: Premature labor or pregnancy complications.
6. GERD (Acid Reflux)
Why to Avoid: Because of its spicy nature, ginger can irritate the esophagus and worsen acid reflux symptoms.
Risk: Increased heartburn and acid discomfort.
7. Before or After Surgery
Why to Avoid: Ginger’s blood-thinning properties can interfere with the body’s ability to form clots, increasing the risk of bleeding during or after surgery.
Risk: Excessive bleeding and delayed healing.
How to Stay Safe with Ginger
-
If you have any chronic condition or take prescription drugs, talk to your doctor before consuming ginger regularly.
-
Keep your intake moderate — around 1–2 grams daily is considered safe for most adults.
-
Avoid large doses in supplement form unless specifically approved by a healthcare professional.
Final Thoughts
Ginger is a natural powerhouse — but even the healthiest ingredients can have side effects when used in the wrong situations. Listen to your body, understand your condition, and use ginger wisely. Sometimes, less is more when it comes to staying healthy. 🌿