When Nighttime Leg Cramps Become a Concern
Waking up in the middle of the night with a stabbing pain in your calf is more common than you might think. Nighttime leg cramps—sudden, involuntary muscle contractions, often in the calves or feet—affect millions of people. While they’re often dismissed as harmless or attributed to aging or dehydration, sometimes these cramps can signal something deeper.
The Occasional Cramp: Usually Harmless
Most nighttime cramps are benign and may be triggered by:
-
Overuse of muscles during the day
-
Dehydration
-
Prolonged standing or sitting
-
Sleeping with feet in awkward positions
-
Electrolyte imbalances (low magnesium, potassium, or calcium)
-
Pregnancy
They often resolve with gentle stretching and may not return for weeks.
When to Be Concerned
Nighttime leg cramps become a medical concern when:
-
They occur frequently – More than three nights a week could signal poor circulation or nerve issues.
-
Pain is severe or long-lasting – Cramps that linger or leave muscles sore for hours may suggest circulatory or neurological problems.
-
Sleep is disrupted – Chronic interruptions can cause fatigue, irritability, or even depression.
-
Other symptoms appear – Such as muscle weakness, swelling, numbness, tingling, dark urine, or unexplained fatigue. These may be linked to conditions like peripheral artery disease, kidney dysfunction, neuropathy, or electrolyte imbalances.
-
They follow new medications – Diuretics, statins, beta blockers, and certain asthma drugs can trigger cramps.
-
You have underlying health issues – Older adults, or those with diabetes, vascular disease, or thyroid problems, may be more at risk.
Common Causes of Nighttime Leg Cramps
-
Dehydration – Low fluid levels affect circulation and nerve signaling.
-
Electrolyte imbalance – Deficiency in magnesium, potassium, or calcium disrupts muscle function.
-
Poor circulation – Reduced blood flow leads to cramping.
-
Nerve compression – Spinal stenosis or similar conditions can interfere with signals.
-
Inactivity – Sitting or lying in one position too long.
-
Overexertion – Vigorous exercise without proper recovery.
How to Prevent Nighttime Leg Cramps
-
Stretch before bed – Gentle calf, hamstring, and ankle stretches keep muscles relaxed.
-
Stay hydrated – Aim for 6–8 glasses of water daily, plus electrolyte-rich foods like bananas, spinach, or avocados.
-
Replenish electrolytes – Magnesium (pumpkin seeds, almonds), potassium (sweet potatoes, oranges), calcium (dairy, tofu), and sodium in moderation.
-
Move throughout the day – Walk, stretch, or change positions regularly. Low-impact exercise supports circulation.
-
Wear supportive shoes – Avoid high heels and flat, unsupportive shoes. Use cushioned soles or orthotics if needed.
-
Adjust your sleep position – Keep feet neutral or flexed; avoid pointing toes downward. Try a pillow under your knees or feet.
-
Use warmth and massage – Warm baths, heating pads, or gentle leg massages before bed can ease tight muscles.
-
Limit alcohol and caffeine – Both can dehydrate and disturb sleep. Swap evening drinks for herbal tea.
-
Check medications – Talk to your doctor if cramps started after beginning a new prescription.
-
Consider magnesium supplements – Safe in moderate doses (200–400 mg daily), especially for older adults or pregnant women. Always consult your doctor first.
Preparing Your Muscles for Rest
Preventing nighttime leg cramps means preparing your body for sleep—hydrated, stretched, and relaxed. Just as you brush your teeth before bed, making stretching and hydration a nightly ritual can help ensure you wake up pain-free.
News in the same category


Health Bruce Willis Moved to Specialized Care Facility as Dementia Progresses, Living Apart from His Family
Scratchy Throat? Try This Tiny Spice for Gentle, Natural Relief
Rub Epsom Salt and Fix These 10 Health Problems (Benefits for Over 50s)
🌿 What Happens When You Eat Cloves Every Day for 30 Days?

Natural Pain Killers You Can Find in Your Kitchen

Audrey Crews Becomes First Woman to Receive Neuralink Brain Implant

Too Much Sugar, Not Cholesterol, May Be Your Heart’s Biggest Threat

🌿 Unlock the Ancient Healing Secrets of Euphorbia Prostrata: Your Natural Path to Wellness

A Gentle Herbal Infusion to Support Kidney Health and Natural Detox
🌿 3 Nourishing Drinks to Support Leg Strength, Circulation & Comfort After 60
Warning Signs in Your Eyes: When to Seek Urgent Medical Attention
Flush Out Toxins Naturally: Support Your Kidneys, Liver, and Lungs for Vibrant Health
8 Common Foods That May Harm Prostate Health – And What to Choose Instead
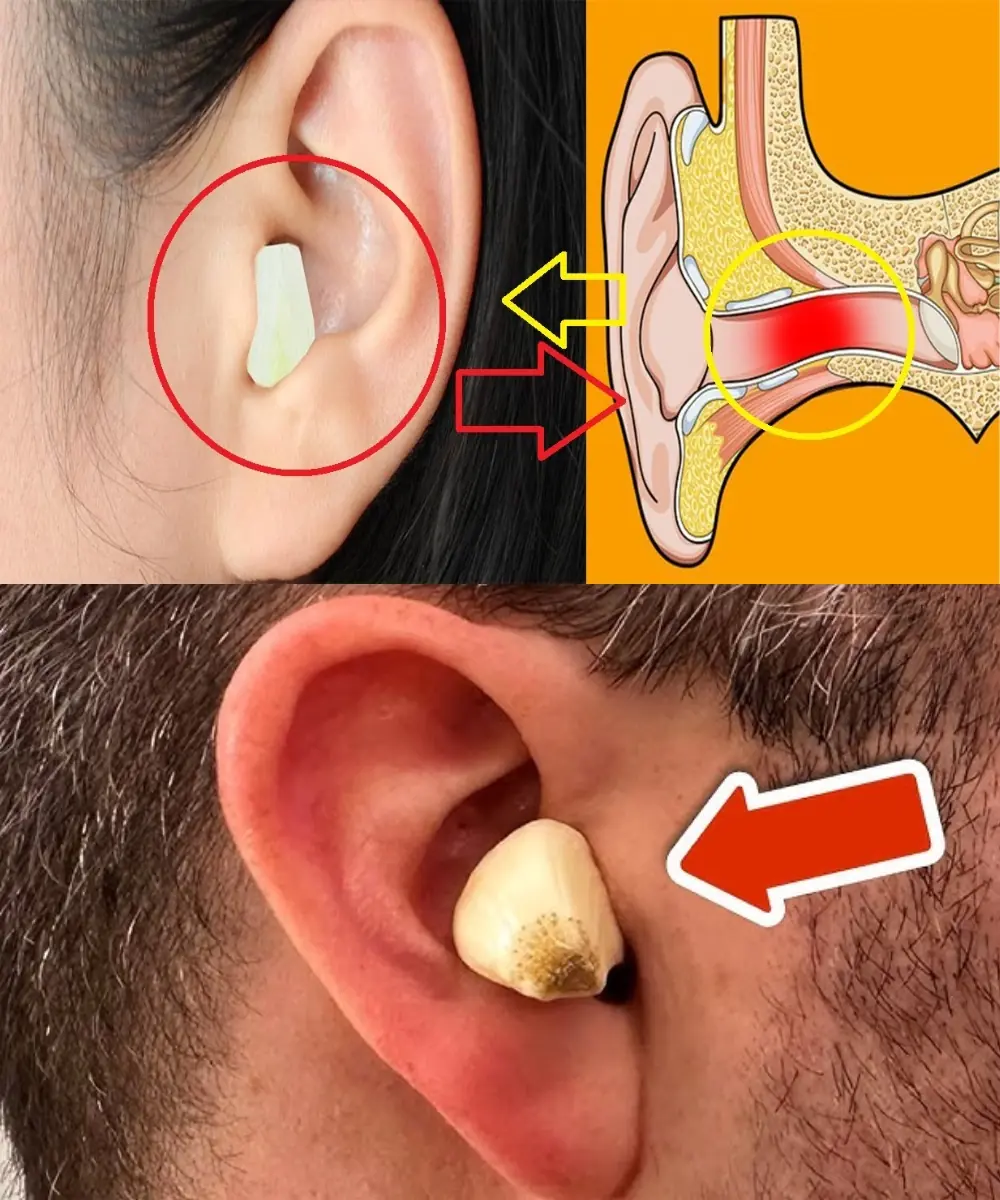
Garlic and Onion: The Natural Secret to Better Hearing
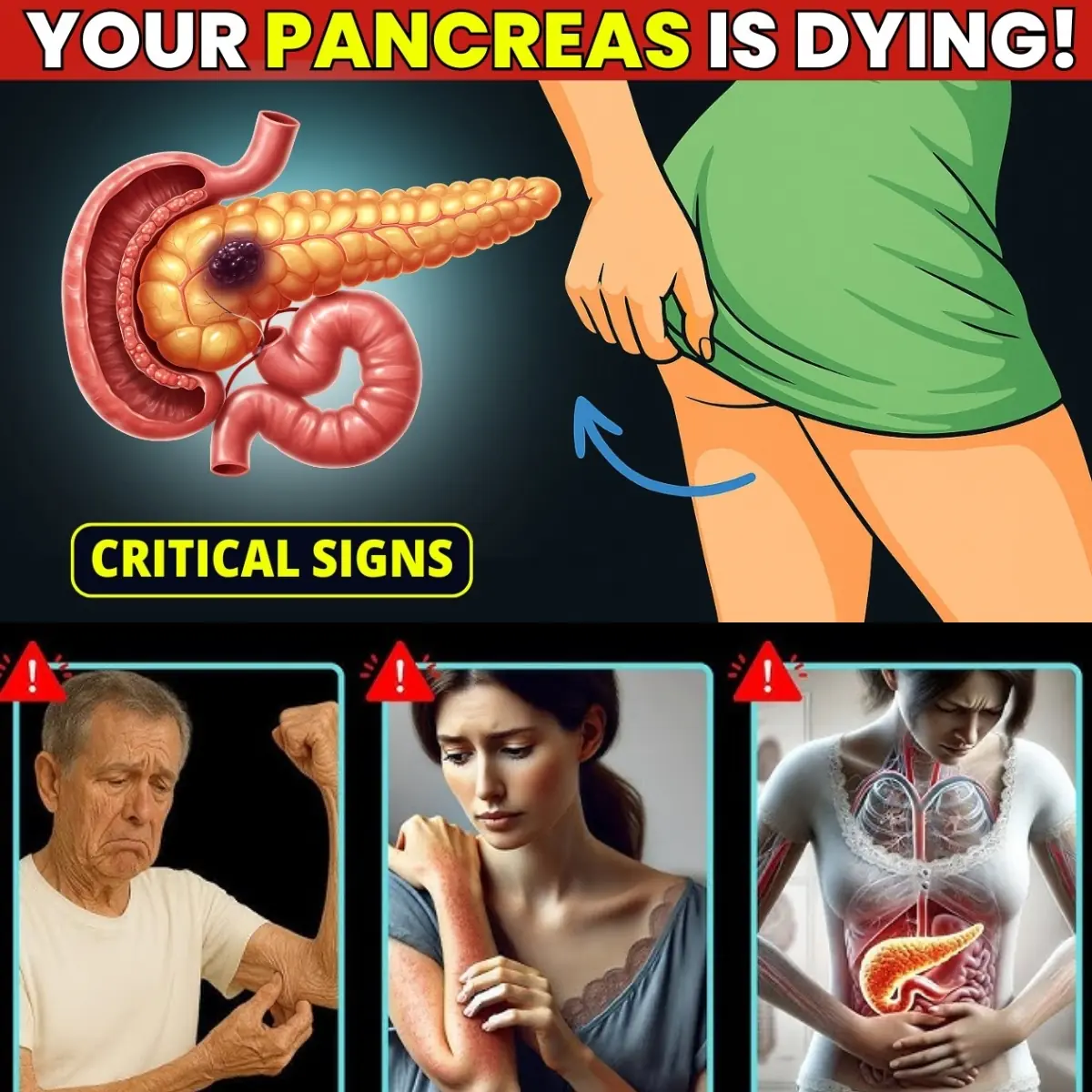
8 Shocking Signs of Pancreatic Cancer You Shouldn't Ignore

Euphorbia Hirta: The Backyard Weed With Golden Healing Powers

Germany’s Cartilage Repair Gel: Hope, Hype, and the Future of Joint Regeneration
News Post

Herbal Teas for Circulation: Gentle Support for Heart & Vitality
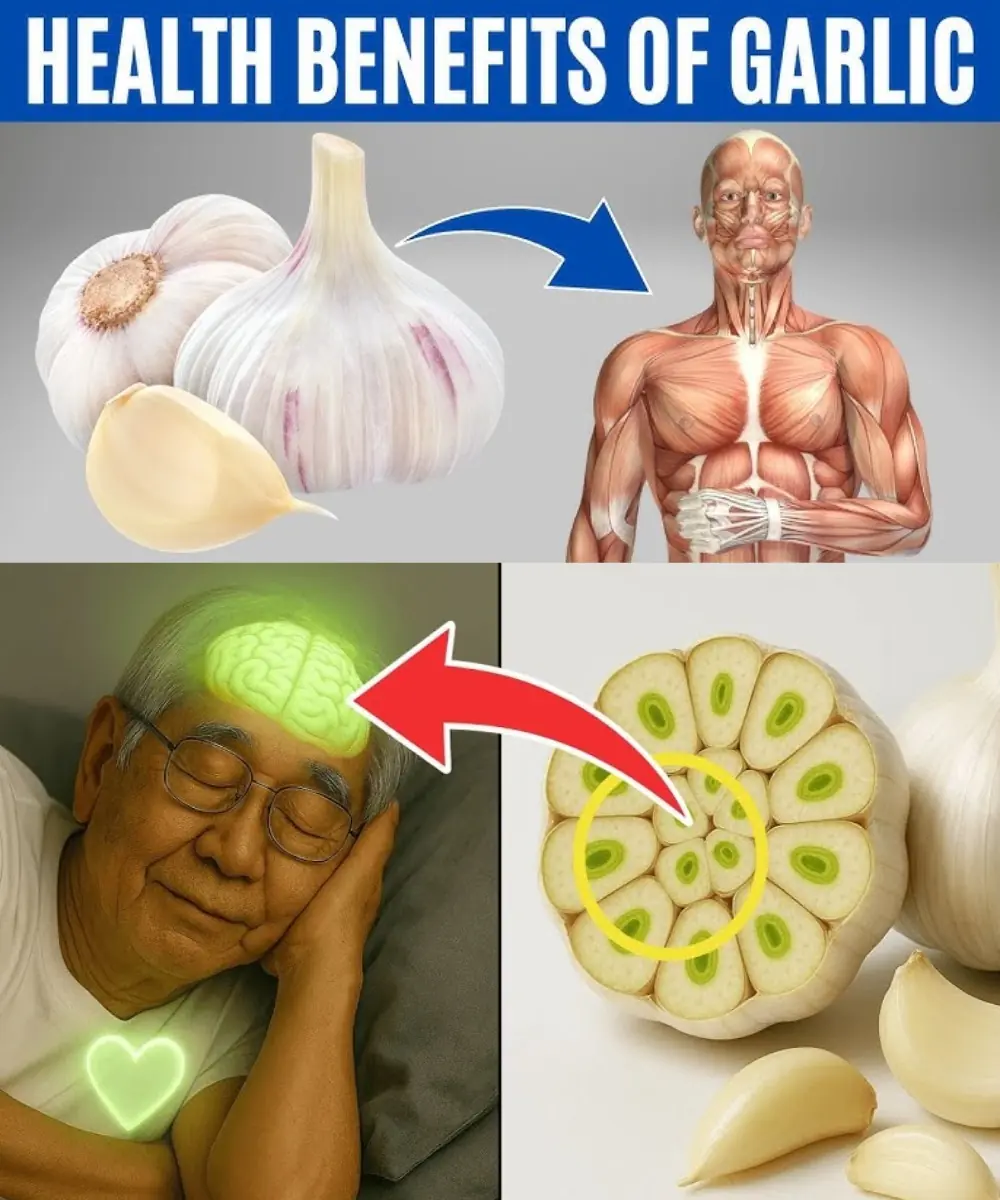
Struggling to Sleep? This Ancient Garlic Remedy May Be the Secret to Restful Nights

Why Boiled Eggs Deserve a Spot on Your Breakfast Table

Keanu Reeves Turns Emergency Landing into a Heartwarming Road Trip

Understanding the Relationship Between Breast Size and Hormonal Health

Morgan Freeman Turns Mississippi Ranch into Bee Sanctuary to Help Save Pollinators
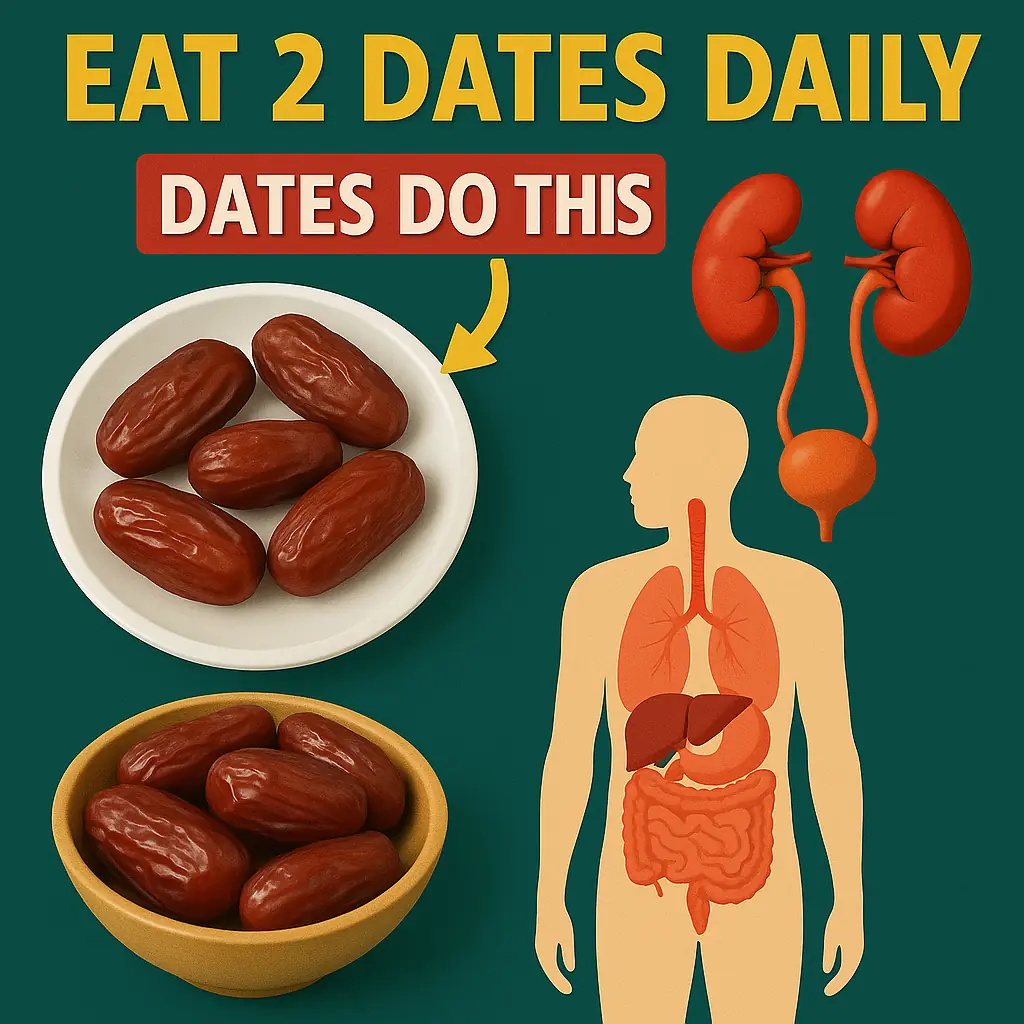
A Sweet Tradition: What Happens When You Eat 2 Dates a Day for a Month

Dutch Regenerative Farms Redefine Agriculture: Inside the Practices of Bodemzicht

Health Bruce Willis Moved to Specialized Care Facility as Dementia Progresses, Living Apart from His Family

Scratchy Throat? Try This Tiny Spice for Gentle, Natural Relief

Rub Epsom Salt and Fix These 10 Health Problems (Benefits for Over 50s)

🌿 What Happens When You Eat Cloves Every Day for 30 Days?
The Heart-Healthy Secret of Raw Garlic: Transform Your Wellness in 30 Days

15 Mind-Blowing Banana Secrets You Need to Know Before Your Next Bite

Unleash the Power of Moringa: 7 Life-Changing Benefits of the Miracle Tree 🌿✨

Purslane: The Superfood That Outshines Meat – 7 Compelling Reasons to Grow It in Your Garden

Discover the Toothpaste and Vaseline Hack for Radiant Skin You’ll Wish You Knew Sooner

Nature’s Secret Weapon: The Garlic, Lemon, Ginger, and Honey Elixir That Transforms Your Life
