
Aloe Vera Remedy: A Natural Support Against Bacteria and Fungi

Did you know that antibiotic resistance is considered one of the biggest health challenges of the 21st century? According to the World Health Organization, millions of infections worldwide are becoming harder to treat because bacteria no longer respond to standard medications. While modern medicine is essential, many cultures have also turned to traditional herbs and plants for centuries to help support the body’s natural defenses.

One of the most remarkable plants in this tradition is Aloe Vera. Famous for its soothing gel, Aloe has been used in Egypt, India, and China for thousands of years. It’s been applied on wounds, consumed for digestion, and even used as part of skin and hair routines. But here’s what’s fascinating: certain preparations of Aloe Vera have been studied for their potential antimicrobial properties, showing that this humble plant may help in the fight against bacteria and fungi naturally.
In this article, we’ll explore why Aloe Vera is considered so powerful, how it compares to traditional remedies like garlic and lemon, and how you can safely prepare and use it at home.
Why Aloe Vera Is Linked to Antimicrobial Support
Aloe Vera is more than just a soothing gel for sunburns—it’s a storehouse of bioactive compounds that have caught researchers’ attention.
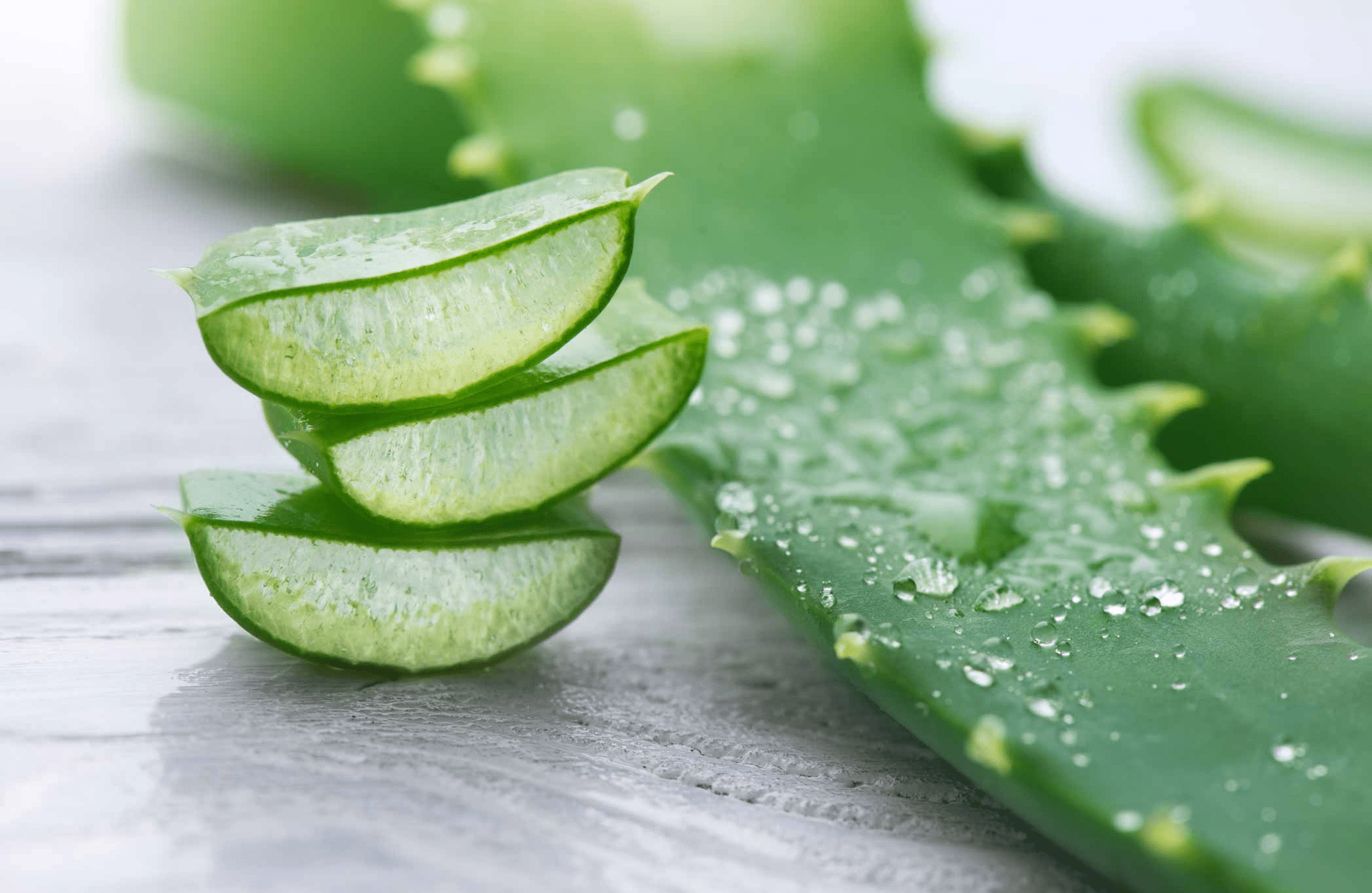

Key properties include:
- Aloin and aloesin: Known for antimicrobial activity against bacteria and fungi.
- Polysaccharides: Support immune response and help cells communicate.
- Saponins: Natural cleansing agents with antiseptic qualities.
- Vitamin C and Vitamin E: Powerful antioxidants that help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress.
When used correctly, Aloe Vera may support the body’s natural ability to defend against infections, especially in the skin, mouth, and digestive tract.
| Compound/Property | Potential Role Against Microbes | Found In Aloe Vera |
|---|---|---|
| Aloin, Aloesin | May inhibit growth of bacteria/fungi | Inner leaf latex |
| Polysaccharides | Immune support, cell communication | Clear gel |
| Saponins | Natural antiseptic cleansing effect | Gel & rind |
| Vitamins C & E | Antioxidants, support tissue repair | Gel |
How Aloe Vera Compares to Garlic and Lemon
Garlic and lemon are well-known natural remedies often praised for their antimicrobial power. Garlic contains allicin, a compound with antibacterial and antifungal effects. Lemon, rich in vitamin C, provides immune support and acidity that discourages microbial growth.

Aloe Vera offers a different yet complementary spectrum of activity:
- Garlic is pungent and heat-producing, Aloe Vera is cooling and soothing.
- Lemon is acidic, Aloe Vera gel is gentle on tissues.
- Combined, these ingredients may create a balanced home remedy for general wellness support.
Traditional Aloe Vera Recipe for Natural Defense
Here’s a simple way people have traditionally prepared Aloe Vera as part of their daily routine:
Ingredients
- 1 large Aloe Vera leaf (fresh)
- 2–3 cloves of garlic
- Juice of 1 lemon
- 1–2 teaspoons of honey (optional)
Preparation
- Wash the Aloe leaf and carefully remove the outer green rind. Scoop out the clear gel inside.
- Blend the gel with crushed garlic and lemon juice until smooth.
- Optionally add honey for sweetness.
- Consume 1–2 tablespoons, diluted in water, preferably in the morning.
This mixture is believed to combine the cooling and soothing effect of Aloe Vera with the potent antimicrobial qualities of garlic and lemon.
Important Note: Aloe latex (the yellowish layer just under the skin) can have strong laxative effects. Only the clear gel should be used for internal consumption.
Everyday Uses of Aloe Vera for Bacteria and Fungi
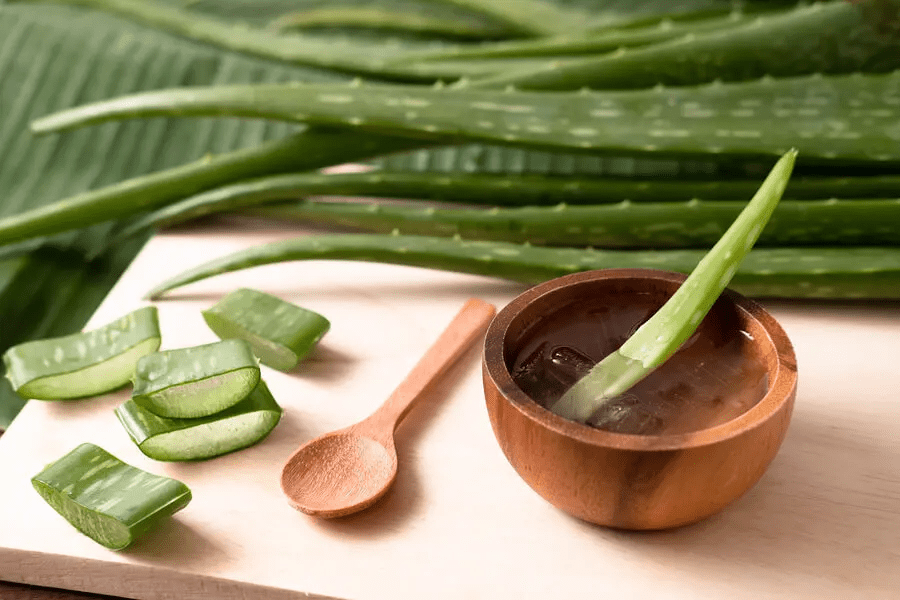

Beyond this recipe, Aloe Vera can be included in daily life in many practical ways:
- Skin care: Apply gel directly on minor cuts, insect bites, or fungal rashes.
- Oral health: Use Aloe Vera mouth rinses (commercially prepared) for gum support.
- Digestive health: Drink Aloe Vera juice (from trusted brands) in small amounts to support gut balance.
- Immune boost: Combine Aloe Vera with turmeric or ginger teas for an added layer of traditional wellness support.
Case Study: A Family Tradition
In southern India, the Fernandes family has kept an Aloe Vera plant by their kitchen door for generations. Whenever someone developed a skin rash or fungal infection from the humid climate, a leaf would be snapped, and the gel applied directly. Recently, younger family members began blending Aloe with garlic and lemon juice during seasonal flu outbreaks as a preventive tonic. While they still visit doctors when needed, this home ritual remains part of their cultural identity.
Such traditions highlight how Aloe Vera is more than just a plant—it’s a living piece of heritage that bridges past wisdom and present-day health concerns.
Other Lifestyle Habits That Protect Against Infections
Aloe Vera is powerful, but it works best when part of a holistic lifestyle:
- Balanced diet: Eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods to strengthen immunity.
- Hygiene: Wash hands regularly and keep surfaces clean.
- Sleep & stress: Adequate rest and stress management are key for immune resilience.
- Medical care: Use herbs as a complement, not as a substitute for prescribed antibiotics.
Conclusion and FAQs
Key Takeaways
- Aloe Vera contains bioactive compounds that may help fight bacteria and fungi naturally.
- When combined with garlic and lemon, it creates a traditional tonic for immune and digestive support.
- Always use the clear gel, not the latex, for safe consumption.
FAQs
Can Aloe Vera replace antibiotics?
No. Aloe Vera may support the body’s defenses, but prescribed antibiotics are necessary for serious infections.
Is it safe to consume Aloe Vera daily?
Small amounts of the gel are generally considered safe, but long-term or high intake should be guided by a healthcare professional.
Can Aloe Vera help with fungal infections like athlete’s foot?
Yes, applying gel topically may soothe symptoms, but persistent infections should be treated medically.
What part of Aloe Vera is toxic?
The yellow latex under the leaf skin contains strong laxatives and should not be consumed.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. It does not substitute professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting new herbal remedies.
News in the same category

7 Silent Sleep Killers Sabotaging Seniors’ Health (And How to Fix Them Tonight)

Moringa Unleashed: Discover the Secret Superfood That Can Revolutionize Your Health

Discover Grandma’s Secret: A Natural Remedy to Banish Varicose Veins
7 Teas That Stop Swollen Legs, Ankles, and Feet for Good

7 Powerful Ways Prosopis Juliflora Boosts Digestive and Heart Health
Purslane: A Natural Support for Lungs and Back Health

Indian Borage (Mexican Mint): A Herbal Drink for Eye Health

Ginger, Onion, Garlic, Lemon & Honey Mix: How to Make It and Why It Matters

4 Teas for 4 Organs: Liver, Stomach, Heart & Brain

Over 60? Drink These 3 Teas to Rebuild Muscle and Walk Strong Again
Knee Pain Relief Starts with THIS Powerful Drink (Must Try for Seniors!)
Seniors, Do This 1 Simple Leg Move to Reverse Hidden Health Problems

Stronger Than Garlic and Lemon: The Bay Leaf Foot Soak That Removes Toxins and Bacteria

Herbal Tea from Stonebreaker Plant for Brain and Memory Support

I Applied Toothpaste and Vaseline on My Face – Here’s What Happened

Parsley Juice for Kidney Cleansing and Stone Relief

All-in-One Master Tonic Shots: Fire Cider with Apple Cider Vinegar, Cinnamon, Clove, Lemon, Ginger, Turmeric, Cayenne & Honey
News Post

Unveil the Mystery: 10 Japanese Rice-Based Secrets for Radiant, Wrinkle-Free Skin
Unleash Your Inner Lion: The Ultimate Egg, Honey, and Coffee Elixir for Men’s Vitality

7 Silent Sleep Killers Sabotaging Seniors’ Health (And How to Fix Them Tonight)

Moringa Unleashed: Discover the Secret Superfood That Can Revolutionize Your Health

Discover Grandma’s Secret: A Natural Remedy to Banish Varicose Veins
A Boy’s Hand Shows Strange Signs After Playing in the Sand

7 Teas That Stop Swollen Legs, Ankles, and Feet for Good

7 Powerful Ways Prosopis Juliflora Boosts Digestive and Heart Health

Purslane: A Natural Support for Lungs and Back Health

Indian Borage (Mexican Mint): A Herbal Drink for Eye Health

Ginger, Onion, Garlic, Lemon & Honey Mix: How to Make It and Why It Matters

4 Teas for 4 Organs: Liver, Stomach, Heart & Brain

Over 60? Drink These 3 Teas to Rebuild Muscle and Walk Strong Again

Knee Pain Relief Starts with THIS Powerful Drink (Must Try for Seniors!)

Seniors, Do This 1 Simple Leg Move to Reverse Hidden Health Problems

Stronger Than Garlic and Lemon: The Bay Leaf Foot Soak That Removes Toxins and Bacteria

Herbal Tea from Stonebreaker Plant for Brain and Memory Support

I Applied Toothpaste and Vaseline on My Face – Here’s What Happened
